Adult Congenital Heart Disease
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
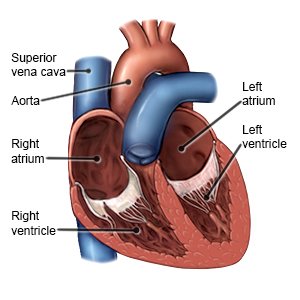
Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) is a term used to describe defects in the structure of the heart. It may also be called congenital heart defect. Congenital means you were born with the heart defect. The defect may include a hole in part of the heart or narrowing of arteries connected to the heart. Blood may not be able to flow to or flow through your heart correctly. The defect may be mild or severe. You might be having symptoms for the first time as an adult. You might be having symptoms even if you had a heart defect repaired as a child. A congenital heart defect should be monitored regularly, even if you do not have problems.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Have someone call your local emergency number (911 in the US) for any of the following:
- You have any of the following signs of a stroke:
- Numbness or drooping on one side of your face
- Weakness in an arm or leg
- Confusion or difficulty speaking
- Dizziness, a severe headache, or vision loss
- You have fainting spells or unexplained falls.
- You have sudden shortness of breath.
Call your cardiologist if:
- Your lips or nails turn blue.
- You have a fever.
- You have chills, a cough, or feel weak and achy.
- You gain 2 to 3 pounds in a day or have new swelling in your ankles or legs.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Medicines may be used to help your heart beat more regularly.
- Blood thinners help prevent blood clots. Clots can cause strokes, heart attacks, and death. Many types of blood thinners are available. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions for the type you are given. The following are general safety guidelines to follow while you are taking a blood thinner:
- Watch for bleeding and bruising. Watch for bleeding from your gums or nose. Watch for blood in your urine and bowel movements. Use a soft washcloth on your skin, and a soft toothbrush to brush your teeth. This can keep your skin and gums from bleeding. If you shave, use an electric shaver. Do not play contact sports.
- Tell your dentist and other healthcare providers that you take a blood thinner. Wear a bracelet or necklace that says you take this medicine.
- Do not start or stop any other medicines or supplements unless your healthcare provider tells you to. Many medicines and supplements cannot be used with blood thinners.
- Take your blood thinner exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not skip a dose or take less than prescribed. Tell your provider right away if you forget to take your blood thinner, or if you take too much.
- Diuretics help your body get rid of extra fluid. This can help you breathe easier. You may urinate more often with this medicine.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Go to cardiac rehabilitation (rehab) if directed:
Cardiac rehab is a program that will help you safely strengthen your heart. This plan includes exercise, relaxation, stress management, and heart-healthy nutrition instructions. Healthcare providers will make sure your medicines are helping to reduce your symptoms.
Manage ACHD:
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause heart and lung damage. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
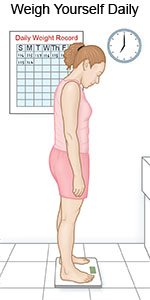
- Weigh yourself every morning. Use the same scale, in the same spot. Weigh yourself after you use the bathroom, but before you eat or drink anything. Wear the same type of clothing each day. Do not wear shoes. Keep a record of your daily weights so you will notice sudden weight gain. Bring the record to appointments with your healthcare providers. Swelling and weight gain are signs of fluid retention.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Extra weight can cause your heart to work harder. Ask your healthcare provider what a healthy weight is for you. He or she can help you create a weight loss plan, if needed.
- Be physically active, as directed. Physical activity, such as exercise, is important for heart health. Your healthcare provider can tell you how much exercise you need each day and which exercises are best for you. You may not be able to do some physical activities or sports. The decision may depend on the type of defect you have and if it was repaired.
- Limit or do not drink alcohol as directed. Alcohol can increase your blood pressure. Limit alcohol to 2 drinks a day if you are a man, or 1 drink a day if you are a woman. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1½ ounces of liquor.
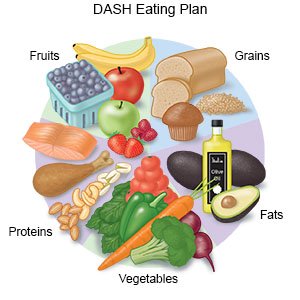
- Eat heart-healthy foods. Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, lean meats, and fish. Choose fish that are high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fresh tuna or salmon. Limit foods that are high in fat. Your healthcare provider may also recommend you limit the amount of sodium (salt) you have each day. Ask for more information on heart-healthy and low-sodium diets.
- Keep your teeth clean and healthy. Get regular dental checkups and brush your teeth as directed. Cavities increase your risk for endocarditis (infection in the lining around your heart). You may need an antibiotic before you have dental procedures. The antibiotic can help prevent an infection caused by bacteria.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about pregnancy. ACHD can cause certain problems during pregnancy. Women with ACHD should work with healthcare providers to plan and monitor pregnancy. Women may need a vaccine to prevent rubella during pregnancy. Both men and women can pass genes for certain congenital heart defects to their children. Talk to your healthcare provider about this risk.
Follow up with your healthcare provider or cardiologist as directed:
Regular follow-up is important, even if you had a defect corrected when you were a child. You may need tests to check for problems from your heart defect or to check for new problems that should be treated. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Adult Congenital Heart Disease
- Atorvastatin (Lipitor): Top 12 Drug Facts You Need to Know
- Do blood pressure drugs interact with alcohol?
- Side Effects of Weight Loss Drugs
Treatment options
Care guides
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
