Corrosive Esophagitis in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jun 5, 2024.
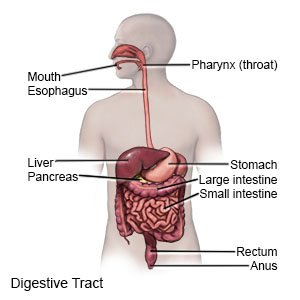
Corrosive esophagitis is damage to your child's esophagus from harmful substances. The damage may cause inflammation, ulcers, or scarring.
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that your child may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your child's medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done to your child. Make sure all of your questions are answered.
An IV
is a small tube placed in your child's vein that is used to give medicine or liquids.
Nutrition:
Your child may need to eat bland, low-acid foods. He or she may also need any of the following:
- Your child may need to eat foods that are soft and easy to swallow. Some examples are applesauce, bananas, cooked cereal, cottage cheese, eggs, and yogurt.
- Tube feedings may be used if your child has trouble swallowing soft foods. The feeding tube will be carefully inserted through your child's nose and down into his or her stomach. Liquid nutrition will be put through the end of the feeding tube and will flow into your child's stomach.
- Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) may be used if your child has problems digesting food. TPN provides your child's body with nutrition through his or her IV.
Medicines:
- Antibiotics help treat or prevent a bacterial infection in your child's esophagus.
- Steroids help decrease inflammation.
- Stomach acid medicine helps decrease irritation from stomach acids.
- Antiulcer medicine helps decrease irritation from stomach acids. They may help increase the protective lining of the esophagus to help it heal.
Tests:
- A barium swallow means your child swallows a thick liquid called barium. Barium helps your child's intestines show up better in x-ray pictures.
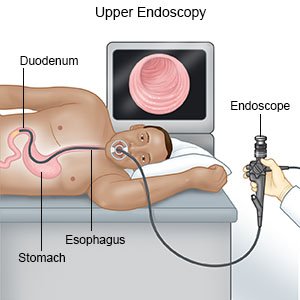
- An endoscopy is used to see the inside of your child's esophagus and stomach. A flexible tube with a small light and camera on the end is used for this procedure. Your child's healthcare provider will look for any bleeding, lumps, narrowing, scars, tears, or pill pieces. He or she may remove a small amount of tissue from your esophagus for a biopsy.
Treatment:
Your child may need any of the following, depending on his or her age and the esophagitis cause:
- Dilatation is a procedure to place a small balloon, dilator, or stent in your child's esophagus to widen it.
- Surgery may be needed to remove an area of your child's esophagus. It may be replaced with a portion of his or her stomach or colon.
RISKS:
Without treatment, your child may continue to feel pain and have trouble swallowing food and liquids. Your child may not be able to eat enough, and he or she may lose weight and feel weak. Food, liquids, or vomit may get in your child's lungs. He or she may choke, get a lung infection, or have trouble breathing. Too much damage in your child's esophagus can cause bleeding that does not stop. These conditions may be life-threatening.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your child's care. Learn about your child's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your child's healthcare providers to decide what care you want for your child.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
