Ankle Arthrotomy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
What you need to know about ankle arthrotomy:
Ankle arthrotomy is surgery to make an opening into the ankle joint. This allows your surgeon to see into the ankle joint directly. He or she may use this surgery to examine, drain, clean, or repair your ankle joint.
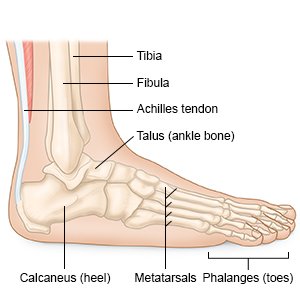 |
How to prepare for surgery:
- Your surgeon will tell you how to prepare. He or she may tell you not to eat or drink anything after midnight before surgery. Arrange to have someone drive you home when you are discharged from the hospital.
- Tell your surgeon about all medicines you currently take. He or she will tell you if you need to stop any medicine for surgery, and when to stop. He or she will tell you which medicines to take or not take on the day of surgery.
- Antibiotics may be given to help prevent a bacterial infection. Anesthesia will be used to numb the surgery area to prevent pain during surgery. Tell your surgeon if you have had an allergic reaction to antibiotics or anesthesia.
What will happen during surgery:
- General anesthesia may be given to keep you asleep and free from pain during surgery. Regional or local anesthesia may instead be given to numb the surgery area. Your surgeon will make one or more incisions.
- Your surgeon may take tissue samples to be tested for diseases. The joint may need to be drained. A tumor or pieces of bone or cartilage may be removed. An ankle fracture or other injury may be repaired.
- The incision or incisions will be closed with stitches. A splint, cast, or walking boot may be applied. The device will depend on the reason you had an ankle arthrotomy.
What to expect after surgery:
- You may need to use crutches to keep some weight off your foot. You may instead wear a splint, cast, or walking boot for a few weeks. These protect your ankle by keeping it stable and preventing movement while it heals.
- You will be given instructions for activities to avoid for 6 to 8 weeks after surgery. The instructions will include when it is okay to put weight on your foot or play sports again.
- Physical therapy may be started after the splint, cast, or boot is removed. A physical therapist can help you strengthen your ankle and improve mobility and flexibility.
Risks of ankle arthrotomy:
You may develop a serious joint infection called septic arthritis. You may develop a life-threatening blood clot. Nerves in your ankle may be damaged. You may have chronic joint stiffness or pain. Scar tissue may form, or you may develop a contracture (shortening) of your ankle ligaments. You may not be able to move your ankle as well as you could before surgery.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have chest pain or sudden trouble breathing.
- You cough up blood.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Penicillin VK
Penicillin VK is used for bacterial infection, clostridioides difficile infection, cutaneous ...
Bicillin L-A
Bicillin L-A is used for bacterial infection, congenital syphilis, glomerulonephritis ...
Omvoh
Omvoh is used to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease in adults. This ...
Bicillin C-R
Bicillin C-R is used for middle ear infections, pneumonia, skin or soft tissue infection ...
Pfizerpen
Pfizerpen is used for actinomycosis, anthrax, aspiration pneumonia, bacteremia, bacterial ...
Bicillin C-R 900/300
Bicillin C-R 900/300 is used for middle ear infections, pneumonia, skin or soft tissue infection ...
Penicillin g benzathine/procaine penicillin
Penicillin g benzathine/procaine penicillin systemic is used for middle ear infections, pneumonia ...
Penicillin g sodium
Penicillin g sodium systemic is used for actinomycosis, anthrax, aspiration pneumonia, bacteremia ...
Penicillin g potassium
Penicillin g potassium systemic is used for actinomycosis, anthrax, aspiration pneumonia ...
Penicillin g benzathine
Penicillin g benzathine systemic is used for bacterial infection, bejel, congenital syphilis ...
Seek care immediately if:
- You have a splint or cast and it gets damaged, starts to feel tighter, or your skin turns blue or pale.
- You have severe pain that does not go away after you take pain medicine.
- Your leg feels warm, tender, and painful. It may look swollen and red.
- Blood soaks through your bandage.
- Your stitches come apart.
Call your doctor or surgeon if:
- You have a fever or chills.
- Your wound is red, swollen, or draining pus.
- Your skin is itchy, swollen, or you have a rash.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Antibiotics help prevent or treat a bacterial infection.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Care for the surgery area:
- Do not swim, soak in a hot tub, or take a bath until your healthcare provider says it is okay. Your healthcare provider will tell you when it is okay to shower after surgery. You may need to cover the area with plastic bags to keep it dry.
- Care for your splint or cast as directed. Do not put pressure on it until your healthcare provider says it is okay. Do not put objects under your splint or cast to scratch your skin. This may cause an infection. Check your skin around the splint or cast for redness, swelling, or open areas. Ask your healthcare provider for more information on how to care for your splint or cast.
- Wear a walking boot as directed if it was applied instead of a cast. A walking boot helps keep your foot stable and keeps your weight off your ankle as it heals. You may need to wear the boot for several weeks after surgery. Your healthcare provider will give you instructions for how long to wear it each day.
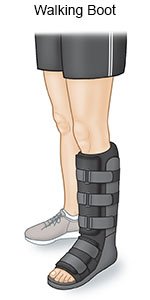
- Keep pressure off your leg as directed. Use crutches or a cane as directed. Do not stand on your leg. This could cause your stitches to come apart. Ask your healthcare provider when you can put weight on your leg.
Self-care:
- Keep weight off of your leg as directed. Your healthcare provider will tell you when you can drive and return to your normal activities. He or she will tell you when it is okay to play sports again.
- Apply ice on your leg for 15 to 20 minutes every hour or as directed. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover it with a towel. Ice helps prevent tissue damage and decreases swelling and pain.
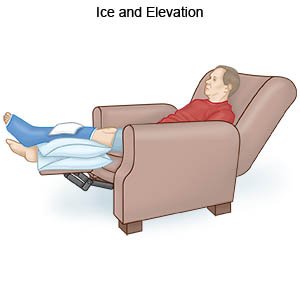
- Elevate your leg above the level of your heart as often as you can. This will help decrease swelling and pain. Prop your leg on pillows or blankets to keep it elevated comfortably.
- Go to physical therapy as directed. A physical therapist teaches you exercises to help improve range of motion (ROM) and strength, and to decrease pain. He or she will teach you ROM exercises. ROM exercises are gentle movements of your joint. ROM exercises will prevent stiffness and help build strength. Do not do ROM exercises unless your healthcare provider says it is okay.
Follow up with your doctor or surgeon as directed:
You may need to have the stitches removed or the ankle joint checked. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
