Pacemaker
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
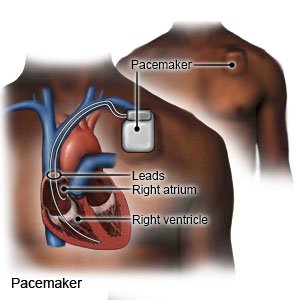
A pacemaker is a small device placed in your chest to help control your heartbeat. You may need a pacemaker if your heartbeat is too slow, too fast, or irregular. A pacemaker is about the size of a large wristwatch. It contains flexible wires (leads) with sensors, a battery, pulse generator, and a small computer. The sensors measure your heartbeat and send the information to the computer. The computer causes the generator to send electrical impulses to your heart. This makes your heart beat correctly. Some pacemakers can also record your heart rate and rhythm.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US), or have someone call if:
- You have any of the following signs of a heart attack:
- Squeezing, pressure, or pain in your chest
- You may also have any of the following:
- Discomfort or pain in your back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or a sudden cold sweat
- You feel lightheaded, short of breath, or have chest pain.
- You cough up blood.
Seek care immediately if:
- Your arm or leg feels warm, tender, and painful. It may look swollen and red.
- You feel weak, dizzy, or faint.
- Your stitches come apart.
- Your pulse is lower or higher than your healthcare provider said it should be.
Call your doctor or cardiologist if:
- You have a fever or chills.
- Your procedure area is red, swollen, or draining pus.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care for the incision area as directed:
Ask your healthcare provider when you can remove your bandage. Wash around the incision area with soap and water. It is okay to let soap and water run over the area. Do not scrub the area. Gently pat the area dry, and apply new, clean bandages as directed. Check every day for redness, swelling, or pus.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Lasix
Lasix is a loop diuretic used to treat fluid retention from heart, liver, or kidney conditions, and ...
Ozempic
Learn about Ozempic (semaglutide) for type 2 diabetes treatment, weight management, cardiovascular ...
Betapace
Betapace and Betapace AF tablets are antiarrhythmic drugs used in the treatment of ventricular ...
Spironolactone
Spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic that is primarily used to treat heart failure, high ...
Propranolol
Propranolol is a beta-blocker that is used to treat tremors, chest pain, high blood pressure, heart ...
Hydrochlorothiazide
HCTZ (hydrochlorothiazide) used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and edema. Includes ...
Activity:
Ask your provider how long to follow these and other safety precautions given to you:
- Do not lift anything heavier than 10 pounds, or as directed.
- Do not lift the arm closest to your pacemaker over your head.
- Do not put pressure on the pacemaker area.
- Do not play contact sports or do vigorous exercises. These activities can damage your pacemaker or cause the wires to move. Ask your healthcare provider which activities are safe for you to do.
Check your pulse, if directed:
Check while you are resting.
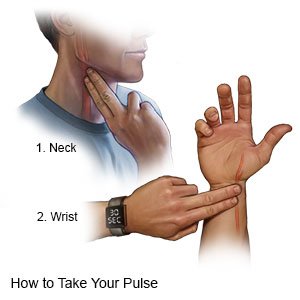 |
- Use a watch with a second hand. Count your pulse for 60 seconds.
- To check the pulse on your wrist, place your index and middle fingers on the inside of your wrist. You should feel your pulse beating just below your thumb.
- To check the pulse on your neck, place your index and middle fingers on one side of your neck. You should feel your pulse beating where your neck meets your jaw.
- Record your information. Include your pulse rate, the date, time, and which side was used to take the pulse. Include anything you notice about your pulse, such as that it is weak, strong, or missing beats. Bring a copy of the information to your follow-up visits.
Pacemaker safety:
Talk to your healthcare provider about driving and playing sports after you have a pacemaker inserted. The following are instructions to keep you safe with a pacemaker:
- Tell all healthcare providers that you have a pacemaker. MRI machines and certain equipment used during surgery can affect how your pacemaker works.
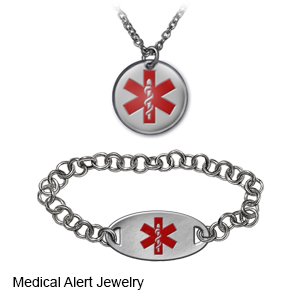
- Wear medical alert identification. Wear medical alert jewelry or carry a card that says you have a pacemaker. Ask your healthcare provider where to get these items.
- Stay away from magnets or machines with electric fields. These can interfere with how your pacemaker works. You will get specific safety information based on the type of pacemaker you have. The following are general safety guidelines:
- Do not lean into a car engine or do welding.
- Do not use an electronic body fat scale or electronic abdominal stimulating exercise machine.
- Check before you have a CT scan. Some CT scan machines may be safe to use with your pacemaker.
- Check before you have electrolysis for hair removal. Your provider may give you instructions on how to get this procedure safely. He or she may need to give you written permission before you can get electrolysis.
- Check before you use a medical alert system, or let your company know you have a pacemaker. The company will be able to tell you if a pacemaker is safe to use with the system.
- Avoid or limit time around electric fence systems. This also includes electric systems to keep pets in a small area. If you cannot avoid it, make your time near it as short as possible.
- Keep your cell phone away from your pacemaker. Do not place your cell phone in a breast pocket over your pacemaker site. Use your cell phone with the ear on the opposite side from your pacemaker.
- Keep headphones away from your pacemaker. Earbud and clip-on headphones for MP3 players might interfere with your pacemaker. Make sure your headphones are always at least 6 inches away from the pacemaker. Do not put headphones in your shirt pocket over the pacemaker. Do not let the headphones hang from your neck onto your chest. Do not let anyone who is using headphones put his or her head on your chest.
- Tell airport security that you have a pacemaker before you go through the metal detectors. Metal detectors may beep because of the metal in your pacemaker. Step away from the machine if you feel dizzy or your heart rate increases. Ask the security agents not to hold a security wand over your pacemaker for more than a few seconds. Your pacemaker function or programming may be affected by the wand.
What you need to know about pacemaker care:
- Your healthcare provider will check your pacemaker about every 3 months. He or she will make sure it is working correctly. You may also need regular EKGs to check the electrical activity of your heart.
- Your pacemaker generator, battery, and leads will need to be replaced. The battery may need to be replaced in 6 to 7 years or longer. The generator will be replaced at the same time. The battery and generator are replaced during surgery. Your leads will need to be replaced if they cause an infection or move out of place. Your healthcare provider will monitor you and decide when these parts need to be replaced.
Follow up with your doctor or cardiologist as directed:
You will need regular checks to make sure your pacemaker is working correctly. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
