Nonspecific Urethritis in Men
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What is nonspecific urethritis?
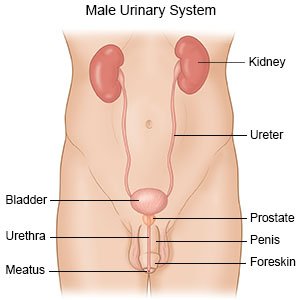
Nonspecific urethritis is a condition that causes inflammation of the urethra. The urethra is the tube where urine passes from the bladder to the outside of the body.
 |
What increases my risk for nonspecific urethritis?
- Being a man who has sex with men
- More than 1 current sex partner
- A sexually transmitted infection (STIs), such as chlamydia, mycoplasma, or trichomonas
- Bath soap, spermicides, or vaginal chemicals from a female sex partner
- Trauma from objects or accidents
- A medical condition, such as Sjogren syndrome
What are the signs and symptoms of nonspecific urethritis?
- Feeling like you need to urinate more often than usual
- Fever
- Abdominal pain
- Pain or a burning feeling when you urinate
- Pain or itchiness in your penis
- Pain when you have sex
- Thin and slightly cloudy, or thick yellow-green discharge from your penis
How is nonspecific urethritis diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask you about medical conditions you have had. You may need any of the following tests:
- Blood tests may be done to check for STIs.
- Urine or urethral fluid tests may be checked for white blood cells, bacteria, or viruses.
How is nonspecific urethritis treated?
Antibiotic medicines may be given to help treat an infection caused by bacteria. You and any sex partner within the past 60 days must be treated to prevent an infection from spreading.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can I manage my symptoms?
- Sit in a warm bath. Do this for 15 minutes at least 2 times each day, or as directed.
- Do not use chemical irritants. This includes bath soaps, spermicides, or other products that may cause irritation.
How can nonspecific urethritis be prevented?
If your urethritis was caused by an infection, the following may help to prevent the spread:
- Ask when it is safe to have sex. This includes oral, vaginal, and anal sex. Do not have sex until you or your partner has finished treatment.
- Use condoms. Wear a condom during oral, vaginal, and anal sex. Ask for more information about the correct way to use condoms.
- Tell your provider if your female partner is pregnant. You may have spread an infection to your partner. Your partner may pass it to the baby during birth.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Macrobid
Macrobid (nitrofurantoin) is an antibiotic used to treat urinary tract infections. Includes side ...
Cipro
Cipro (ciprofloxacin) is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections. Learn ...
Ozempic
Learn about Ozempic (semaglutide) for type 2 diabetes treatment, weight management, cardiovascular ...
Bactrim
Bactrim (sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim) is an antibiotic used to treat ear infections, urinary ...
Amoxil
Amoxil (amoxicillin) is a penicillin antibiotic used to treat many different types of infections ...
Augmentin
Augmentin is a prescription antibiotic combining amoxicillin and clavulanate to treat bacterial ...
Doxycycline
Doxycycline is a tetracycline antibiotic used to treat many different bacterial infections such as ...
Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is a penicillin antibiotic that fights bacteria. It is used to treat many types of ...
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim systemic is used for acne, bacterial infection, bacterial skin ...
Levofloxacin
Levofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat serious bacterial infections and prevent ...
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have chest pain or trouble breathing.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have joint stiffness, muscle pain, or eye inflammation.
- You have pain and swelling in your scrotum.
- You have severe abdominal pain.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have a fever.
- You have chills, a cough, or feel weak and achy.
- You continue to have signs or symptoms after being treated for nonspecific urethritis.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Nonspecific Urethritis
- Antibiotic Resistance: The Top 10 List
- Antibiotics 101: Common Names, Types & Their Uses
- Antibiotics For UTI Treatment - What Are My Options?
- Antibiotics and Birth Control Pill Interactions
- Anticholinergic Drugs to Avoid in the Elderly
- Can You Drink Alcohol with Antibiotics?
- Common Side Effects from Antibiotics, and Allergies and Reactions
- Why Don’t Antibiotics Kill Viruses?
Treatment options
Care guides
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases in Adolescents
- Urinary Tract Infection in Men
- Urinary Tract Infection in Women
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
