Kegel Exercises for Men
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
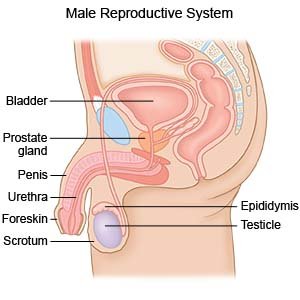
Kegel exercises help strengthen your pelvic muscles. Pelvic muscles hold your pelvic organs, such as your bladder, in place. Kegel exercises help prevent or control certain conditions, such as urine incontinence (leakage) or sexual dysfunction.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your doctor or physical therapist if:
- You cannot feel your pelvic muscles tighten or relax.
- You continue to leak urine.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Cialis
Cialis (tadalafil) increase increases blood flow to a certain area of the body and is used to treat ...
Viagra
Viagra (sildenafil) is used to treat erectile dysfunction or impotence in men. Includes Viagra side ...
Ozempic
Learn about Ozempic (semaglutide) for type 2 diabetes treatment, weight management, cardiovascular ...
Myrbetriq
Myrbetriq (mirabegron) is used to treat overactive bladder with symptoms of frequent or urgent ...
Botox
Botox is used to treat chronic migraines, excessive sweating, bladder conditions, eye muscle ...
VESIcare
Vesicare is used to treat symptoms of overactive bladder such as incontinence and frequent ...
OnabotulinumtoxinA
OnabotulinumtoxinA information from Drugs.com, includes OnabotulinumtoxinA side effects ...
Darifenacin
Darifenacin systemic is used for overactive bladder, urinary frequency, urinary incontinence
Dextranomer/sodium hyaluronate
Dextranomer/sodium hyaluronate systemic is used for fecal incontinence
Solifenacin
Solifenacin systemic is used for neurogenic bladder, neurogenic detrusor overactivity, overactive ...
Use the correct muscles:
Pelvic muscles are the muscles you use to control urine flow. To target these muscles, stop and start the flow of urine several times. This will help you become familiar with how it feels to tighten and relax these muscles.
How to do Kegel exercises:
- Get into a comfortable position. You may lie down, stand up, or sit down to do these exercises. When you first try to do these exercises, it may be easier if you lie down.
- Tighten or squeeze your pelvic muscles slowly. It may feel like you are trying to hold back urine or gas. Hold this position for 3 seconds. Relax for 3 seconds. Repeat this cycle 10 times. Do not hold your breath when you do Kegel exercises. Keep your stomach, back, and leg muscles relaxed.
- Do 10 sets of Kegel exercises, at least 3 times a day. When you know how to do Kegel exercises, use different positions. This will help to strengthen your pelvic muscles as much as possible. You can do these exercises while you lie on the floor, watch TV, or while you stand. Tighten your pelvic muscles before you sneeze, cough, or lift to prevent urine leakage. You may notice improved bladder control within about 6 weeks.
Follow up with your doctor or physical therapist as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
