Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What is developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)?
DDH is a condition that prevents parts of your child's hip joints from fitting together correctly.
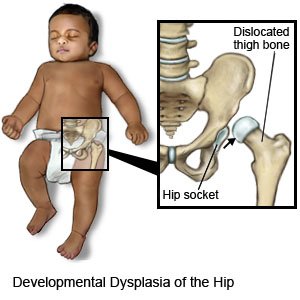 |
What increases my child's risk for DDH?
- Loose or stretched ligaments
- Breech delivery
- A family history of DDH or other hip problems
- Being female
- Being a firstborn child
- Low levels of amniotic fluid (fluid that surrounds your baby in the womb) during pregnancy
- Medical conditions such as Ehlers-Danlos or Marfan syndromes
What are the signs and symptoms of DDH?
- Hips are not stable and pop in and out with movement
- Extra folds or wrinkles on the thigh
- One leg that is shorter than the other
- Pops and clicks heard or felt when your child moves his or her hips
- Problems crawling, walking, or moving
How is DDH diagnosed?
Your child's healthcare provider will ask about your child's and your health history. The provider may also ask if your child has a family history of DDH or hip problems. The movement of your child's hips will be examined.
- An ultrasound uses sound waves to show pictures of your child's hips to check for DDH. Your child may need an ultrasound before he or she is 6 months old if he or she is at risk for DDH.
- An x-ray, CT, or MRI may be used to see if your child's hipbone is in the right place. Contrast liquid may used to help your child's healthcare provider see the hip joint and the area around it. Tell the healthcare provider if your child has ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not let your child enter the MRI room with anything metal. The MRI uses a powerful magnet. Metal can cause serious injury from the magnet. Tell the healthcare provider if your child has any metal in or on his or her body.
How is DDH treated?
Treatment depends on your child's age and how bad the dysplasia is. The head of your child's femur may need to be put back into the hip socket.
- A splint called a Pavlik harness holds the hip in place for a few months. This harness makes the head of the femur fit correctly into the hip socket.

- A cast may be needed if your child is already walking when DDH is diagnosed. Healthcare providers may place your child in a cast that covers him or her from the chest down to the legs or knees. The cast will prevent your child's hips from moving and allow proper healing.
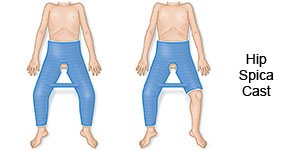
- Closed reduction is a procedure to realign a bone or bring the hip joint back to its normal position. This is done by moving the hips and femur without opening the skin.
- Surgery and a hip brace may also be used to fix and correct your child's hip problem.
- Traction pulls on the hip or thigh bones to pull them back into place. A pin may be put in your child's bone or cast, and hooked to ropes and a pulley. Weight is hung on the rope to help stretch the soft tissues around the hip bones. This helps the hip fit into the hip socket.
- Physical and occupational therapy may be needed. A physical therapist teaches your child exercises to help improve movement and strength. An occupational therapist teaches your child skills to help with daily activities.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your child feels lightheaded, short of breath, and has chest pain.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your child's splint or cast gets damaged or breaks.
- Your child's skin around his or her toes or hips is blue, cold, or numb.
When should I call my child's doctor?
- Your child's pain is getting worse, even after he or she has taken pain medicine.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your child's care. Learn about your child's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your child's healthcare providers to decide what care you want for your child. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
