Arteriogram of Carotid Arteries
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 7, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
What you need to know about an arteriogram of my carotid arteries:
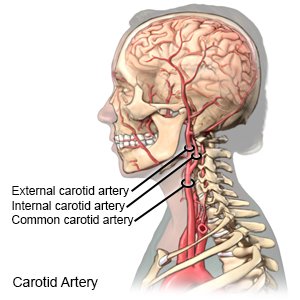
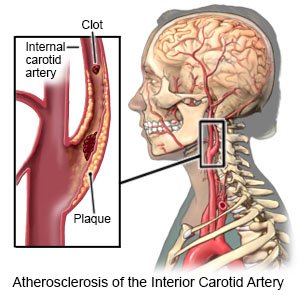
An arteriogram, or angiogram, is a test that finds narrow or blocked arteries in your neck. X-rays and contrast liquid help your healthcare provider see the arteries better. Procedures called angioplasty or stent placement may also be done during an arteriogram. Angioplasty uses a balloon to open blocked or narrow arteries. Stent placement means placing a small wire tube in the blocked artery to keep it open.
 |
 |
How to prepare for an arteriogram:
Your healthcare provider may tell you to not eat or drink 4 to 8 hours before your procedure. You may be asked to remove jewelry, dentures and dental bridges, and metal objects. These items may cause problems with the x-ray pictures. Arrange to have someone drive you home. If you get medicine to help you relax, you should not drive for 24 hours after your procedure.
What will happen during an arteriogram:
A sedative will be given to decrease your anxiety and help you relax. A local anesthetic is given in your groin where a puncture will be made. Your healthcare provider will make a puncture and place a small catheter (long, thin tube) into an artery. The catheter is slowly moved up into your neck. Contrast liquid is injected into the catheter to reach the area. You may feel burning or warmth as the contrast liquid is put into the catheter. Several x-rays are taken to help healthcare providers see your carotid arteries clearly.
What will happen after an arteriogram:
You will go to a recovery room with the catheter in place. A nurse or other healthcare professional will remove the catheter. Strong pressure will be applied at your puncture site to manage bleeding. You will need to lay flat on your back and not raise your head for a period of time.
Risks of an arteriogram:
You may have a stroke or heart attack that could lead to death. You may have an allergic reaction to the contrast liquid used. Rarely, the catheter damages the artery.
Call 911 if:
- The puncture site in your groin suddenly swells.
- You have bleeding at the puncture site.
- Your leg or foot turns blue and you cannot move it.
Contact your healthcare provider if:
- The area around the puncture site looks more bruised.
- Your leg or foot on the procedure side is numb or tingles.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Drink plenty of fluids:
The fluids will help flush the contrast liquid from your body. Ask your healthcare provider how much fluid to drink and which fluids are best for you.
Prevent problems with your arteries:
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can damage your blood vessels. If you smoke, it is never too late to quit. Ask for information if you need help quitting. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Limit alcohol. Your healthcare provider will tell you if alcohol is safe for you to drink. Alcohol can make your blood vessel problems worse and interact with your medicine. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1½ ounces of liquor.
- Eat heart healthy foods. You may need to eat foods that are low in salt, fat, or cholesterol. Heart healthy foods will decrease your risk for blockage in your blood vessels. Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, beans, lean meats, and fish. Ask your healthcare provider for more information about a heart healthy diet.
- Manage other health conditions. Follow your healthcare provider's advice on how to manage other conditions that can affect your blood vessels. These include diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. You may need to take medicines for these conditions and make other lifestyle changes.
- Exercise regularly. Exercise at least 30 minutes each day, on most days of the week. Exercise helps to lower high cholesterol and high blood pressure. It can also help you maintain a healthy weight. Ask your healthcare provider about the kind of exercise you should do and how to get started.
Follow up with your healthcare provider as directed:
Your healthcare provider will want to go over the results of your arteriogram. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
