Anterior Posterior Spinal Fusion
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
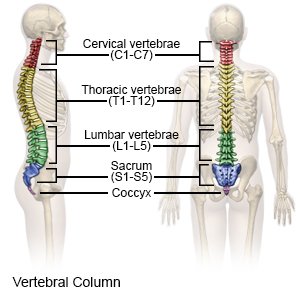
Spinal fusion is surgery to repair vertebrae in your spine. Cervical spine fusion is usually done from the front. Thoracic and lumbar fusion surgeries are usually done from the back. During surgery, 2 or more vertebrae are joined together using bone grafts or implants, screws, and rods.
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
An IV
is a small tube placed in your vein that is used to give you medicine or liquids.
Before surgery:
- Blood tests may be needed to give healthcare providers information about how your body is working.
- A blood transfusion may be needed if you lose a large amount of blood during surgery. You may be able to store blood to be used during surgery. Your healthcare provider will give you more information.
- A heart monitor may be used during surgery. This is also called an ECG or EKG. Sticky pads placed on your skin record your heart's electrical activity.
- An arterial line may be used for measuring your blood pressure or for taking blood.
- A pulmonary artery catheter is used to measure pressure in your heart and lungs. The catheter is put into a vein and guided to your pulmonary artery. The catheter is attached to a monitor that shows the pressure measurements.
- You may be given medicine to help you relax or make you drowsy.
- General anesthesia will keep you asleep and free from pain during surgery. Anesthesia may be given through your IV. You may instead breathe it in through a mask or a tube placed down your throat. The tube may cause you to have a sore throat when you wake up.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Dextroamphetamine
Dextroamphetamine systemic is used for ADHD, drowsiness, fatigue, narcolepsy, sexual dysfunction ...
Amantadine
Easy-to-read patient leaflet for amantadine. Includes indications, proper use, special ...
Omvoh
Omvoh is used to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease in adults. This ...
Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate is used to treat attention deficit disorder (ADD) and attention deficit ...
Amphetamine/dextroamphetamine
Amphetamine/dextroamphetamine systemic is used for ADHD, fatigue, narcolepsy
During surgery:
- Incisions will be made in the front, back, or both sides of your body. One or more pieces of bone may be taken from another area of your body to use as grafts. Bone grafts or artificial bone will be placed between the vertebrae. Metal plates, screws, and cages may be placed to hold the vertebrae together while the bone grafts heal or to help straighten the spine.
- The incisions will be closed with sutures. Drains may be used to remove fluid from around your incision. Bandages will be put over the incisions.
After surgery:
You may need to stay in the hospital for several days. A brace may give you support and help you feel more comfortable. It will limit your neck movement while you heal. You may need to wear the brace for up to 3 months.
- Medicines may be given to relieve pain, prevent a bacterial infection, or calm your stomach and help prevent vomiting.
- Physical therapy may start soon after surgery and continue after you go home. A physical therapist teaches you exercises to help improve movement and strength, and to decrease pain. You will also be show how to move safely after surgery. Healthcare providers will teach you how to log roll in bed. This means that you must move your entire body as a unit and not twist your spine.
- Blood clot prevention starts with healthcare providers helping you walk soon after surgery. You may also need to wear pressure stockings or pneumatic boots in bed to improve blood flow. The stockings are tight and put pressure on your legs. The boots have an air pump that tightens and loosens different areas of the boots.
- Intake and output may be measured. Healthcare providers will keep track of the amount of liquid you are getting. They also may need to know how much you are urinating. Ask healthcare providers if they need to measure or collect your urine. A Foley catheter may be put into your bladder to drain urine into a bag.
- You will be able to drink liquids and eat certain foods when your stomach function returns after surgery. You may be given ice chips at first. Then you will get liquids such as water, broth, juice, and clear soft drinks. If your stomach does not become upset, you may then be given soft foods, such as ice cream and applesauce. When you can eat soft foods easily, you may slowly begin to eat solid foods. A nasogastric (NG) tube may be guided into your stomach. Food and medicine may be given through an NG tube if you cannot swallow.
- Ice may be used to decrease swelling, pain, and redness. Healthcare providers will place an ice pack on your incisions for 15 to 20 minutes every hour as long as you need it.
- Take deep breaths and cough 10 times each hour. This will decrease your risk for a lung infection. Take a deep breath and hold it for as long as you can. Let the air out and then cough strongly. Deep breaths help open your airway. You may be given an incentive spirometer to help you take deep breaths. Put the plastic piece in your mouth and take a slow, deep breath, then let the air out and cough. Repeat these steps 10 times every hour.
- A chest tube may be used to remove air, blood, or fluid from around your lungs or heart. The chest tube is attached to a container to collect the blood or fluid. You may need more than one chest tube.
- A pulse oximeter is a device that measures the amount of oxygen in your blood. A cord with a clip or sticky strip is placed on your finger, ear, or toe. The other end of the cord is hooked to a machine. You may be given extra oxygen if your level is too low.
RISKS:
Nerves in the area where the disc is removed could be injured. You may need to have more surgery to fix this problem. You may have temporary or permanent numbness or pain that limits movement. You may have problems controlling your bowel or bladder. If you are a man, you may have trouble getting or keeping an erection. A life-threatening blood clot may develop in your leg or arm. Tissue covering the spinal cord could be torn. This may cause fluid to leak out of the spinal cord. You may have to lie flat for a few days or may need surgery to fix this.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
