Elbow Bursitis Exercises
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Mar 10, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Elbow bursitis exercises
help decrease pain and swelling. They also help increase the movement and strength of your elbow. You will need to start with range-of-motion exercises. When you can do these exercises without pain, you will move to strength exercises. Your healthcare provider or physical therapist will show you how to do movement and strength exercises. He or she will tell you how often to do the exercises.
Call your doctor or physical therapist if:
- You have a fever or chills.
- The skin around your elbow is red or warm.
- Your pain and swelling increase.
- Your symptoms do not improve after 10 days of treatment.
- You have questions or concerns about elbow bursitis exercises.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Humira
Humira is a tumor necrosis factor blocker that is used to treat many inflammatory conditions such ...
Celebrex
Celebrex is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug used to treat pain or inflammation. Learn about ...
Plaquenil
Plaquenil is used to treat or prevent malaria and to treat the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis ...
Rituxan
Rituxan IV infusion is a cancer medicine that interferes with the growth and spread of cancer cells ...
Xeljanz
Xeljanz (tofacitinib) is an oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor that may be used alone or with other ...
Rinvoq
Rinvoq (upadacitinib) is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, atopic ...
Meloxicam
Meloxicam is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug used to treat pain or inflammation caused by ...
Prednisone
Prednisone is used to treat allergic disorders, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis and arthritis. Learn ...
Hydroxychloroquine
Hydroxychloroquine is a quinoline drug used to treat or prevent malaria. It's also used to treat ...
Adalimumab
Adalimumab is used to treat plaque psoriasis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid ...
Exercises to increase range of motion:
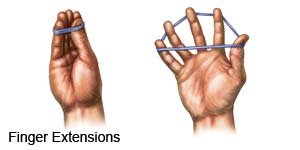
- Finger extensions: Hold the fingertips of your injured arm close together with your fingers and thumb straight. Put a rubber band around the outside of your fingertips and thumb. Spread your fingers apart and then slowly bring them together without letting the rubber band fall off. Repeat 40 times.
- Grip: Hold a soft rubber ball or tennis ball in your hand. Squeeze the ball as hard as you can and hold this position. Ask your healthcare provider how long to hold this position. Repeat this exercise as directed by your healthcare provider.
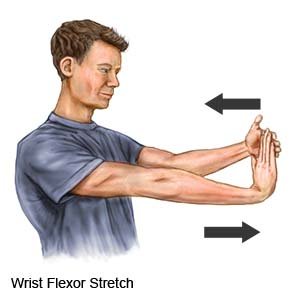
- Wrist flexor stretch: Hold your arm straight out in front of you with your palm facing down. Use your other hand to grasp your fingers. Keep your elbow straight and slowly bend your hand back. Your fingertips should point up and your palm should face away from you. Do this until you feel a stretch in the top of your wrist. Hold for 10 seconds. Repeat 5 times.
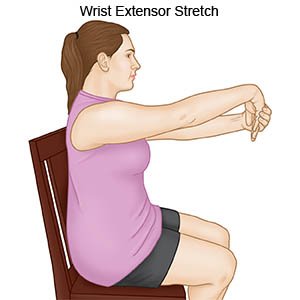
- Wrist extensor stretch: This stretch is the opposite of the wrist flexor stretch. Hold your arm straight out in front of you with your palm facing down. Use your other hand to grasp your fingers. Keep your elbow straight and slowly bend your hand down. Your fingertips should point down and your palm should face you. Do this until you feel a stretch in your wrist. Hold for 10 seconds. Repeat 5 times.
- Elbow flexor stretch: Bend your elbow, and keep your palm facing toward you. Your healthcare provider or physical therapist will tell you how far to bend your elbow. You may injure your elbow if you fully bend it too early. Use your other hand to press gently on the back of your forearm so your arm moves toward you. Do this until you feel a stretch in the back of your upper arm. Hold for 15 to 30 seconds. Repeat 5 times.

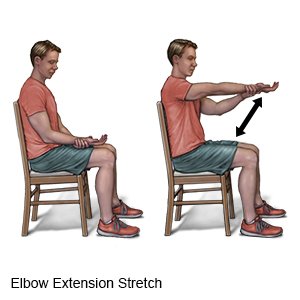
- Elbow extension stretch: This exercise is the opposite of the elbow flexor stretch. Sit in a chair with your arm resting on your thigh. Hold your wrist with the other hand. Slowly straighten your arm so it is extended as far as possible. Keep holding your wrist as you move your arm slowly back to the starting position. Repeat 5 times.
Exercises to increase strength:
Your healthcare provider or physical therapist will tell you how much weight to use.
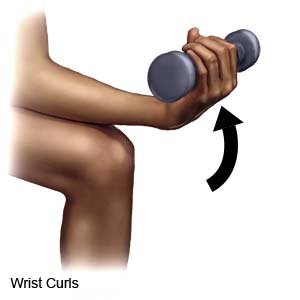
- Wrist curls: Sit in a chair with your forearm resting on your thigh or on a table. Hold a dumbbell with your palm facing up. Bend your wrist up and then slowly lower it down. Repeat 20 times.
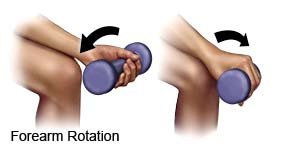
- Forearm rotation: Sit in a chair with your forearm resting on your thigh or on a table. Hold a dumbbell with your palm facing up. Slowly turn your forearm until your palm faces down. Then slowly return to the starting position. Repeat 20 times.
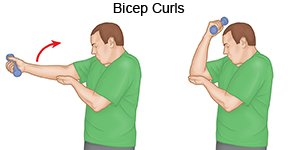
- Biceps curls: Place your hand under your injured elbow for support. Turn your palm so that it faces up and hold a weight in your hand. Slowly bend and straighten your elbow. Repeat 30 times.
Follow up with your doctor or physical therapist as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
