Carotid Artery Disease
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jun 5, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
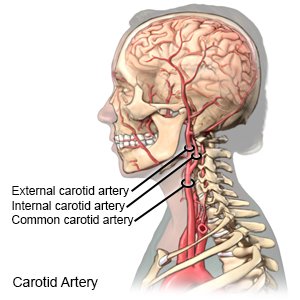
Carotid artery disease (CAD)
means the major blood vessels in your neck are narrowed or becoming blocked. These 2 major blood vessels are called the carotid arteries. They supply your brain with blood. The narrow or blocked blood vessels increase your risk for a stroke. CAD is also called carotid artery stenosis.
 |
Have someone call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have any of the following signs of a stroke:
- Numbness or drooping on one side of your face
- Weakness in an arm or leg
- Confusion or difficulty speaking
- Dizziness, a severe headache, or vision loss
- You have any of the following signs of a heart attack:
- Squeezing, pressure, or pain in your chest
- You may also have any of the following:
- Discomfort or pain in your back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or a sudden cold sweat
Call your doctor if:
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Common signs and symptoms:
CAD develops slowly. You may have no signs or symptoms until you have a mini-stroke, or transient ischemic attack (TIA). A TIA is a temporary lack of blood flow to your brain. A TIA goes away quickly and does not cause permanent damage. A TIA may be a warning sign that you are about to have a stroke. If you have any symptoms of a TIA or stroke, seek care immediately.
Warning signs of a stroke:
The words BE FAST can help you remember and recognize warning signs of a stroke:
- B = Balance: Sudden loss of balance
- E = Eyes: Loss of vision in one or both eyes
- F = Face: Face droops on one side
- A = Arms: Arm drops when both arms are raised
- S = Speech: Speech is slurred or sounds different
- T = Time: Time to get help immediately
 |
Treatment
depends on how narrow your arteries have become. Treatment also depends on your symptoms and your general health. The goal of treatment is to lower your risk for a stroke. You may need any of the following:
- Medicines:
- Aspirin, or other blood thinner, may be recommended. These will help prevent blood clots from forming in your carotid arteries. If your healthcare provider wants you to take aspirin, do not take acetaminophen or ibuprofen instead.
- Cholesterol medicine lowers your cholesterol level.
- Blood pressure medicine lowers or helps control your blood pressure.
- Procedures can help open blocked arteries:
- Carotid endarterectomy (CEA) is used to cut and remove plaque buildup from your arteries.
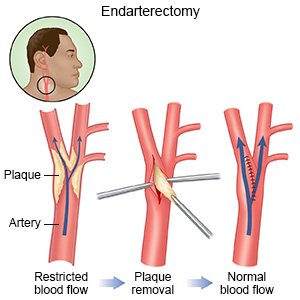
- Carotid angioplasty and stenting (CAS) is used to push the plaque against the artery wall with a balloon device. Then, a stent is placed to keep the artery open. A stent is a small metal mesh tube.
- Carotid endarterectomy (CEA) is used to cut and remove plaque buildup from your arteries.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Prevent a stroke:
- Do not smoke, and avoid secondhand smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars increase your risk for a stroke. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your provider before you use these products.
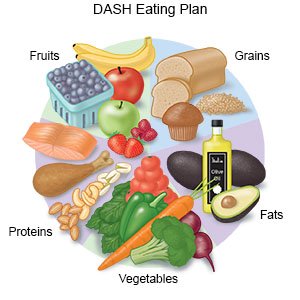
- Eat a variety of healthy foods. Healthy foods include fruit, vegetables, whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, chicken, and fish. Choose fish that are high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and fresh tuna. Ask your provider for more information on a heart healthy diet and the DASH eating plan.
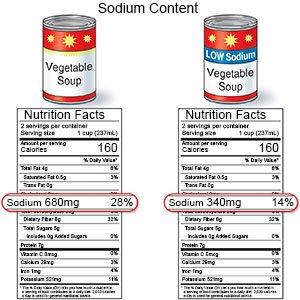
- Limit sodium (salt). Sodium may increase your blood pressure. Add less table salt to your foods. Read food labels and choose foods that are low in sodium. Your provider may suggest you follow a low sodium diet.
- Reach or maintain a healthy weight. Extra weight makes your heart work harder. Ask your provider what a healthy weight is for you. Your provider can help you create a safe weight-loss plan, if needed. Even a weight loss of 10% of extra body weight can help your heart function better.
- Exercise regularly. Exercise helps improve heart function and can help you manage your weight. Exercise can also help lower your cholesterol and blood sugar levels. Try to get at least 30 minutes of exercise 5 times each week. Try to be physically active every day. This may include walking, riding a bicycle, or swimming. Your provider can help you create an exercise plan that works best for you.
- Limit alcohol. Alcohol can increase your blood pressure and triglyceride levels. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1½ ounces of liquor.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Carotid Artery Disease
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
