Baker Cyst
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What is a Baker cyst?
A Baker cyst is a bulging lump of fluid behind your knee. A Baker cyst can develop if you have a knee injury, or a condition such as osteoarthritis or a connective tissue disorder. A Baker cyst may also be called a popliteal cyst.
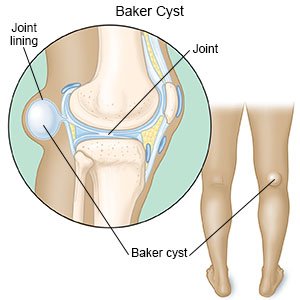 |
What are the signs and symptoms of a Baker cyst?
- A lump or swelling in the back of your knee when you stand or walk
- Knee swelling that goes away when you bend your knee
- Knee pain
- Stiffness or tightness in your knee that may get worse with movement
How is a Baker cyst diagnosed?
- Transillumination is a test that can show if the cyst is filled with fluid. Your healthcare provider will shine a light through your cyst.
- X-ray, MRI, or ultrasound pictures may be taken of the bones and tissues in your knee joint. The pictures will show any problems, such as arthritis, a knee injury, or fluid buildup. You may be given contrast liquid to help problems show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
How is a Baker cyst treated?
A Baker cyst will usually go away on its own. If it is large and painful, you may need any of the following:
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Steroid medicine may be injected into the cyst to decrease fluid, redness, pain, and swelling.
- Aspiration is a procedure used to drain fluid from the cyst through a needle.
- Arthroscopic surgery is done to remove the cyst completely or repair any torn or damaged cartilage. A scope and small surgical instruments are inserted through a small incision in your knee. A scope is a flexible tube with a light, camera, and magnifying glass on the end.
How can I care for my knee?
- Rest as needed. Limit movement as your knee heals. This will help decrease the risk of more damage to your knee. You may need crutches to take weight off your injured knee. Use crutches as directed.
- Ice your knee. Ice helps decrease swelling and pain. Use an ice pack, or put ice in a plastic bag. Cover it with a towel before you place it on your skin. Ice your knee for 15 to 20 minutes, 3 to 4 times each day. Do this for 2 to 3 days.
- Support your knee. Wrap your knee with an elastic bandage. Ask your healthcare provider if you need a brace for more support. This will help decrease swelling and movement so your knee can heal.
- Elevate your knee. Use pillows to raise your knee above the level of your heart as often as you can. This will help decrease swelling. Do not put the pillow directly under your knee. Put it under your calf instead.

- Go to physical therapy as directed. A physical therapist teaches you exercises to help improve movement and strength, and to decrease pain.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have severe pain.
- You have bruising on the ankle below the cyst.
- Your calf turns blue below the cyst.
- Your calf or knee is swollen or bleeding.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have a fever.
- Your pain does not improve with medicine.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
