Adult CPR Steps
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
CPR can save a person's life. Do compressions even if you cannot give rescue breaths.- Check the person:
- Tap the person's shoulder. Ask loudly, "Are you okay?" Check to see if the person is breathing. You may check for a pulse, but do not spend more than 10 seconds doing this.
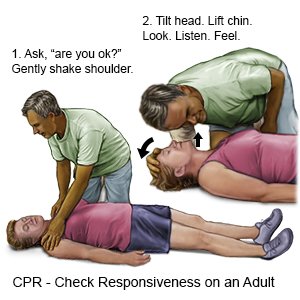
- Tap the person's shoulder. Ask loudly, "Are you okay?" Check to see if the person is breathing. You may check for a pulse, but do not spend more than 10 seconds doing this.
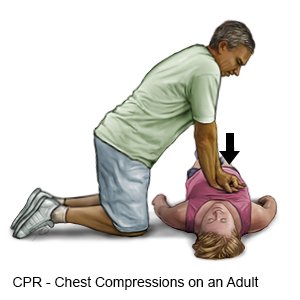
- Start compressions:
- Kneel beside the person's chest.
- Put one of your hands on top of the other.
- Put the heel of your bottom hand where the person's ribs meet in the middle of his or her chest, between the nipples.
- Press straight down on the sternum (breastbone) at least 2 inches (5 centimeters).
- Do 30 chest compressions at a rate of at least 100 to 120 every minute (2 per second).
- Count the compressions out loud to help you do them at a steady, even speed.
-
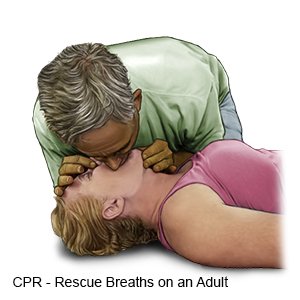
- Give 2 rescue breaths:
- Place one hand on the person's forehead and 2 fingers under the chin.
- Tilt the head back and open the mouth.
- Gently pinch the person's nose closed.
- Take a deep breath and put your lips around the person's mouth, making an airtight seal.
- Blow into the person's mouth. His or her chest will rise with each breath if air is going into the lungs.
- Let the persons's chest fall before giving another breath.
-
- Repeat the cycle of 30 compressions and 2 breaths for 5 cycles .
- CALL:
- Your local emergency number (911 in the US)
- Continue CPR until help arrives or the person begins to respond.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
