Neck Exercises
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What do I need to know about neck exercises?
Neck exercises help reduce neck pain, and improve neck movement and strength. Neck exercises also help prevent long-term neck problems.
What do I need to know about neck exercise safety?
- Move slowly, gently, and smoothly. Avoid fast or jerky motions.
- Stand and sit the way your healthcare provider shows you. Good posture may reduce your neck pain. Check your posture often, even when you are not doing your neck exercises.
- Follow the exercise program recommended by your healthcare provider. He or she will tell you which exercises are best for your condition. He or she will also tell you how many repetitions to do and how often you should do the exercises.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Kenalog-40
Kenalog-40 is a long-acting corticosteroid injection for intramuscular (into the muscle) or ...
Fioricet
Fioricet (acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine) is used to treat tension headaches that are ...
Omvoh
Omvoh is used to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease in adults. This ...
Celebrex
Celebrex is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug used to treat pain or inflammation. Learn about ...
Qutenza
Qutenza patches are used to treat neuropathic pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia and ...
Mobic
Mobic (meloxicam) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug used to treat pain or inflammation ...
Triamcinolone
Triamcinolone is used to treat allergies, skin conditions, ulcerative colitis, and arthritis. Learn ...
Acetaminophen/butalbital/caffeine
Acetaminophen/butalbital/caffeine systemic is used for headache
Hydrocodone
Hydrocodone (Hysingla ER and Zohydro ER) is used for around-the-clock treatment of severe pain ...
How do I perform neck exercises safely?
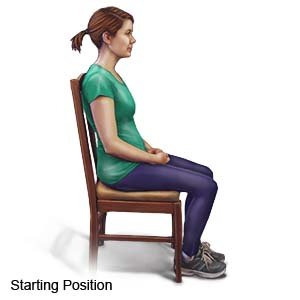
- Exercise position: You may sit or stand while you do neck exercises. Face forward. Your shoulders should be straight and relaxed, with a good posture.
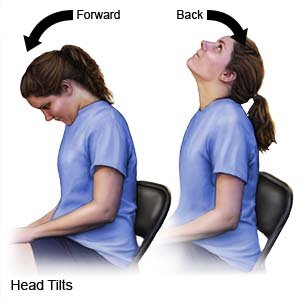
- Head tilts, forward and back: Gently bow your head and try to touch your chin to your chest. Your healthcare provider may tell you to push on the back of your neck to help bow your head. Raise your chin back to the starting position. Tilt your head back as far as possible so you are looking up at the ceiling. Your healthcare provider may tell you to lift your chin to help tilt your head back. Return your head to the starting position.
- Head tilts, side to side: Tilt your head, bringing your ear toward your shoulder. Then tilt your head toward the other shoulder.

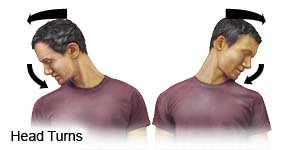
- Head turns: Turn your head to look over your shoulder. Tilt your chin down and try to touch it to your shoulder. Do not raise your shoulder to your chin. Face forward again. Do the same on the other side.
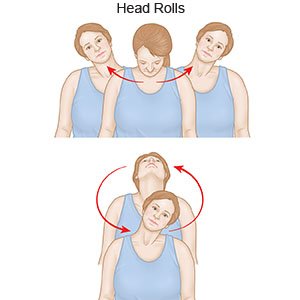
- Head rolls: Slowly bring your chin toward your chest. Next, roll your head to the right. Your ear should be positioned over your shoulder. Hold this position for 5 seconds. Roll your head back toward your chest and to the left into the same position. Hold for 5 seconds. Gently roll your head back and around in a clockwise circle 3 times. Next, move your head in the reverse direction (counterclockwise) in a circle 3 times. Do not shrug your shoulders upwards while you do this exercise.
When should I call my doctor?
- Your pain does not get better, or gets worse.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition, care, or exercise program.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
