Hypertension in Adolescents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Hypertension
is high blood pressure (BP). BP is the force of the blood moving against the walls of the arteries. Hypertension causes your teen's heart to work much harder than normal. This can damage his or her heart. High BP in adolescence increases your teen's risk for hypertension and cardiovascular disease as an adult. A controlled BP helps protect your teen's organs, such as his or her heart, lungs, brain, and kidneys.
Common signs and symptoms:
Your teen may have no signs or symptoms, or any of the following:
- Chest pain or palpations (changes in his or her heartbeat)
- Headache
- Changes in vision
- Dizziness
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your teen has chest discomfort that feels like squeezing, pressure, fullness, or pain.
- Your teen becomes confused or has difficulty speaking.
- Your teen suddenly feels lightheaded or has trouble breathing.
- Your teen has back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm pain.
Seek care immediately if:
- Your teen has a severe headache or vision changes.
- Your teen feels faint, dizzy, confused, or drowsy.
Related medications
Call your teen's doctor if:
- Your teen's BP is higher than it should be, even with BP medicine.
- You have questions or concerns about Your teen's condition or care.
Stages of hypertension:
Your child's healthcare provider will give him or her a BP goal based on age, health, and risk for cardiovascular disease. When your teen is 13, his or her BP will start being recorded as one of the following stages:
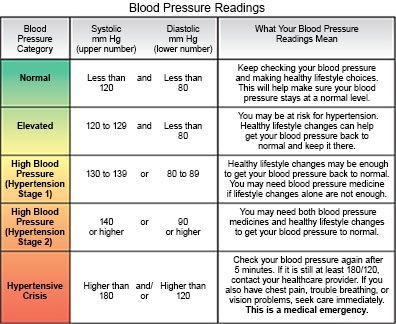
- Normal BP is 119/79 or lower . Your teen's healthcare provider may only check his or her BP each year if it stays at a normal level.
- Elevated BP is 120/79 to 129/79 . This is sometimes called prehypertension. Your teen's provider may suggest lifestyle changes to help lower his or her BP to a normal level. He or she may then check it again in 3 to 6 months.
- Stage 1 hypertension is 130/80 to 139/89 . Your teen's provider may recommend lifestyle changes, medication, and checks every 3 to 6 months until the BP is controlled.
- Stage 2 hypertension is 140/90 or higher . Your teen's provider will recommend lifestyle changes and may have him or her take 2 kinds of hypertension medicines. Your teen will also need to have his or her BP checked monthly until it is controlled.
 |
Treatment:
The cause of the high BP may need to be treated. If no cause is found, treatment usually starts with lifestyle changes. Your teen may also need medicine if lifestyle changes alone are not enough. Your teen's healthcare provider may recommend any of the following, based on your teen's needs:
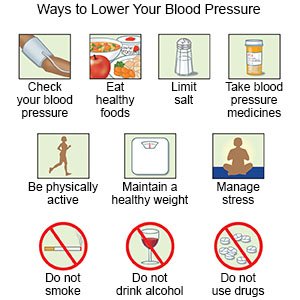 |
- Weight loss helps lower BP and keep it in a normal range. Your teen's healthcare provider can tell you what weight is healthy for him or her. The provider can help create a weight loss plan, if needed. Even a small amount of weight loss can make a big difference for your teen's BP.
- Activity helps lower BP and can help your teen maintain a healthy weight. Most teens need at least 60 minutes of physical activity each day.

- A healthy meal plan may mean changes to the amount or kinds of food your teen eats. You and your teen will be given more information on the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) eating plan. The DASH eating plan encourages eating fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. You may also meet with a dietitian to create a meal plan to fit your teen's needs.
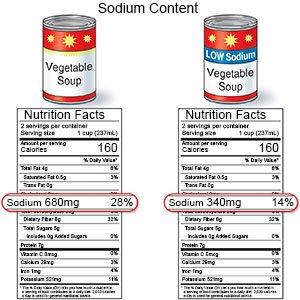
- Sodium (salt) limits can help prevent fluid from building up in your teen's body. Fluid buildup can affect his or her BP. You and your teen may be taught how to check labels to find low-sodium or no-salt-added foods. Some use potassium salts for flavor. Too much potassium can also cause health problems. Healthcare providers will tell you how much sodium and potassium are safe to have in a day.
- A regular sleep routine can prevent high BP from getting worse. Your teen should go to sleep and wake up at the same times each day. He or she should not use electronic devices or watch TV for at least 1 hour before bed.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Help manage your teen's hypertension:
Your teen may be taught how to take his or her own BP. He or she may need to continue taking BP readings as an adult.
- Check his or her BP at home, if directed.
- Use the right size cuff for your teen. Your healthcare provider can check to make sure the cuff fits properly. Follow the directions that came with the BP monitor.
- Have him or her sit and rest for 5 minutes before you take the BP. Extend his or her arm and support it on a flat surface. The arm should be at heart level.
- You may be asked to check your teen's BP more than 1 time each day. Choose the same times each day. Keep a record of the BP readings and bring it to follow-up visits.
- Manage any other health conditions. Health conditions such as kidney disease or diabetes can increase the for hypertension. Your teen's provider may recommend tests for obstructive sleep apnea or other problems that can keep him or her from sleeping well. Follow all instructions from healthcare providers.
- Talk to your teen about drugs, alcohol, and tobacco products, if needed. Help him or her understand that these increase BP and make hypertension harder to manage. Ask your teen's healthcare provider for information if he or she uses any of these and needs help to quit.
Follow up with your teen's doctor as directed:
Take him or her to all follow-up appointments. He or she will need to have regular BP checks. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Hypertension
- Do blood pressure drugs interact with alcohol?
- FDA-Approved Weight Loss Drugs: Can They Help You?
- Which Drugs Cause Weight Gain?
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
