Lactose Intolerance
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Dec 2, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Lactose intolerance
means your body does not produce enough enzymes to properly digest lactose. Lactose is a sugar found in milk and other dairy foods. Lactose intolerance can lead to low levels of calcium if you do not eat or drink enough dairy foods.
Common signs and symptoms include the following:
- Abdominal bloating or a feeling of fullness
- Gas
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Nausea and vomiting
Call your doctor if:
- You continue to have symptoms, even after you make suggested changes.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Manage lactose intolerance:
- Limit or avoid dairy products. Your healthcare provider may recommend that you avoid dairy foods at first. You can slowly start to add dairy products in small amounts one at a time. Avoid having a dairy product by itself. You may be able to tolerate lactose better if you have it with non-dairy items. For example, have milk with cereal or cheese with crackers.
- Eat and drink lactose-free or low-lactose foods. Try lactose-free, almond, rice, or soy milk. Infants with lactose intolerance may need to drink a lactose-free formula. Low-lactose foods include aged cheese (Swiss, cheddar, or parmesan), cream cheese, cottage cheese, and ricotta cheese. Read labels on all foods carefully because lactose is found in many foods. Ask your dietitian for more information about how to avoid or limit foods that contain lactose.
- Ask your provider about enzyme supplements. You may be able to tolerate some dairy products if you take an enzyme supplement (lactase tablet) right before you have the dairy product.
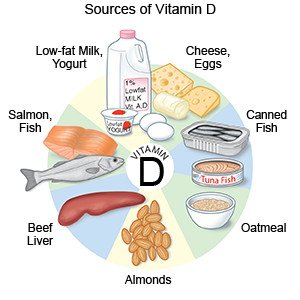
- Get enough calcium and vitamin D. If you have very little or no dairy foods, you need to get calcium and vitamin D from other sources. Other foods that contain calcium include sardines, canned salmon, tofu, shellfish, dried beans, and almonds. Kale, spinach, broccoli, turnip greens, almonds, and calcium-fortified orange juice also contain calcium. Ask your provider if you need to take calcium supplements. Vitamin D is in fish oils, some vegetables, and fortified milk, cereal, and bread. Vitamin D is also formed in the skin when it is exposed to the sun.

Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Lactose Intolerance
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
