Carotid Artery Stent Placement
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
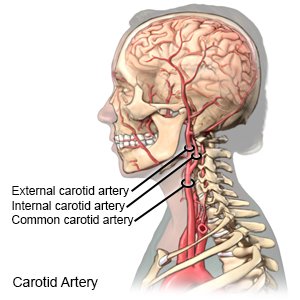
A carotid artery stent placement is a procedure to widen a narrowed carotid artery. The carotid arteries are 2 large blood vessels on each side of your neck. They carry blood and oxygen from your heart to your brain. A stent is a wire mesh tube that helps hold your carotid artery open.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call 911 for any of the following:
- You have any of the following signs of a heart attack:
- Squeezing, pressure, or pain in your chest
- You may also have any of the following:
- Discomfort or pain in your back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or a sudden cold sweat
- You have any of the following signs of a stroke:
- Numbness or drooping on one side of your face
- Weakness in an arm or leg
- Confusion or difficulty speaking
- Dizziness, a severe headache, or vision loss
- You feel lightheaded, short of breath, and have chest pain.
- You cough up blood.
- You have trouble breathing.
- You cannot stop the bleeding from your wound even after you hold firm pressure for 10 minutes.
Seek care immediately if:
- Blood soaks through your bandage.
- Your stitches come apart.
- Your arm or leg feels numb, cool, or looks pale.
- Your wound gets swollen quickly.
Contact your healthcare provider if:
- You have a fever or chills.
- Your wound is red, swollen, or draining pus.
- Your wound looks more bruised or there is new bruising on the side of your leg or arm.
- You have nausea or are vomiting.
- Your skin is itchy, swollen, or you have a rash.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Crestor
Crestor (rosuvastatin) is used to treat high cholesterol and high triglycerides in the blood ...
Plavix
Plavix (clopidogrel) is used to prevent blood clots after a recent heart attack or stroke. Includes ...
Ozempic
Learn about Ozempic (semaglutide) for type 2 diabetes treatment, weight management, cardiovascular ...
Xarelto
Xarelto (rivaroxaban) is a factor Xa inhibitor used to reduce the risk of blood clots and stroke in ...
Zontivity
Zontivity is used for the prevention of cardiovascular events. Includes Zontivity side effects ...
Vorapaxar
Vorapaxar systemic is used for peripheral arterial disease, prevention of atherothrombotic events ...
Rivaroxaban
Rivaroxaban systemic is used for atrial fibrillation, cardiovascular risk reduction, congenital ...
Rosuvastatin
Rosuvastatin is a prescription medication used to treat high cholesterol and prevent heart disease ...
Clopidogrel
Clopidogrel systemic is used for acute coronary syndrome, acute coronary syndrome, prophylaxis ...
Isoxsuprine
Isoxsuprine systemic is used for cerebrovascular insufficiency, coronary artery disease, raynaud's ...
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Blood thinners help prevent blood clots. Clots can cause strokes, heart attacks, and death. Many types of blood thinners are available. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions for the type you are given. The following are general safety guidelines to follow while you are taking a blood thinner:
- Watch for bleeding and bruising. Watch for bleeding from your gums or nose. Watch for blood in your urine and bowel movements. Use a soft washcloth on your skin, and a soft toothbrush to brush your teeth. This can keep your skin and gums from bleeding. If you shave, use an electric shaver. Do not play contact sports.
- Tell your dentist and other healthcare providers that you take a blood thinner. Wear a bracelet or necklace that says you take this medicine.
- Do not start or stop any other medicines or supplements unless your healthcare provider tells you to. Many medicines and supplements cannot be used with blood thinners.
- Take your blood thinner exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not skip a dose or take less than prescribed. Tell your provider right away if you forget to take your blood thinner, or if you take too much.
- Antiplatelets , such as aspirin, help prevent blood clots. Take your antiplatelet medicine exactly as directed. These medicines make it more likely for you to bleed or bruise. If you are told to take aspirin, do not take acetaminophen or ibuprofen instead.
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Bathing:
You may be able to shower the day after your procedure. Remove your pressure bandage before you shower. Do not take baths or go in hot tubs or pools. Carefully wash around the wound with soap and water. Pat the area dry.
Care for your wound as directed:
Change your bandage when it gets wet or dirty. A small band-aid can be placed on your wound after you remove the pressure bandage. Monitor your wound everyday for signs of infection such as redness, swelling, or pus. Mild bruising is normal and expected. Do not put powders, lotions, or creams on your wound.
Self-care:
- Apply firm, steady pressure if bleeding occurs. A small amount of bleeding from your wound is possible. Apply pressure with a clean gauze or towel for 5 to 10 minutes. Call 911 if bleeding becomes heavy or does not stop.
- Do not lift anything heavier than 5 pounds for 48 hours. Heavy lifting can put stress on your wound and cause bleeding. Do not push or pull with the arm that was used for the procedure.
- Do not do vigorous activity for at least 48 hours. Vigorous activity may cause bleeding from your wound. Rest and do quiet activities. Short walks to the bathroom and around the house are okay. Do not walk or stand for more than 10 minutes. Ask your healthcare provider when you can return to your normal activities.
- Limit stair climbing to prevent bleeding from your wound. Plan activities on one floor and use stairs 2 times a day or less.
- Drink liquids to flush the contrast liquid from your body and prevent blood clots. Ask how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
- Restart your blood thinners as directed. Your healthcare provider may tell you to start taking your blood thinners after your procedure or he or she may have you wait a few days.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can block your arteries. They can also increase your risk for heart disease, heart attack, and stroke. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
Follow up with your healthcare provider as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
