Gangrene
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
Gangrene may be caused by conditions that stop blood flow, or a bacterial infection. Gangrene is a life-threatening condition that needs immediate treatment. Gangrene is treated with surgery to remove the dead tissue. In severe cases, part of your arm or leg may also be removed.
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
Monitoring:
Your heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing will be monitored closely. Your intake and output will be measured. Healthcare providers will keep track of the amount of liquid you are getting. They also may need to know how much you are urinating. You may need a Foley catheter to help measure your urine. A Foley catheter is a tube that is put into your bladder to drain urine.
Medicines:
- Antibiotics help treat an infection caused by bacteria.
- Pain medicine may be given. Do not wait until the pain is severe before you ask for more medicine.
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Plavix
Plavix (clopidogrel) is used to prevent blood clots after a recent heart attack or stroke. Includes ...
Xarelto
Xarelto (rivaroxaban) is a factor Xa inhibitor used to reduce the risk of blood clots and stroke in ...
Ozempic
Learn about Ozempic (semaglutide) for type 2 diabetes treatment, weight management, cardiovascular ...
Zontivity
Zontivity is used for the prevention of cardiovascular events. Includes Zontivity side effects ...
Vorapaxar
Vorapaxar systemic is used for peripheral arterial disease, prevention of atherothrombotic events ...
Rivaroxaban
Rivaroxaban systemic is used for atrial fibrillation, cardiovascular risk reduction, congenital ...
Clopidogrel
Clopidogrel systemic is used for acute coronary syndrome, acute coronary syndrome, prophylaxis ...
Tests:
- Blood and urine tests may be done to check for infection, blood cell levels, and kidney function.
- X-ray, ultrasound, or CT pictures may be done to check for damage to deeper tissues. You may be given contrast liquid to help the tissues show up better in pictures. Tell a healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
Treatment:
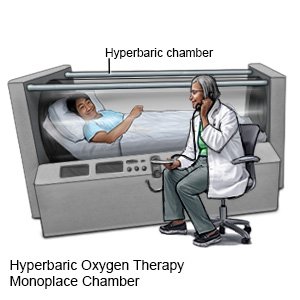
- Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy is used to increase oxygen to your tissues. This will help you heal faster and prevent the infection from getting worse. The oxygen is given under pressure inside a pressure chamber. You may need to have this therapy more than 1 time.
- Surgery is needed to remove the dead tissue.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
RISKS:
The infection may spread to the rest of your body. This may lead to shock or a coma. Shock is a condition that causes your organs to stop working correctly.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Gangrene
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
