Mitral Valve Open Commissurotomy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
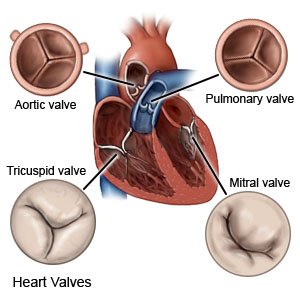
Mitral valve open commissurotomy is surgery to repair the mitral valve in your heart. The mitral valve normally opens and closes to let blood pass through the heart. If the valve does not open or close correctly, blood may not flow well through your heart.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have any of the following signs of a heart attack:
- Squeezing, pressure, or pain in your chest
- You may also have any of the following:
- Discomfort or pain in your back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or a sudden cold sweat
- You have chest pain when you take a deep breath or cough.
- You cough up blood.
Seek care immediately if:
- Your stitches or staples come apart.
- Blood soaks through your bandage.
- Your arm or leg feels warm, tender, and painful. It may look swollen and red.
Call your cardiologist or heart surgeon if:
- You have a fever, chills, or feel weak and achy.
- The skin around your stitches is red, swollen, or you have pus coming from the incision.
- Your skin is itchy, swollen, or has a rash.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Antiplatelets help prevent blood clots. This medicine makes it more likely for you to bleed or bruise.
- Blood thinners help prevent blood clots. Clots can cause strokes, heart attacks, and death. Many types of blood thinners are available. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions for the type you are given. The following are general safety guidelines to follow while you are taking a blood thinner:
- Watch for bleeding and bruising. Watch for bleeding from your gums or nose. Watch for blood in your urine and bowel movements. Use a soft washcloth on your skin, and a soft toothbrush to brush your teeth. This can keep your skin and gums from bleeding. If you shave, use an electric shaver. Do not play contact sports.
- Tell your dentist and other healthcare providers that you take a blood thinner. Wear a bracelet or necklace that says you take this medicine.
- Do not start or stop any other medicines or supplements unless your healthcare provider tells you to. Many medicines and supplements cannot be used with blood thinners.
- Take your blood thinner exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not skip a dose or take less than prescribed. Tell your provider right away if you forget to take your blood thinner, or if you take too much.
- Heart medicine may help strengthen or regulate your heartbeat.
- Blood pressure medicine helps lower your blood pressure.
- Diuretics decrease edema (extra fluid) that collects in a part of your body, such as your legs. Diuretics can also remove excess fluid from around your heart or lungs and decrease your blood pressure. It is often called water pills. You may urinate more often when you take this medicine.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Care for the surgery area:
Do not take a bath, sit in a hot tub, or go swimming until the area has healed. Carefully wash the area with soap and water. Dry the area and put on new, clean bandages as directed. Change your bandages when they get wet or dirty.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Coumadin
Coumadin is used to prevent heart attacks, strokes, and blood clots in veins and arteries. Learn ...
Ecotrin
Ecotrin is used for angina, angina pectoris prophylaxis, ankylosing spondylitis, antiphospholipid ...
Ozempic
Learn about Ozempic (semaglutide) for type 2 diabetes treatment, weight management, cardiovascular ...
Bayer Aspirin
Bayer Aspirin is used for angina, angina pectoris prophylaxis, ankylosing spondylitis ...
Persantine
Persantine is used for prosthetic heart valves - thrombosis prophylaxis, radionuclide myocardial ...
Arthritis Pain
Arthritis Pain is used for angina, angina pectoris prophylaxis, ankylosing spondylitis ...
Dipyridamole
Dipyridamole systemic is used for prosthetic heart valves - thrombosis prophylaxis, radionuclide ...
Jantoven
Jantoven is used for antiphospholipid syndrome, chronic central venous catheterization, deep vein ...
Halfprin
Halfprin is used for angina, angina pectoris prophylaxis, ankylosing spondylitis, antiphospholipid ...
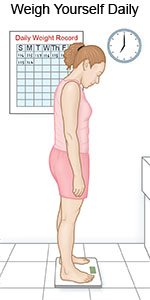
Weigh yourself daily:
Weigh yourself at the same time every morning after you urinate, but before you eat. Weight gain can be a sign of extra fluid in your body. Contact your cardiologist or cardiac surgeon if you have gained at least 2 pounds in a day, or 5 pounds in a week.
 |
Cardiac rehabilitation (rehab):
Your cardiologist or heart surgeon may recommend rehab. This is a program run by specialists who will help you safely strengthen your heart and prevent more heart disease. The plan includes exercise, relaxation, stress management, and heart-healthy nutrition. Healthcare providers will also check to make sure any medicines you are taking are working. The plan may also include instructions for when you can drive, return to work, and do other normal daily activities.
Self-care:
- Do not strain. Do not lift heavy objects. Prevent constipation so you will not strain when you have a bowel movement. Prune juice and water are good liquids to drink. High-fiber foods, extra liquids, and regular exercise can help you prevent constipation. Examples of high-fiber foods are fruit and bran.

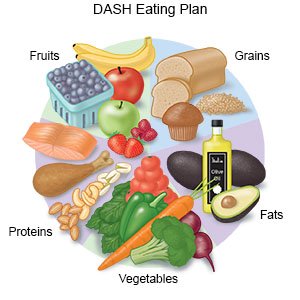
- Eat heart-healthy foods. Heart-healthy foods are low in unhealthy fats and sodium (salt) and high in healthy fats and fiber. Healthy foods include fresh, frozen, or canned fruits and vegetables, whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, beans, lean meats, and fish. Sources of healthy fats include walnuts, salmon, and canola and soybean oils. Ask if you need to be on a low-sodium (salt) or low-fat diet.
- Get plenty of rest. Rest as needed. Slowly start to do more each day. Return to your daily activities as directed. Tell your healthcare provider or cardiologist if you are having problems sleeping.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can make your symptoms worse or increase the risk that you may need surgery again. Your risk for heart or lung disease is also increased. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Ask about vaccines to prevent illness. Get the flu vaccine each year as soon as it becomes available. Ask if you also need the vaccine to prevent pneumonia. The flu and pneumonia can be dangerous for a person who has heart problems. Ask about other vaccines you may also need.
Prevent blood clots and swelling in your legs:
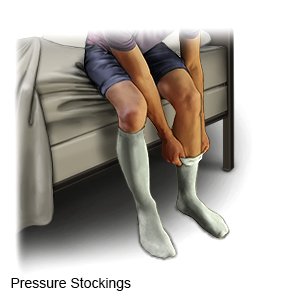
- Wear pressure stockings, if directed. These are long, tight stockings that put pressure on your legs to increase blood flow and prevent clots.
- Do not cross your legs or ankles for long periods of time.
- Stand and walk every 1 to 2 hours when you travel or sit for a long period of time.
- Do not wear tight clothing.
- Drink liquids as directed. Liquid helps keep your blood thin. Healthcare providers will tell you how much liquid to drink each day, and which liquids are best for you.
Pregnancy:
If you are a woman, talk to your healthcare provider or cardiologist if you want to become pregnant. Pregnancy puts more demands on the heart. You may need special care while you are pregnant.
Follow up with your cardiologist or heart surgeon as directed:
You may need to return for blood tests. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
