Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH)
is a condition that causes the pressure inside your skull to be higher than normal for no known reason. IIH can seem like a brain tumor, but no tumor is found. The cause of IIH may not be known. It may be caused by an increased amount of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in your skull. CSF is a clear fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord and protects them from injury. IIH may happen when your body makes too much CSF or does not absorb it correctly.
Common signs and symptoms of IIH:
- Headache behind both eyes that is worse in the morning and with eye movement or straining
- Nausea, vomiting, or dizziness
- Pulsing or ringing in your ears
- Temporary blind spots in one or both eyes
- Blurred or double vision or loss of vision
- Trouble seeing with your peripheral vision (tunnel vision)
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US), or have someone call if:
- You suddenly cannot see.
- You have sudden neck pain or cannot move your arms or legs.
- You have sudden trouble breathing.
- You are confused or cannot think clearly.
Seek care immediately if:
- You have a severe headache.
- You have a seizure.
Call your doctor if:
- You have a fever.
- Your headache gets worse or does not go away with treatment.
- Your vision loss does not improve with treatment.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment
may not be needed. IIH may go away on its own. You may need any of the following if your symptoms continue or get worse:
- Medicines may be given to control migraines or decrease the amount of CSF you produce. This will help relieve pressure in your skull. You may need medicines to decrease extra fluid that collects in your body. You may also need pain medicine. Your healthcare provider may prescribe pain medicine or recommend an over-the-counter medicine such as an NSAID or acetaminophen.
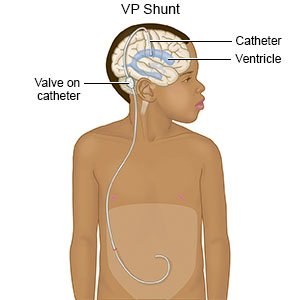
- Surgery may be used to make a small opening in the sheath (cover) around the optic nerve. This allows extra CSF to drain and relieve eye pressure. Your healthcare provider may also use surgery to place a shunt (passageway) in your brain or spinal cord to drain extra CSF into another area of the body. This helps relieve pressure in your skull.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Manage IIH:
- Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your healthcare provider what a healthy weight is for you. Ask your provider to help you create a weight loss plan, if needed.
- Eat a variety of healthy foods. You may need to limit the amount of fats and salt you eat. You may also need to limit foods rich in vitamin A and tyramine. Foods rich in vitamin A include beef liver, sweet potatoes, carrots, tomatoes, and leafy greens. Food and drinks that are high in tyramine include cheese, pepperoni, salami, beer, and wine. Ask if you need to be on a special diet.

- Drink liquids as directed. Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
You may need to return for eye exams every 10 to 14 days. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
Treatment options
Care guides
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
