Meningococcal Vaccine for Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is the meningococcal vaccine?
The meningococcal vaccine is given as a shot to protect your child from certain types of meningococcal disease. Meningococcal disease is an infection caused by meningococci bacteria. The infection may cause serious disease, such as meningitis. Meningitis causes swelling of the fluid and lining that covers your child's brain and spinal cord. Meningococcal disease is spread from person to person through the air. The vaccine begins to protect your child 1 to 2 weeks after he or she gets it. The vaccine may protect your child for 3 to 5 years.
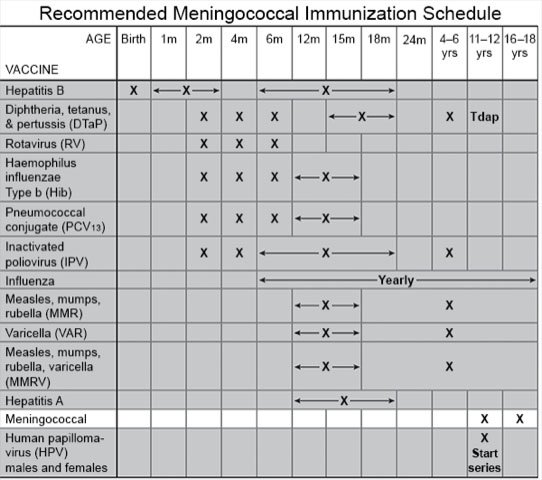
When should my child get the meningococcal vaccine?
Your child's healthcare provider can help you choose the right vaccine, based on your child's age and infection risk. The vaccine is usually given in 2 doses between ages 11 and 16. Children at high risk may get the vaccine as young as 8 weeks. The number of doses your child needs depends on his or her age when the first dose is given. Your child's provider will tell you when your child should get each dose.
 |
What are reasons my child should not get the meningococcal vaccine?
- Your child had an allergic reaction to a dose of the vaccine.
- Your child has a known allergy to any part of the vaccine, such as thimerosal (mercury). Tell your child's healthcare provider if your child has any severe allergies.
What are reasons my child may need to wait to get the meningococcal vaccine?
- Your child is sick or has a fever on the vaccine appointment day.
- Your child is or may be pregnant. Your child's healthcare provider may want your child to wait to get the vaccine until after the baby is born or stops breastfeeding. The provider can tell you and your child the possible risks from the vaccine. Your child may still need to get the vaccine if the risk for meningitis is high.
Related medications
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
- measles virus vaccine/mumps virus vaccine/rubella virus vaccine/varicella virus vaccine
- ProQuad
- Rotarix
- RotaTeq
- rotavirus vaccine
What are the risks of the meningococcal vaccine?
The most common problems are redness, warmth, swelling, or pain where the shot was given. Your child may feel tried, or he or she may get a headache, fever, or chills. Your child may also have muscle or joint pain, or nausea or diarrhea. These symptoms may last up to 7 days. Rarely, your child may develop severe shoulder pain that lasts longer than 2 days. Your child may have an allergic reaction to the vaccine. This can be life-threatening.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your child's mouth and throat are swollen.
- Your child is wheezing or has trouble breathing.
- Your child has chest pain or his or her heart is beating faster than usual.
- Your child faints.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your child's face is red or swollen.
- Your child has hives that spread over his or her body.
When should I call my child's doctor?
- Your child feels weak or dizzy.
- Your child has increased pain, redness, or swelling around the area where the shot was given.
- You have questions or concerns about the meningococcal vaccine.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your child's care. Learn about your child's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your child's healthcare providers to decide what care you want for your child. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Meningococcal Vaccine for Children
Treatment options
Care guides
- Meningococcal Vaccine for Adults
- The Importance of Immunizations (Vaccines) for Adults
- The Importance of Immunizations (Vaccines) for Children
- Typhoid Vaccine
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
