Anal Cancer
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
What do I need to know about anal cancer?
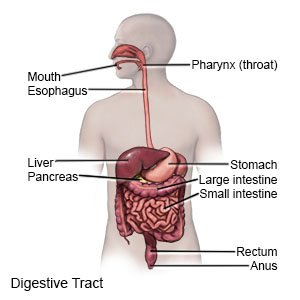
Anal cancer is a type of cancer that begins inside the anus. The anus is the opening where bowel movements leave the body. The most common type of anal cancer is squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). SCC cells are found in the skin, organs, respiratory tract, and digestive tract.
 |
What increases my risk for anal cancer?
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
- A weakened immune system
- A history of anal warts, HIV infection, or certain cancers
- Tobacco or alcohol use
- Receptive anal sex, or unprotected sex
What are the signs and symptoms of anal cancer?
- Bleeding from your anus
- Blood or mucus in your bowel movements
- Small lumps around your anus
- Pain and itching around your anus
- Not being able to control your bowel movements
How is anal cancer diagnosed?
Anal cancer may be found during an exam for another reason, such as hemorrhoids. Any of the following may be used if you have symptoms of anal cancer or are at increased risk for it:
- A digital rectal exam (DRE) means your healthcare provider inserts gloved fingers into your anus to check for tumors. Other tests may also be needed if you are at high risk for anal cancer.
- Anoscopy is used to check your anus for tumors, bleeding, or other problems. Your provider will guide the anoscope (tube with a light and camera) into your anus. The camera will help your provider examine your anus. Your provider may take tissue samples to be tested for cancer.
- A bowel movement sample may be tested for blood.
- Ultrasound, MRI, CT, or PET scan pictures may be used to find tumors. You may be given contrast liquid to help tumors show up better. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. The MRI uses a powerful magnet. Metal can cause serious injury from the metal.
How is anal cancer treated?
Your healthcare provider can help you understand which treatment may be best for you:
- Chemotherapy (chemo) medicine is used to kill cancer cells. Chemo may be used to shrink the tumor or lymph nodes before surgery. Chemo may be combined with external beam radiation therapy (ERBT) for treatment called chemoradiation. This helps treat anal cancer without harming the sphincter (muscles that help hold the anus closed).
- Radiation may be used without chemo to shrink cancer cells.
- Surgery may be used to remove a small tumor or if other treatment does not work. Surgery may damage the sphincter, so other treatments may be tried first.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
What can I do to manage or prevent anal cancer?
Your healthcare provider may recommend screening every 1 to 3 years if you are at high risk for anal cancer. Your provider can give you more information about screening tests. The following are general ways to prevent or manage anal cancer:
- Prevent an HPV infection. Some types of HPV increase your risk for anal cancer. HPV may be spread through sexual activity. The HPV vaccine is usually given at 11 or 12 years of age. It can be given from 9 years through 45 years of age, if needed. Use a new condom, contraceptive barrier, or dental dam each time you have sex. This includes oral, vaginal, and anal sex.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars increase the risk for anal cancer. Ask your provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes and smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your provider before you use these products.
- Eat healthy foods. Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, beans, lean meats, and fish. You may need to change what you eat during treatment. Do not eat foods or drink liquids that cause gas, such as cabbage, beans, onions, or soda. A dietitian may help to plan the best meals and snacks for you.

- Be physically active as directed. Physical activity, such as exercise, may improve your energy levels and appetite. Ask about the best activity plan for you.

- Ask your provider about sex during treatment, if needed. Your provider will tell you if it is okay to have sex while the cancer is being treated. Ask about safe ways to have anal, vaginal, or oral sex during this time.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have new or worsening symptoms.
When should I call my doctor or oncologist?
- You have a fever.
- Your pain is worse or does not go away after you take your pain medicine.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Anal Cancer
Treatment options
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
