Chest Contusion
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
A chest contusion is a bruise that appears on your skin after an injury. A bruise happens when small blood vessels tear but skin does not. Blood leaks into nearby tissue, such as soft tissue or muscle.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Return to the emergency department if:
- You have increased chest pain.
- You have shortness of breath.
- You start to cough up blood.
- Your pain does not improve with pain medicine.
Call your doctor if:
- You develop a cough or fever.
- You find a new lump in the injured area.
- Your symptoms do not improve with treatment.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. It is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to take and how often to take it. Follow directions. Read the labels of all other medicines you are using to see if they also contain acetaminophen, or ask your doctor or pharmacist. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions. Do not give these medicines to children younger than 6 months without direction from a healthcare provider.
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Manage a chest contusion:
- Rest as directed. Do not play sports or do physical activity until your healthcare provider says it is okay.
- Apply ice to decrease swelling and pain. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover the bag with a towel before you place it on your bruise. Apply ice for 15 to 20 minutes every hour, or as directed.
- Do deep breathing exercises as directed to prevent pneumonia:
- Take 10 deep breaths every hour, even when you wake up during the night. Brace your chest with your hands or a pillow while you take deep breaths or cough. This will help decrease your pain.
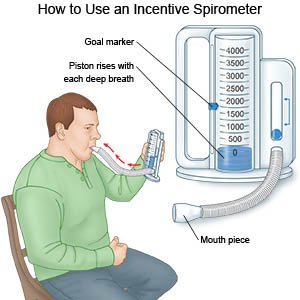
- You may need to use an incentive spirometer to help you take deeper breaths. Put the plastic piece into your mouth and take a deep breath. Hold your breath as long as you can. Then let out your breath. Do this 10 times in a row every hour while you are awake.
- Do not drink alcohol as directed. Alcohol may slow healing.
- Do not stretch your upper body right after your injury. Ask your healthcare provider when and how you may safely stretch after your injury. Gentle stretches can help increase your flexibility.
- Do not massage the area or put heating pads on the bruise right after your injury. Heat and massage may slow healing. Your healthcare provider may tell you to apply heat after several days. At that time, heat will start to help the injury heal.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
