Menopause
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is menopause?
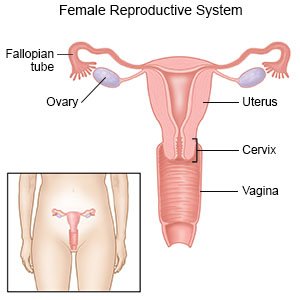
Menopause is a normal stage in a person's life when monthly periods stop. You are considered to be in menopause when you have not had a period for a full year after the age of 40. Menopause usually occurs between ages 47 to 53. Perimenopause is a stage before menopause that may cause signs and symptoms similar to menopause. Perimenopause may start about 4 years before menopause.
 |
What causes menopause?
Menopause starts when the ovaries stop making the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. After menopause, you are no longer able to become pregnant. Any of the following may trigger menopause or early menopause:
- Surgery, including a hysterectomy or oophorectomy
- Family history of early menopause
- Smoking
- Chemotherapy or pelvic radiation
- Chromosome abnormalities, including Turner syndrome and Fragile X syndrome
- Premature ovarian insufficiency (the ovaries stop producing eggs before age 40)
What are the signs and symptoms of menopause?
- Irregular menstrual cycles with heavy vaginal bleeding followed by decreased bleeding until it stops
- Hot flashes (feeling warm, flushed, and sweaty)
- Vaginal changes such as increased dryness
- Mood changes such as anxiety, depression, or decreased desire to have sex
- Trouble sleeping, joint pain, headaches
- Brittle nails, hair on chin or chest where it is normally absent
- Decrease in breast size and change in skin texture
- Weight gain
Related medications
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How is menopause treated or managed?
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is medicine that replaces your low hormone levels. HRT contains estrogen and sometimes progestin.
- HRT has several benefits. HRT helps prevent osteoporosis, which decreases your risk for bone fractures. HRT also protects you from colorectal cancer.
- HRT also has some risks. HRT increases your risk for breast cancer, blood clots, heart disease, a heart attack, or a stroke. If you are 65 years or older, HRT can also increase your risk for dementia. Your risk for uterine or endometrial cancer, gallbladder disease, and urinary incontinence is higher if you take estrogen-only HRT.
- Manage hot flashes. Hot flashes are brief periods of feeling very warm, flushed, and sweaty. Hot flashes can last from a few seconds to several minutes. They may happen many times during the day, and are common at night. Layer your clothing so that you can easily remove some clothing and cool yourself during a hot flash. Cold drinks may also be helpful. Non-hormone medicines can help relieve or prevent hot flashes. Examples include certain antidepressants, nerve medicines, and high blood pressure medicines.
- Reduce vaginal dryness by using over-the-counter vaginal creams. Vaginal dryness may cause you to have pain or discomfort during sex. Only use creams that are made for vaginal use. Do not use petroleum jelly. You may put an estrogen cream in and around your vagina. Estrogen cream may help decrease vaginal dryness and lower your risk of vaginal infections.
- Continue to use birth control during perimenopause if you do not want to get pregnant. You may need to use birth control until it has been 1 year since your periods stopped. Ask your healthcare provider when you can stop using birth control to prevent pregnancy.
How can I live a healthy lifestyle during and after menopause?
After menopause, your risk for heart disease and bone loss increases. Ask about these and other ways to stay healthy:
- Exercise regularly. Exercise helps you maintain a healthy weight. Exercise can also help to control your blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Include weight-bearing exercise for strong bones. Weight bearing exercise is recommended for at least 30 minutes, 3 times a week. Ask your healthcare provider about the best exercise plan for you.

- Eat a variety of healthy foods. Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains (whole-wheat bread, pasta, and cereals), low-fat dairy, and lean protein foods (beans, poultry, and fish). Limit foods high in sodium (salt). Ask your healthcare provider for more information about a meal plan that is right for you.

- Do not smoke. If you smoke, it is never too late to quit. You are more likely to have a heart attack, lung disease, blood clots, and cancer if you smoke. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you need help quitting.
- Take supplements as directed. You may need extra calcium and vitamin D to help prevent osteoporosis.

- Limit alcohol and caffeine. Alcohol and caffeine may worsen your symptoms.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have vaginal bleeding after menopause.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Menopause
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
