Evar (Endovascular Aortic Aneurysm Repair)
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
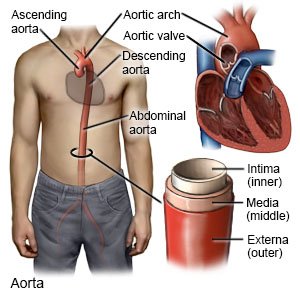
An endovascular aortic aneurysm repair (EVAR)
is a procedure to prevent an abdominal aortic aneurysm from rupturing (bursting).
 |
How to prepare for a planned EVAR:
- Your healthcare provider will talk to you about how to prepare for your procedure. You may be told not to eat or drink anything after midnight on the day of your procedure. Arrange to have someone drive you home and stay with you after your procedure.
- You may need blood tests, an ultrasound, or a CT angiography scan before your procedure. These tests will help your provider plan for your procedure. Talk to your provider about these or other tests you may need.
- Tell your provider about all your current medicines. Your provider will tell you if you need to stop any medicine for the procedure, and when to stop. You may need to stop taking blood thinning medicine several days before your procedure. Your provider will tell you which medicines to take or not take on the day of your procedure.
- Tell your provider about any allergies you have, including to medicines or anesthesia. You may be given an antibiotic or contrast liquid during your procedure. Tell your provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to antibiotics or contrast liquid.
What will happen during EVAR:
- You may be given local anesthesia to numb the catheter sites. With local anesthesia, you may still feel pressure or pushing, but you should not feel pain. You may instead be given general anesthesia to keep you asleep and free from pain during your procedure.
- Your healthcare provider will insert a catheter into an artery on each side of your groin. A wire and stent-graft will be guided through each catheter and up into your abdominal aorta. A stent-graft is a long tube covered with metal mesh. The wire helps get the stent-graft to the correct place. Your provider may inject contrast liquid so your blood vessels will show up more clearly in x-rays.
- Your provider will inflate a balloon inside the stent-graft to push it against the artery wall. The mesh has hooks that help hold the stent-graft in place. Blood will flow through the stent-graft instead of to the aneurysm. This will decrease pressure on the aneurysm and lower the risk for a rupture.
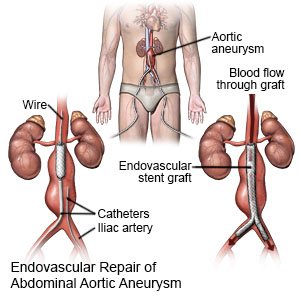
- Your provider will remove the catheters and wires. Clamps, stitches, or other devices will be used to close the catheter sites. Pressure will be applied to each site for several minutes to stop any bleeding. A pressure bandage or other pressure device may be placed over each site. This will help prevent more bleeding.
What to expect after EVAR:
- You will be attached to a heart monitor until you are fully awake. A heart monitor is an EKG that stays on continuously to record your heart's electrical activity. You will spend 1 to 2 days in the hospital.
- You will need to lie flat with your legs straight for 2 to 4 hours. Do not get out of bed until your healthcare provider says it is okay. Leg movements can cause serious bleeding.
- Healthcare providers will monitor your vital signs and pulses in your legs. They will check your pressure bandages for bleeding or swelling.
- You may have pain and bruising where the catheters were placed. Medicines may be given to prevent or treat pain, a blood clot, or a bacterial infection.
- You will need ongoing tests to check the graft position and size of your aneurysm.
Risks of EVAR:
You may bleed more than expected or develop an infection. You may need surgery to repair damage to your blood vessels from the catheter. You may also need surgery to stop bleeding. The graft may move out of place or leak blood into your aneurysm. A leak may need to be treated. You may develop a blood clot in your leg. A blood clot may block the graft and decrease blood flow through your abdominal aorta. The graft or catheter may stop blood flow to your legs. Even with EVAR, your aneurysm may rupture and cause life-threatening bleeding. You may need more than 1 EVAR.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) or have someone call if:
- You have any of the following signs of a heart attack:
- Squeezing, pressure, or pain in your chest
- You may also have any of the following:
- Discomfort or pain in your back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or a sudden cold sweat
- You feel lightheaded, short of breath, and have chest pain.
- You cough up blood.
- You have trouble breathing.
- You cannot stop the bleeding from a catheter site even after you hold firm pressure for 10 minutes.
- You faint or lose consciousness.
- You cannot be woken.
Seek care immediately if:
- You have sudden sharp pain in your abdomen, groin, back, legs, or buttocks.
- You feel dizzy.
- You have stiffness or swelling in your abdomen, or a lump in your abdomen.
- You have trouble walking or moving your legs.
- Your leg feels warm, tender, and painful. It may look swollen and red.
- Blood soaks through your bandage.
- Your stitches come apart.
- A catheter site gets swollen quickly.
- Your leg feels numb, cool, or looks pale.
- The skin in your buttocks feels cold and is pale, purple, or black.
- You have blood in your bowel movements.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Metoprolol
Metoprolol is used to treat angina (chest pain) and hypertension (high blood pressure). Learn about ...
Call your doctor if:
- You have a fever or chills.
- A catheter site is red, swollen, or draining pus.
- A catheter site looks more bruised or new bruising appears on the side of your leg.
- You cannot control your urine or bowel movements.
- You have nausea or are vomiting.
- Your skin is itchy, swollen, or you have a rash.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Blood thinners help prevent blood clots. Clots can cause strokes, heart attacks, and death. Many types of blood thinners are available. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions for the type you are given. The following are general safety guidelines to follow while you are taking a blood thinner:
- Watch for bleeding and bruising. Watch for bleeding from your gums or nose. Watch for blood in your urine and bowel movements. Use a soft washcloth on your skin, and a soft toothbrush to brush your teeth. This can keep your skin and gums from bleeding. If you shave, use an electric shaver. Do not play contact sports.
- Tell your dentist and other healthcare providers that you take a blood thinner. Wear a bracelet or necklace that says you take this medicine.
- Do not start or stop any other medicines or supplements unless your healthcare provider tells you to. Many medicines and supplements cannot be used with blood thinners.
- Take your blood thinner exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not skip a dose or take less than prescribed. Tell your provider right away if you forget to take your blood thinner, or if you take too much.
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. It is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to take and how often to take it. Follow directions. Read the labels of all other medicines you are using to see if they also contain acetaminophen, or ask your doctor or pharmacist. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Apply firm, steady pressure if bleeding continues:
A small amount of bleeding from the catheter sites is possible. Apply pressure with a clean gauze or towel for 5 to 10 minutes. Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if bleeding becomes heavy or does not stop.
Care for the catheter sites as directed:
- Keep the catheter sites clean and dry. Keep a small bandage or gauze on each site for 72 hours, or as directed. Your healthcare provider will tell you when you can shower. Carefully wash around the sites with soap and water. Do not rub the site. Do not take baths or go in hot tubs or pools until your provider says it is okay. These increase the risk for infection.
- Care for the catheter sites as directed. Change a bandage or gauze if it gets wet or dirty. Check the catheter sites each day for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or pus. Mild bruising is normal and expected. Do not put powders, lotions, or creams on the catheter sites.
Activity limits
will help prevent bleeding from the catheter sites. Follow these guidelines for as long as shown below, or as directed.
- Do not have sex for 2 days.
- Do not drive for 2 to 3 days.
- Do not lift anything heavier than 5 pounds for 1 week.
- Limit stair climbing for 1 week.
- Avoid intense exercise for 2 to 4 weeks.
Self-care:
- Rest as needed. Short walks to the bathroom and around the house are okay. Ask your healthcare provider when you can return to work or other activities.
- Drink liquids as directed. Liquids help flush the contrast liquid from your body and prevent blood clots. Ask how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars delay healing and increase your risk for another abdominal aortic aneurysm. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your provider before you use these products.
Stent safety:
- Carry your stent card with you at all times.
- Let all healthcare providers know that you have a stent.
- If you need an MRI, wait at least 6 to 8 weeks after stent placement, or as directed.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
You will need to return for CT scans to check the graft and the size of your aneurysm. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
