Cervical Fracture
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What is a cervical fracture?
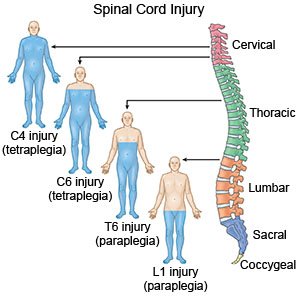
A cervical fracture is a break in a vertebra (bone) in your neck. The 7 cervical vertebrae are called C1 through C7. Cervical vertebrae support your head and allow your neck to bend and twist. The vertebrae enclose and protect the spinal cord. Nerves in the spinal cord control your ability to move.
 |
What are the signs and symptoms of a cervical fracture?
- Pain, tenderness, swelling, or muscle spasms in your neck
- Not being able to turn or twist your neck freely
- Trouble swallowing or breathing
- Loss of feeling or pinprick pain in your arms or legs
- Numbness, pain, or tingling at the base of your head
- Double vision or loss of consciousness
How is a cervical fracture diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask how your injury occurred. He or she will ask about your signs and symptoms and feel for painful areas on your neck. Your provider will check for problems with your muscles, reflexes, and sense of touch. You may also need any of the following tests:
- X-rays may be used to check for broken bones or other neck problems.
- A CT scan or MRI may show pressure on or damage to your spinal cord. You may be given contrast liquid to help your spinal cord show up better in pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Tell the provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
How is a cervical fracture treated?
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Immobilization is used to keep your head and neck from moving as your cervical fracture heals. You may need the following:
- A halo brace and vest prevent most head and neck movements. The halo brace is attached to your head with pins placed in your skull. It will not be removed while you are getting treatment.
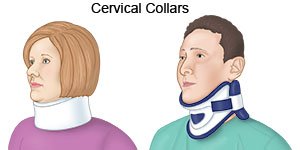
- A semirigid collar uses plastic plates to stop side-to-side or up-and-down motion in your neck.
- A soft collar is a flexible brace placed around the neck. It is often used after a more rigid collar.
- Surgery may be needed to repair the fracture. You may also have surgery after immobilization if your fracture has not healed.
- Therapy may be recommended. A physical therapist and an occupational therapist may exercise your arms, legs, and hands. They may also teach you new ways to do things around the house. A speech therapist may work with you to help you talk or swallow.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) or have someone else call if:
- You feel lightheaded, short of breath, or have chest pain.
- You cough up blood.
- You cannot feel or move your arms or legs.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have a sudden, severe headache with nausea and vomiting.
- You are seeing double or suddenly cannot see.
- You cannot stay awake.
- The pins in your halo brace have loosened or look deeper in the skin than before.
- You feel new weakness or numbness in your hands or fingers.
- Your arm or leg feels warm, tender, and painful. It may look swollen and red.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have a fever.
- You see a skin rash, redness, or sores under your brace.
- You have problems swallowing while you are wearing your halo brace.
- Your neck pain is not getting better even with treatment.
- You have questions or concerns about your cervical fracture, medicine, or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
