Ovarian Torsion
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What is ovarian torsion?
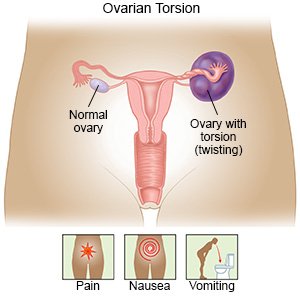
Ovarian torsion is a condition that causes twisting of a ligament that supports the ovary. The ovary may also become twisted with the fallopian tube. Blood flow to the ovary is reduced or blocked. The lack of blood flow can cause ovary necrosis (tissue death). Ovarian torsion needs immediate care to prevent this from happening. Torsion usually happens to only one ovary but can happen to both.
 |
What increases my risk for ovarian torsion?
The cause may not be known. Any of the following may increase your risk:
- A large mass on the ovary, such as a tumor or cyst
- Pregnancy
- Fertility treatment to become pregnant
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- A past ovarian torsion
What are the signs and symptoms of ovarian torsion?
- Severe pain in your abdomen or pelvis that is worse with movement
- Pain that goes to your back or down your side
- Nausea and vomiting
- Tender abdomen or pelvis
- A fever
How is ovarian torsion diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine you and ask about your symptoms. Include when the symptoms began and how severe they are. You may need other tests than those listed below to rule out another condition, such as appendicitis. Any of the following may be used to find ovarian torsion or a health problem it is causing:
- An ultrasound uses sound waves to show pictures on a monitor. An ultrasound may show ovarian torsion and any problems in your ovary, such as an enlarged ovary or abnormal blood flow.
- A pelvic exam is done to check for a mass or other condition that may be causing your symptoms.
- Blood tests are used to check for a problem ovarian torsion can cause, such as anemia (low red blood cells). If you are a person of childbearing age, blood tests may be used to check for pregnancy.
- Surgery may be needed so healthcare providers can see your ovary to check for torsion.
How is ovarian torsion treated?
You must see a healthcare provider as soon as possible. You may need any of the following:
- Surgery is used to untwist the ovary. Your surgeon will also check to see if a lack of blood flow damaged the ovary. The ovary may need to be removed. If you have not gone through menopause yet, your surgeon may try to leave the ovary in place. Any cysts on the ovary may be removed. The fallopian tube may also need to be removed if it is twisted with the ovary.
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
What can I do to prevent ovarian torsion?
- Know what to do if you are at high risk for ovarian torsion. An ovarian cyst, pregnancy, or fertility treatment put you at high risk. Seek immediate care if you have any signs or symptoms of ovarian torsion, such as sudden, severe pelvic pain.
- Birth control pills may be prescribed if you are a person of childbearing age. Certain birth control pills help prevent ovulation. This helps prevent ovarian cysts that may lead to ovarian torsion. Talk to your healthcare provider about family planning, if needed.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have a fever that is getting higher.
- You have new or worsening symptoms, such as increased pain or vomiting.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
