Liver Fibrosis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jun 5, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
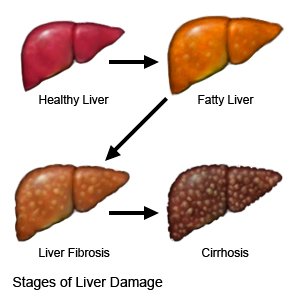
Liver fibrosis
is scar tissue in the liver created when the liver tries to repair an injury. The scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue over time. The liver makes enzymes and bile that help digest food and gives your body energy. It also removes harmful material from your body, such as alcohol and other chemicals. Liver fibrosis does not cause signs or symptoms. You may have signs or symptoms of a condition causing the fibrosis, or if you develop cirrhosis over time.
 |
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have shortness of breath.
- You have trouble thinking clearly or are confused.
Seek care immediately if:
- You feel lightheaded or faint.
- You have shaking, chills, and a fever.
- You are vomiting blood or you see blood in your bowel movement.
Call your doctor if:
- You have new or increased pain or swelling in your abdomen.
- You feel more tired than usual.
- You bruise or bleed easily.
- Your skin or the whites of your eyes look yellow.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment:
If liver fibrosis is found early, your liver may be able to repair itself without treatment. You may need treatment if the fibrosis develops to a point that your liver cannot heal on its own. Liver fibrosis is not treated directly. The cause of your liver fibrosis will need to be treated. Some causes cannot be treated. An example is congenital hepatic fibrosis. If the cause of your fibrosis can be treated, your healthcare provider will talk to you about your options. Your provider may make changes to your medicines. You may be given antiviral medicines if the cause is a virus. You may need treatment to reduce the amount of iron or other metals in your blood. Medicines may also be given to reduce inflammation in your liver.
Prevent or manage liver fibrosis:
- Do not drink alcohol. Alcohol can damage your liver and make liver fibrosis worse. If your fibrosis is caused by alcohol, you may need to quit drinking permanently. This can help prevent worse liver conditions, such as alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis. Ask your healthcare provider for more information if you need help quitting.
- Talk to your provider about hepatitis B and C. You may need a vaccine for hepatitis B. Hepatitis C cannot be prevented with a vaccine, but you can take steps to prevent hepatitis C. Your provider can give you more information on preventing hepatitis.
- Ask about medicines. Some medicines can harm your liver. Acetaminophen is an example. Talk to your provider about all your medicines. Do not take any over-the-counter medicine or herbal supplements until your provider says it is okay.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Extra weight increases your risk for fatty liver disease. This can lead to liver fibrosis. Ask your provider what a healthy weight is for you. Ask your provider to help you create a weight loss plan, if needed.
- Exercise as directed. Aerobic exercise 3 times a week for 20 to 45 minutes can help decrease fat buildup in your liver. Ask your provider about the best exercise plan for you.

- Eat a variety of healthy foods. Examples are vegetables, fruits, whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, beans, lean meats, and fish. Foods low in simple carbohydrates, high fructose corn syrup, and trans fat may help decrease fat buildup in your liver. Liver disease may change the way your body uses nutrients from food. Ask if you need to be on a special diet.

Follow up with your doctor as directed:
You may need ongoing tests to check your liver function. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
