Endometriosis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
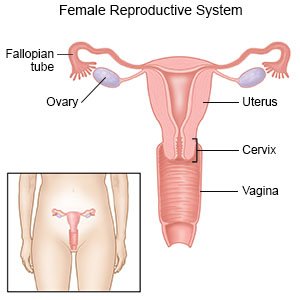
Endometriosis is a condition in which tissue that is normally only in your uterus grows outside of the uterus. Endometriosis causes tissue that should be shed during a monthly period to grow on your ovaries, fallopian tubes, bladder, or other organs. Organs and tissue may stick together and cause inflammation and pain.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Return to the emergency department if:
- You have severe pain that does not go away after you take pain medicine.
Contact your healthcare provider if:
- Your symptoms return after treatment.
- You have heavy or unusual vaginal bleeding.
- You see blood in your urine or bowel movement.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Tylenol
Tylenol is a pain reliever and a fever reducer used to treat many conditions such as headaches ...
Dilaudid
Dilaudid (hydromorphone) is a narcotic pain reliever used to treat moderate to severe pain ...
Omvoh
Omvoh is used to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease in adults. This ...
Qutenza
Qutenza patches are used to treat neuropathic pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia and ...
OxyContin
OxyContin (oxycodone) is an opioid pain reliever used to treat moderate to severe pain. Includes ...
Percocet
Percocet (acetaminophen and oxycodone) is used to relieve moderate to severe pain. Includes ...
Acetaminophen/hydrocodone
The combination of hydrocodone and acetaminophen is used to relieve moderate to severe pain ...
Hydrocodone
Hydrocodone (Hysingla ER and Zohydro ER) is used for around-the-clock treatment of severe pain ...
Oxycodone
Oxycodone is an opioid analgesic used to treat moderate to severe pain; it has a high potential for ...
Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen is a widely used pain reliever and fever reducer for conditions like headaches ...
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Medicines:
- Hormones may help shrink endometrial tissue and decrease pain and inflammation. You may be given birth control pills, androgen hormones, or medicine that makes your body produce less of certain hormones.
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to take and how often to take it. Follow directions. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Self-care:
- Apply heat on your abdomen for 20 to 30 minutes every 2 hours for as many days as directed. Heat helps decrease pain and muscle spasms.
- Exercise regularly to help reduce symptoms, such as pain. Ask about the best exercise plan for you.

Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Endometriosis
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
