Breastfeeding and Breast Engorgement
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What do I need to know about breast engorgement?
Breast engorgement develops when too much milk builds up in your breast. It is normal for your breasts to feel swollen, heavy, and tender when your milk comes in. This is called breast fullness. When your breast starts to feel painful and hard, the fullness has developed into engorgement. Breast engorgement usually happens 3 to 5 days after you give birth. Engorgement can happen if you are not breastfeeding or expressing milk often, or produce a lot of milk. Your baby may have a hard time latching on (attaching) to your breast to feed. Without treatment, engorgement can lead to plugged milk ducts or a breast infection called mastitis.
What are the signs and symptoms of breast engorgement?
- A swollen, tender breast
- A breast that feels hard to the touch or looks tight or shiny
- Warm, red, or throbbing breast
- Flat nipple
- A low fever
What can I do to manage my symptoms?
- Breastfeed or pump every 2 or 3 hours. Frequent breastfeeding helps decrease engorgement discomfort. Express or pump milk from your breasts before you breastfeed. This will help soften your breast and your nipple, and allow your baby to latch on better.
- Massage your breast. Breast massage helps empty your engorged breast and decrease pain. Gently massage your breast before and during breastfeeding to help increase your milk flow. Gently stroke your breast, starting from the outer areas and working your way toward the nipple. Breast massage may also help prevent breast engorgement if done in the first few days after you give birth.
- Apply a cool compress in between feedings. The cold may help decrease swelling and pain in your engorged breast. Wet a washcloth in cold water, wring it out, and place it on your breast. Ask how long and how often to use a cool compress.
- Wear a supportive bra. The bra should fit well but not be too tight.
What can I do to prevent breast engorgement?
- Help your baby get a good latch. Hold the nape of his or her neck to help him or her latch onto your breast. Touch his or her top lip with your nipple and wait for him or her to open his or her mouth wide. Your baby's lower lip and chin should touch the areola (dark area around the nipple) first. Help him or her get as much of the areola in his or her mouth as possible. You should feel as if your baby will not separate from your breast easily. Gently break suction and reposition if your baby is only sucking on the nipple. Talk to a lactation consultant if you need help with your baby's latch.
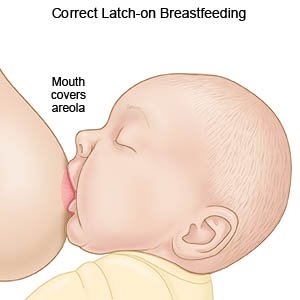
- Empty your breasts completely. Take your time when you breastfeed to allow your baby to empty your breast. Try not to switch breasts too early. Express or pump after you breastfeed if your baby is not emptying your breasts when he or she feeds.
- Apply warmth to your breast before you breastfeed. Put a warm, wet cloth on your breast or take a warm shower. This can help increase your milk flow.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have a fever with chills or body aches.
- You have pain and swelling in one or both breasts that keeps you from breastfeeding.
When should I contact my healthcare provider?
- You have a tender breast lump that grows slowly and usually forms on one side of your breast.
- You have a small, white bump on your nipple.
- Your symptoms do not get better within 24 hours.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Further information
- American Academy of Pediatrics
345 Park Boulevard
Itasca , IL 60143
Phone: 1- 800 - 433-9016
Web Address: http://www.aap.org
- La Leche League International
957 North Plum Grove Road
Schaumburg , IL 60173
Phone: 1- 847 - 519-7730
Phone: 1- 800 - 525-3243
Web Address: http://www.lalecheleague.org
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
