Foot Contusion
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What is a contusion?
A contusion is a bruise that appears on your skin after an injury. A bruise happens when small blood vessels tear but skin does not. Blood leaks into nearby tissue, such as soft tissue or muscle.
What increases my risk for a foot contusion?
- A foot injury
- A disorder that makes you bleed more easily
- Medicines such as blood thinners or certain over-the-counter medicines and herbal medicines
- Weakened skin and muscles from older age or nutrition problems
What are the signs and symptoms of a foot contusion?
- An area that may be black, blue, red, or darker than the skin around it
- Pain that increases when you touch the bruise, walk, or use the area around the bruise
- Swelling or a lump at the site of the bruise or near it
- Stiffness or problems moving your foot
How is a foot contusion diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider may ask about any injuries or bleeding problems you had in the past. Your provider will check the skin over the injured area and touch it to see where it hurts. You may also need any of the following:
- Blood tests may be used to check for blood disorders or to see how long it takes for your blood to clot.
- Ultrasound pictures may show how deep the bruise is and if you have any other injury in your foot.
- MRI pictures may show if a hematoma (pooling of blood) has started to form. You may be given contrast liquid to help the pictures show up better. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. The MRI machine uses a powerful magnet. Metal can cause serious injury from the magnet. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
How is a foot contusion treated?
Treatment may not be needed. The bruise may become lighter or change to green or yellow as it heals. You may need any of the following if the contusion is severe or does not heal easily:
- Medicine may be needed to treat or prevent pain or swelling.
- Aspiration is a procedure to drain pooled blood in your muscle. This prevents increased pressure in the muscle.
- Surgery may be done to repair a muscle tear or relieve pressure caused by swelling.
How do I manage a foot contusion?
Follow your treatment plan to help decrease your pain and improve your muscle movement. The following are general instructions:
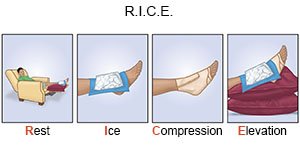
- Rest your foot for 1 to 2 days after your injury. You may then be given gentle exercises to improve your foot movement and help decrease stiffness. Ask when you can return to your normal activities or sports.
- Apply ice to decrease swelling and pain. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover the bag with a towel before you apply it to your foot. Apply ice for 15 to 20 minutes every hour, or as directed.
- Use compression to decrease swelling and support your foot. Follow instructions about how to apply the bandage. Make sure the bandage is not too tight. You should be able to put a finger between the bandage and your foot. Do not massage your foot. Massage may cause more damage or pain.
- Keep your foot raised above the level of your heart while you are sitting or lying down. This will help decrease or limit swelling. Use pillows, blankets, or rolled towels to elevate your foot comfortably.
 |
How can I prevent a foot contusion?
- Stretch and warm up before you play sports or exercise.
- Wear protective gear when you play sports. Examples are shin guards and padding.
- If you begin a new physical activity, start slowly to give your body a chance to adjust.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have increased swelling on your foot.
- You have severe foot pain.
- You are not able to move your foot.
When should I call my doctor?
- You find a new lump in the injured area.
- Your symptoms do not improve with treatment after 4 to 5 days.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
