How to Give A Subcutaneous Injection
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jun 5, 2024.
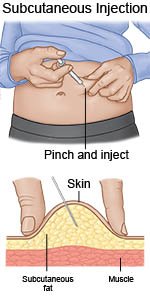
A subcutaneous injection is a shot given into the fat layer between your skin and muscle. Subcutaneous injections are used to give small amounts and certain kinds of medicine.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
About the syringe:
There are 3 parts to a syringe: the needle, the barrel and the plunger. The needle goes into your skin. The barrel holds the medicine and has markings on it like a ruler. The markings are for milliliters (mL). The plunger is used to get medicine into and out of the syringe.
- Insulin syringe: This holds a maximum of 1 mL of medicine. The syringe has markings from 10 to 100. The marking at 100 is the same as 1 mL. The marking at 50 is the same as ½ mL.
- Tuberculin syringe: This syringe holds up to 1 mL of medicine. It has a needle that is slightly longer than an insulin syringe. The syringe is marked every 0.1 mL.
Where to give a subcutaneous injection:
The following are sites where you can give a subcutaneous injection:
- Abdomen: Uncover your abdomen. You may give an injection within the following area: below the waist to just above the hip bone and from the side to about 2 inches from the belly button. Avoid the belly button.
- Thigh: Uncover the entire leg. Find the area halfway between the knee and hip and slightly to the side. Gently grasp the area to make sure you can pinch 1 to 2 inches of skin.
- Lower back: Uncover the back from the waist to the top of the buttocks. Imagine a line that runs across the back just above the crack between the buttocks. An injection may be given below the waist and above this line. Give the injection halfway between the spine and the side.
- Upper Arm: Uncover the arm to the shoulder. Have the person getting the injection stand with his hand on his hip. Stand next to and a little behind the person. Find the area halfway between the elbow and shoulder. Gently grasp the skin at the back of the arm between your thumb and first 2 fingers. You should be able to grasp 1 to 2 inches of skin.
Placement for a subcutaneous injection:
- Keep track of where injections are given: Make a list of the sites you use. Write down the date, time, and the site each time you give an injection.
- Change sites for the injections: It is important to use a different site each time you give an injection. This prevents scars and skin changes. The sites where injections are given should be at least 1 inch away from each other. Ask if you need to inject the medicine in a certain site.
Items needed to give a subcutaneous injection:
- One alcohol wipe
- One sterile 2 x 2 gauze pad
- A new needle and syringe that are the correct size
- Disposable gloves, if you have them
How to give a subcutaneous injection:
Subcutaneous injections can be given straight in at a 90 degree angle or at a 45 degree angle. Give the injection at a 90 degree angle if you can grasp 2 inches of skin between your thumb and first finger. If you can grasp only 1 inch of skin, give the injection at a 45 degree angle. Wash your hands with soap and water. You may want to wear gloves.
- Open the alcohol wipe: Wipe the area where you plan to give the injection. Let the area dry. Do not touch this area until you give the injection.
- Remove the cover from the needle: Hold the syringe with your writing hand and pull the cover off with your other hand. Place the syringe between your thumb and first finger. Let the barrel of the syringe rest on your second finger.
- Grasp the skin: With your other hand, grasp the skin.
- Insert the needle into the skin: Hold the syringe barrel tightly and use your wrist to inject the needle into the skin. Once the needle is all the way in, push the plunger down to inject the medicine.
- Pull out the needle: Remove the needle at the same angle you put it in. Gently wipe the area with the dry sterile gauze 2 x 2 pad.
How to get rid of used syringes and needles:
It is important to dispose of your needles and syringes correctly. Do not throw needles into the trash. You may receive a hard plastic container made especially for used syringes and needles. You can also use a soda bottle or other plastic bottle with a screw lid. Make sure that both the syringe and needle fit into the container easily and cannot break through the sides. Ask your healthcare provider or a pharmacist what your state or local requirements are for getting rid of used syringes and needles.
Contact your healthcare provider if:
- There is a lump, swelling, or bruising where the injection was given that does not go away.
- A fever, sneezing, or coughing develops after the injection is given.
- You have questions about how to give an injection.
Seek care immediately if:
- A rash or itching develops after the injection is given.
- Shortness of breath develops after the injection is given.
- The mouth, lips, or face swells after the injection is given.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
