Hepatitis C
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Hepatitis C
is inflammation of the liver caused by hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection.
 |
Signs and symptoms:
You may not have any signs or symptoms at first. Any of the following may develop if HCV damages your liver:
- Fatigue
- Dark urine or pale bowel movements
- Fever
- Jaundice (yellow skin or eyes) and itchy skin
- Joint pain, body aches, or weakness
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Pain in the upper right side of your abdomen
Seek care immediately if:
- You have severe abdominal pain.
- You are too dizzy to stand up.
- You vomit blood or material that looks like coffee grounds.
- You feel confused or are very sleepy.
- Your bowel movements are red or black, and sticky.
Call your doctor or hepatologist if:
- You have a fever.
- You are vomiting and cannot keep food or liquids down.
- Your abdomen or legs have a rash or are swollen.
- You are bruising easily.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
What you need to know about hepatitis C screening:
Screening means you are tested for hepatitis C before you have signs or symptoms. This helps healthcare providers find and treat hepatitis C early. Screening is usually recommended 1 time for all adults who are 18 to 79 years of age. Screening may also be recommended during pregnancy to lower the risk for HCV being passed from mother to baby. Screening may start before age 18 or after 79 if your risk is high and continue regularly if your risk remains high.
Treatment:
Your body may be able to fight an HCV infection on its own. An infection that continues longer than 6 months will need treatment. Treatment helps prevent health problems hepatitis C can cause, such as liver failure or cirrhosis. You may need any of the following:
- Antiviral medicines help control HCV. These medicines will not get rid of the virus, but they can make it inactive in your body. Antivirals can also shorten the amount of time you have symptoms or make them less severe. You will need to take a combination of antivirals for at least 8 to 12 weeks.
- Surgery may be needed to remove part of your liver. A liver transplant may be done if your liver stops working. Your diseased liver is removed and replaced with a healthy, donated liver.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Manage hepatitis C:
- Do not drink alcohol or use illegal drugs. Alcohol and drugs cause or increase your risk for liver damage. Ask your healthcare provider for more information if you need help quitting.
- Do not use any medicines without talking to your provider. This includes medicine that has been ordered for you and over-the-counter medicine. Ask before you use acetaminophen, vitamins, herbs, herbal teas, laxatives, or food supplements. Any of these could harm your liver.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine can damage blood vessels and make it more difficult to manage hepatitis C. Do not use e-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco in place of cigarettes or to help you quit. They still contain nicotine. Ask your provider for information if you currently smoke and need help quitting.
- Eat a variety of healthy foods. Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy products, beans, and lean meats and fish. Ask if you need to be on a special diet.

- Get more rest. Slowly return to your normal activities when you feel better.
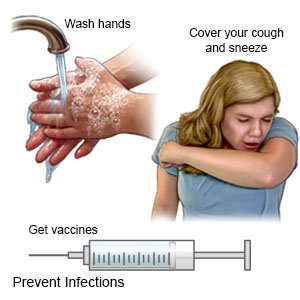
- Talk to your provider about vaccines. You may need to get vaccines to protect you from hepatitis A or B. You may also need a pneumonia vaccine. Get the flu vaccine as soon as recommended each year, usually in September or October. Get all recommended COVID-19 vaccine doses and boosters. Ask your provider about other vaccines you need.
Prevent the spread of HCV:
No vaccine is available to prevent hepatitis C. The following can help prevent HCV from spreading to others:
- Wash your hands often. Use soap and water. Wash your hands several times each day. Wash after you use the bathroom, change a child's diaper, and before you prepare or eat food. Wash for at least 20 seconds. Rinse with warm, running water for several seconds. Then dry your hands with a clean towel or paper towel. Use hand sanitizer that contains alcohol if soap and water are not available. Do not touch your eyes, nose, or mouth without washing your hands first.

- Cover any open cuts or scratches. If blood from your wound gets on a surface, clean the surface with bleach right away. Throw away any items with blood or body fluids on them, as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Do not share personal items. These items include toothbrushes, nail clippers, and razors. Do not share needles.
- Tell household members and sex partners that you have HCV. They should be tested for HCV. Do not have sex, including oral and anal sex, until your healthcare provider tells you it is okay. If you have sex, make sure the male partner wears a latex condom.
- Protect your baby. If you are currently pregnant, your provider will give you more information on protecting your baby from HCV. Medicines used to treat hepatitis C are not routinely used during pregnancy. Your provider may recommend antivirals if the benefits to you and your baby outweigh the risks. Your provider will talk to you about the benefits and risks. It is okay to breastfeed your baby unless your nipples are cracked or bleeding.
- Do not donate blood, body organs, semen, or other tissues. Donations are checked for HCV, but it is best not to donate.
 |
Follow up with your doctor or hepatologist as directed:
If you took medicine to treat hepatitis C, your blood will be checked for HCV 12 weeks later. You may need ongoing tests or treatment. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Hepatitis C
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
