Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition that prevents your body from controlling blood clotting and bleeding. Initially, blood clots form in many areas of your body. Your body responds by overproducing an agent to break down the blood clots. This leads to excessive bleeding, which can be life-threatening.
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
Oxygen:
Oxygen may be needed if your blood oxygen level is lower than it should be. You may get oxygen through a mask or through small tubes placed in your nostrils. Ask your healthcare provider before you take off the mask or oxygen tubing.
Medicines:
- Antibiotics are given to help treat infection caused by bacteria.
- Anticoagulants are also called blood thinners. They help decrease the ability of the blood to clot.
- Antifibrinolytics increase the levels of fibrinogen in your blood. Fibrinogen is a blood protein that helps your blood to clot.
Monitoring:
- Telemetry is continuous monitoring of your heart rhythm.
- An IV is a small tube placed in your vein that is used to give you medicines or liquids.
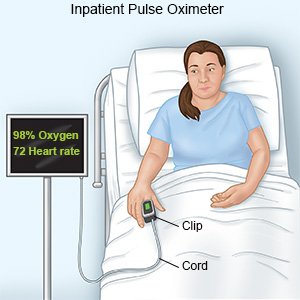
- A pulse oximeter is a device that measures the amount of oxygen in your blood.
Tests:
- Blood tests will check your body's ability to clot.
- A chest x-ray may be used to look for signs of infection. Chest x-rays may also show tumors, broken ribs, or fluid around your heart and lungs.
Treatment:
- A blood transfusion may be needed to help replace blood. You will get whole or parts of blood through an IV during a transfusion.
- Surgery may be needed to remove tumors, retained placenta, or repair bleeding blood vessels.
RISKS:
Without treatment, you may have severe, life-threatening bleeding. You may also have a decrease of blood flow to your organs because of clots. This can damage your organs or lead to tissue death.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
