Diabetes Type 1: Management
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 7, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Type 1 diabetes
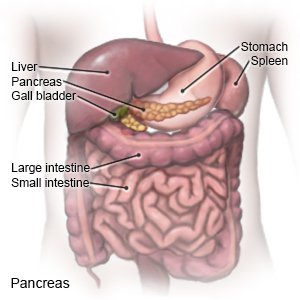
is a disease that affects how your body makes insulin and uses glucose (sugar). Normally, when the blood sugar level increases, the pancreas makes more insulin. Insulin helps move sugar out of the blood so it can be used for energy. Type 1 diabetes develops because the immune system destroys cells in the pancreas that make insulin. The pancreas cannot make enough insulin, so the blood sugar level continues to rise. A family history of type 1 diabetes may increase your risk. Type 1 diabetes is treated with insulin.
 |
Signs and symptoms of uncontrolled type 1 diabetes:
- More thirst than usual
- Urinating often
- Hunger most of the time
- Weight loss without trying
- Blurred vision
Type 1 diabetes management
means you control your blood sugar levels and prevent diabetes complications. Management will help you feel well and enjoy your daily activities. Your diabetes care team providers can help you make a plan to fit diabetes care into your schedule. Your plan can change over time to fit your needs and your family's needs. Tell your care team if you have trouble following any part of your care plan.
Complications of type 1 diabetes:
High blood sugar levels can become life-threatening. Long-term high blood sugar levels can cause problems such as the following:
- Heart and blood vessel conditions, such as heart attack, stroke, or narrowing of blood vessels
- Kidney damage that leads to kidney failure
- Neuropathy (nerve damage), weakness, pain, and numbness, usually in hands and feet
- Eye damage that leads to blindness
- Skin and mouth conditions, including infections and gum disease
- Foot damage that can lead to amputation
Have someone call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You cannot be woken.
- You have signs of diabetic ketoacidosis:
- confusion, fatigue
- vomiting
- rapid heartbeat
- fruity smelling breath
- extreme thirst
- dry mouth and skin
- You have any of the following signs of a heart attack:
- Squeezing, pressure, or pain in your chest
- You may also have any of the following:
- Discomfort or pain in your back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or a sudden cold sweat
- You have any of the following signs of a stroke:
- Numbness or drooping on one side of your face
- Weakness in an arm or leg
- Confusion or difficulty speaking
- Dizziness, a severe headache, or vision loss
Seek care immediately if:
- Your blood sugar level is above 240 mg/dL and does not come down with treatment.
- You have symptoms of hypoglycemia, such as trouble thinking, sweating, or a pounding heartbeat.
Call your doctor or diabetes care team provider if:
- You have a sore or wound that will not heal.
- You have a change in the amount you urinate.
- Your skin is red, dry, warm, or swollen.
- You have trouble managing diabetes, or you feel anxious or depressed.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Manage your blood sugar level:
- Check your blood sugar level as directed and as needed. You will be given information on when and how to check your blood sugar level. You will learn what to do if the level is too high or too low. Make a list of the times you checked your blood sugar level and the results of your checks. Take the list to all follow-up appointments.
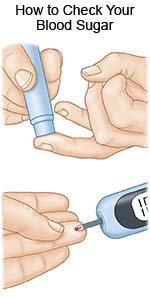
- A glucose meter is a device that uses a test strip to check the level. You put a small drop of blood from a finger on the test strip. The strip is put into the device. The device then figures out how much sugar is in your blood.
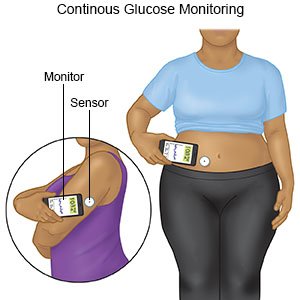
- A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) uses a sensor to check the level. The sensor is placed on your abdomen or arm. A transmitter on the sensor gets a glucose reading. CGM data may be linked to an insulin pump.
- A glucose meter is a device that uses a test strip to check the level. You put a small drop of blood from a finger on the test strip. The strip is put into the device. The device then figures out how much sugar is in your blood.
- Know what to do if your blood sugar level is too high or too low. Levels that remain too high or too low can be life-threatening. Learn the signs or symptoms of high blood sugar levels, such as increased urination and fatigue. Also learn the signs or symptoms of low levels, such as shakiness, sweating, or irritability. Always have glucose tablets or glucose gel to take if levels are too low.

- Use insulin as directed. You will need insulin each day. You will learn how much insulin you need and when to use it. You will also be taught how to match insulin with blood sugar levels, activity, and carbohydrates. Insulin may be given through a pump or pen, or injected. You and your care team will discuss the best method for you:
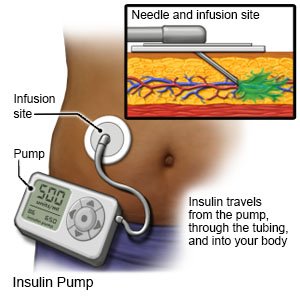
- A pump is a wearable medical device that gives continuous insulin. An insulin pump prevents the need for multiple insulin injections in a day.
- A pen is a device prefilled with insulin. Most insulin pens are disposable. You throw the pen away after it is empty or used for a certain amount of time. Some pens have a replaceable cartridge filled with insulin. You keep the pen and only throw away the cartridge.
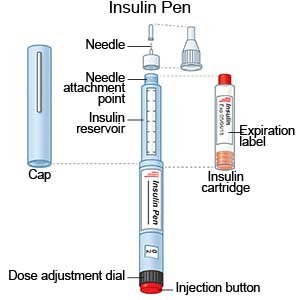
- Insulin injections are given with a needle and syringe. You and your family members will be taught how to draw up and give insulin if this is the best method for you. You will also be taught how to dispose of used needles and syringes.
- A pump is a wearable medical device that gives continuous insulin. An insulin pump prevents the need for multiple insulin injections in a day.
- Count your carbs, protein, and fats correctly. Each meal should have a balance of carbs, proteins, and fats. Work with your dietitian to create meal plans so your blood sugar level stays steady throughout the day.
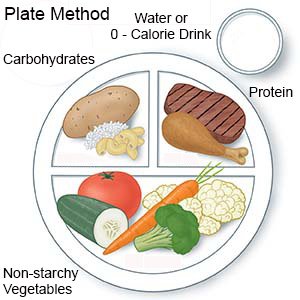
- Include high-fiber foods in your meal plans. Fiber helps improve blood sugar levels. Fiber also lowers your risk for heart disease and other problems diabetes can cause. Examples of high-fiber foods include vegetables, whole-grain bread, and beans such as pinto beans. Your dietitian can tell you how much fiber to have each day.

- Know the risks if you choose to drink alcohol. Alcohol can cause your blood sugar levels to be low if you use insulin. Alcohol can cause high blood sugar levels and weight gain if you drink too much. One drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1½ ounces of liquor.
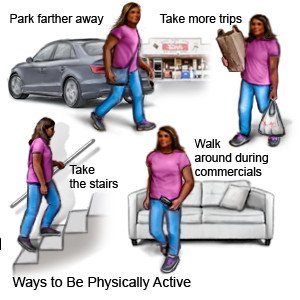
- Be physically active as directed. Physical activity helps control your blood sugar level, manage your weight, and prevent kidney and heart problems. Your provider can help you create an activity plan. The plan will include daily and weekly physical activity goals. Check your blood sugar level before and after you are physically active. Your care team will tell you what your levels should be.

- Go to follow-up appointments. You may be sent to different types of providers to check for complications of diabetes. Types of providers include heart (cardiologist), kidney (nephrologist), and nerve (neurologist) specialists. Complications of diabetes can start 3 to 5 years after your diagnosis. You will need to get your eyes checked every year or if you have problems with your vision.
More ways to manage type 1 diabetes:
- Wear medical alert identification. Wear medical alert jewelry or carry a card that says you have diabetes. Ask your diabetes care team provider where to get these items.
- Talk to your provider if you become stressed about diabetes care. Sometimes being able to fit diabetes care into your life can cause increased stress. The stress can cause you not to take care of yourself properly. Your provider can help by offering tips about self-care. Your provider may suggest you talk to a mental health provider. The mental health provider can listen and offer help with self-care issues.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause lung and blood vessel damage. It also makes it more difficult to manage your diabetes. Ask your provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. Do not use e-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco in place of cigarettes or to help you quit. They still contain nicotine.
- Check your feet each day for cuts, scratches, calluses, or other wounds. Look for redness and swelling, and feel for warmth. Wear shoes that fit well. Check your shoes for rocks or other objects that can hurt your feet. Do not walk barefoot or wear shoes without socks. Wear cotton socks to help keep your feet dry.
- Ask about vaccines you may need. You have a higher risk for serious illness if you get the flu, pneumonia, COVID-19, or hepatitis. Ask your provider if you should get vaccines to prevent these or other diseases, and when to get the vaccines.
- Have screening tests as directed. Type 1 diabetes increases your risk for other autoimmune diseases. Talk to your provider about how often you should be screened.
Follow up with your doctor or diabetes care team provider as directed:
You may need to follow up more often if you are having problems. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
