Dental Cavities in School Aged Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What are dental cavities?
Dental cavities, also called caries, are holes in teeth caused by bacteria. The bacteria mix with carbohydrates from foods and create acids. The acids break down areas of enamel, which covers the outside of a tooth.
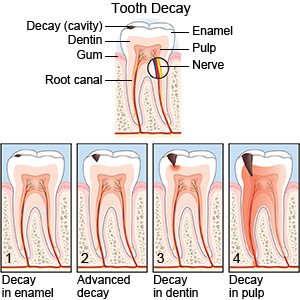 |
What increases my child's risk for dental cavities?
- Poor tooth care
- Sugary foods and drinks, such as cookies, candy, fruit snacks, juice, or soda
- Not going to the dentist every 6 months
- Tightly spaced teeth that are hard to clean and floss
- Being born early or weighing less than normal at birth
- Not enough fluoride in water or not using dental products with fluoride
What are the signs or symptoms of dental cavities?
Your child may not have any symptoms if cavities have just started to form. When cavities reach deeper parts of your child's tooth, he or she may have pain. Your child may also have any of the following:
- Pain when your child chews or eats hot or cold foods
- Chalky white, yellow, or brown tooth
- Gum swelling
How are dental cavities diagnosed?
The dentist will look at your child's teeth to check for signs of dental cavities. He or she may also use x-rays to find cavities.
How are dental cavities treated?
- A fluoride treatment may be given during dental visits. Your child may use products with fluoride at home. Your child's dentist will tell you what kind of fluoride your child needs and how to use it.
- A filling may be placed in your child's tooth after the decayed portion is removed. The filling may help to protect your child's tooth from more decay.
- A root canal may be needed if the tooth is infected or the decay is severe.
How can I help my child prevent dental cavities?
- Help your child care for his or her teeth until he or she can do it properly. Your child should start caring for his or her own teeth at age 7 or 8.
- Brush for 2 minutes, 2 times each day. It may help to play a song that is at least 2 minutes long while your child brushes. You should only need to do this until your child is used to the time.
- Have your child spit the toothpaste out after brushing. He or she does not need to rinse with water. The small amount of toothpaste that stays in your child's mouth can help prevent cavities.
- Your child will also need to floss 1 time each day.
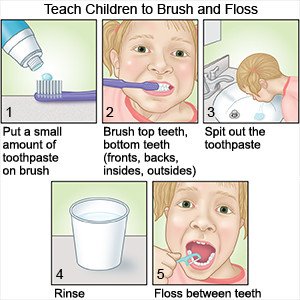
- Bring your child to the dentist 2 times each year. A dentist can find and treat problems early. This may help prevent dental cavities. The dentist can give your child a fluoride treatment to help prevent cavities.
- Give your child healthy foods and drinks. Choose foods and drinks that are low in sugar. Read food labels to help you choose foods that are low in sugar. Limit candy, cookies, soda, and fruit juice.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your child has severe pain in his or her tooth or jaw.
- Your child has swelling in his or her jaw or cheek.
When should I call my child's dentist?
- Your child has a fever.
- Your child's tooth pain gets worse.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your child's care. Learn about your child's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your child's healthcare providers to decide what care you want for your child. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
