Cellulitis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is cellulitis?
Cellulitis is a skin infection caused by bacteria. Cellulitis is common and can become severe. Cellulitis usually appears on the lower legs. It can also appear on the arms, face, and other areas. Cellulitis develops when bacteria enter a crack or break in your skin, such as a scratch, bite, or cut.
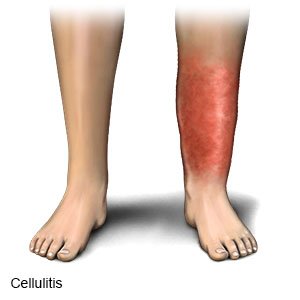 |
What are the signs and symptoms of cellulitis?
Signs and symptoms usually appear on one side of your body. You may have any of the following:
- A fever
- A red, warm, swollen area on your skin
- Pain when the area is touched
- Red spots, bumps, or blisters
- Bumpy, raised skin that feels like an orange peel
How is cellulitis diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider may know you have cellulitis by looking at your skin. You may need blood tests to show what kind of bacteria are causing your infection. Other tests may be needed to see how much the infection has spread.
How is cellulitis treated?
You should start to see improvement in 3 days. If your cellulitis is severe, you may need IV antibiotics in the hospital. If cellulitis is not treated, the infection can spread through your body and become life-threatening. You may need any of the following medicines:
- Antibiotics help treat a bacterial infection.
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. It is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to take and how often to take it. Follow directions. Read the labels of all other medicines you are using to see if they also contain acetaminophen, or ask your doctor or pharmacist. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can I manage my symptoms?
- Wash the area with soap and water every day. Gently pat dry. Use bandages if directed by your healthcare provider.
- Apply cream or ointment as directed. These help protect the area. Most over-the-counter products, such as petroleum jelly, are good to use. Ask your healthcare provider about specific creams or ointments you should use.
- Place a cool, damp cloth on the area. Use clean cloths and clean water. You can do this as often as you need to. Cool, damp cloths may help decrease pain.
- Elevate the area above the level of your heart as often as you can. This will help decrease swelling and pain. Prop the area on pillows or blankets to keep it elevated comfortably.

How can I help prevent cellulitis?
- Do not scratch bug bites or areas of injury. You increase your risk for cellulitis by scratching these areas.
- Do not share personal items, such as towels, clothing, and razors.
- Clean exercise equipment with germ-killing cleaner before and after you use it.
- Treat athlete's foot. This can help prevent the spread of a bacterial skin infection.
- Wash your hands often. Use soap and water. Wash your hands after you use the bathroom, change a child's diapers, or sneeze. Wash your hands before you prepare or eat food. Use lotion to prevent dry, cracked skin.

When should I seek immediate care?
- Your wound gets larger and more painful.
- You feel a crackling under your skin when you touch it.
- You have purple dots or bumps on your skin, or you see bleeding under your skin.
- You see red streaks coming from the infected area.
When should I call my doctor?
- The red, warm, swollen area gets larger.
- Your fever or pain does not go away or gets worse.
- The area does not get smaller after 3 days of antibiotics.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Cellulitis
- Can You Drink Alcohol with Antibiotics?
- Common Side Effects from Antibiotics, and Allergies and Reactions
Treatment options
Care guides
- Abscess
- Cellulitis in Children
- Impetigo
- Lymphangitis
- Periorbital Cellulitis in Children
- Pitted Keratolysis
- Umbilical Granuloma
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
