Atherectomy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What do I need to know about atherectomy?
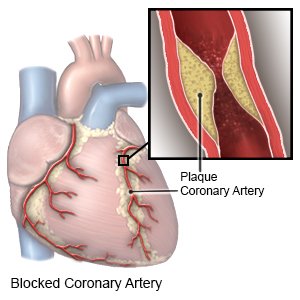
Atherectomy is a procedure used to remove plaque that narrows or blocks your arteries. Plaque is fat, cholesterol, or tissues that build up on the inner artery wall. Blood flow is decreased when plaque builds up and narrows the arteries. Decreased blood flow can cause chest pain or a heart attack.
 |
How do I prepare for the procedure?
- Your healthcare provider will talk to you about how to prepare. He or she may tell you not to eat or drink anything after midnight on the day of your procedure.
- Arrange to have someone drive you home after the procedure.
- Tell your healthcare provider about any allergies you have. Tell him or her if you have ever had an allergic reaction to local anesthesia.
- Tell your provider about all the medicines you currently take. Include prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and supplements. Your provider will tell you if you need to stop taking any of these before the procedure, and when to stop. He or she will tell you which medicines to take or not take on the day of your procedure.
- You may need blood tests, an EKG, or a chest x-ray before your procedure.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Crestor
Crestor (rosuvastatin) is used to treat high cholesterol and high triglycerides in the blood ...
Nitroglycerin
Nitroglycerin systemic is used for anal fissure and fistula, angina, angina pectoris prophylaxis ...
Ozempic
Learn about Ozempic (semaglutide) for type 2 diabetes treatment, weight management, cardiovascular ...
Tramadol
Tramadol is an opioid medication that may be used to treat moderate to moderately severe chronic ...
Aspirin
Aspirin is used to treat mild to moderate pain and to reduce fever or inflammation. Learn about ...
Clopidogrel
Clopidogrel systemic is used for acute coronary syndrome, acute coronary syndrome, prophylaxis ...
Gabapentin
Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types ...
Ranexa
Ranexa (ranolazine) is used to chronic treat angina (chest pain). Learn about side effects ...
Plavix
Plavix (clopidogrel) is used to prevent blood clots after a recent heart attack or stroke. Includes ...
What will happen during the procedure?
A small incision will be made in your groin, arm, or wrist. A catheter will be inserted into your artery and moved to the blockage. Contrast liquid may be used to help your surgeon see the blockage clearly. He or she will use a cutting device to remove the plaque from your artery. Your incision will be closed with stitches.
What should I expect after the procedure?
- You will need to lie flat and still for a few hours. Healthcare providers will get you up to walk as soon as possible to help prevent blood clots.
- A bandage or pressure device may be put on your incision area to prevent bleeding.
- Medicines may be given to manage pain or nausea. Antiplatelets, such as aspirin, may be given to help prevent blood clots.
What are the risks of the procedure?
You may bleed more than expected or get an infection. Your artery may be damaged or tear. Your arteries may become completely blocked during the procedure. This stops blood flow and may lead to a heart attack. You may need coronary artery bypass graft surgery. You may get a blood clot in your limb. This may become life-threatening.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Atherectomy
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
