Hypothyroidism in Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What is hypothyroidism?
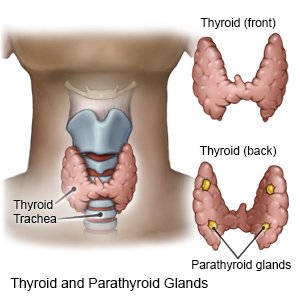
Hypothyroidism is a condition that develops when the thyroid gland makes little or no thyroid hormone. Thyroid hormones help control body temperature, heart rate, growth, and how you gain or lose weight.
 |
What increases my risk for hypothyroidism?
- Autoimmune disease, such as Hashimoto's disease, or type 1 diabetes
- Medicines
- Radiation therapy or thyroid surgery
- History of hypothyroidism, thyroid cancer, or an enlarged thyroid
- Family history of hypothyroidism or an autoimmune disease
- Low iodine level
What are the signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism during pregnancy?
- Exhaustion, depression, or irritability
- Sensitivity to cold
- Constipation
- Dry, flaky skin, brittle nails, or thinning hair
- Muscle pain or weakness
- Swollen thyroid gland
How is hypothyroidism diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms and examine you. He or she will ask what medicines you take. Tell him or her about your medical history and if anyone in your family has hypothyroidism. You will have blood tests to check your thyroid hormone level.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Synthroid
Synthroid (levothyroxine) treats hypothyroidism (low thyroid hormone) and different types of ...
Armour Thyroid
Armour Thyroid is used for hashimoto's disease, hypothyroidism, after thyroid removal, thyroid ...
Ozempic
Learn about Ozempic (semaglutide) for type 2 diabetes treatment, weight management, cardiovascular ...
Levoxyl
Levoxyl treats hypothyroidism (low thyroid hormone) and treats or prevents goiter. Learn about side ...
Cytomel
Cytomel is used for hypothyroidism, after thyroid removal, myxedema, myxedema coma, thyroid ...
Tirosint
Tirosint is used for hashimoto's disease, hypothyroidism, after thyroid removal, myxedema coma ...
Nature-Throid
Nature-Throid is used for hashimoto's disease, hypothyroidism, after thyroid removal, thyroid ...
Unithroid
Unithroid is used for hashimoto's disease, hypothyroidism, after thyroid removal, myxedema coma ...
Euthyrox
Euthyrox (levothyroxine) is used to treat hypothyroidism and to treat or prevent goiter. Includes ...
Liothyronine
Liothyronine systemic is used for hypothyroidism, after thyroid removal, myxedema, myxedema coma ...
How is hypothyroidism treated?
Thyroid medicine will bring your thyroid hormone level back to normal. The dose may be adjusted during your pregnancy. Your thyroid hormone level will be checked regularly to make sure you get the right dose. You may also need iodine supplements or eat foods higher in iodine. Ask your healthcare provider for more information on other medicines you may need.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can I manage hypothyroidism?
- Get more iodine. The thyroid gland uses iodine to work correctly and to make thyroid hormones. Your healthcare provider may tell you to eat foods that are rich in iodine. He or she will tell you how much of these foods to eat. Milk and seafood are good sources of iodine. You may also need iodine supplements.
- Keep track of your baby's movements. Keep track of how much your baby moves every day. Wait 1 hour after you eat. Write down every movement that you feel from your baby.
- Keep track of your blood pressure and weight:
- Check your blood pressure and write it down as often as directed. It is important to measure your blood pressure on the same arm and in the same position each time. Keep track of your blood pressure readings, along with the date and time you took them. Take this record with you to your prenatal visits.

- Weigh yourself daily before breakfast after you urinate. More weight gain than recommended during your pregnancy may be a sign of extra fluid in your body. Keep track of your daily weights and take the record with you to your prenatal visits.
- Check your blood pressure and write it down as often as directed. It is important to measure your blood pressure on the same arm and in the same position each time. Keep track of your blood pressure readings, along with the date and time you took them. Take this record with you to your prenatal visits.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You faint or have a seizure.
- You have sudden chest pains or trouble breathing, or swelling in your legs, ankles, or feet.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your water breaks, or you are bleeding from your vagina.
- You have diarrhea, tremors, or trouble sleeping.
When should I call my doctor?
- You feel your baby is restless and always kicking, or is very still and not moving at all.
- You are losing weight without trying.
- Your signs and symptoms return or become worse.
- You are out of thyroid medicine.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Hypothyroidism
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
