Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 6, 2025.
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. The bone marrow makes white blood cells (WBC), red blood cells (RBC), and platelets. WBCs help fight infection. RBCs help carry oxygen throughout the body. Platelets help the blood clot. ALL causes your body to make too many immature (young) white blood cells (WBC). These cells are cancer (leukemia) cells, and cannot fight infection like healthy WBCs. Cancer cells crowd the bone marrow and prevent it from making healthy blood cells. Without enough healthy blood cells, you are at risk for infection, bleeding, and anemia. Anemia is a low level of red blood cells.
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
Rest:
You may need to rest in bed. You may be allowed to get out of bed once you are feeling better. Call a healthcare provider before you get up for the first time. If you feel weak or dizzy, sit or lie down right away. Then call a healthcare provider.
Diet:
It is important that you get good nutrition when you have cancer. Eat a variety of healthy foods. Eating healthy foods may help you feel better and have more energy. If you have trouble swallowing, you may be given foods that are soft or in liquid form. Ask your healthcare provider about any extra nutrition you may need, such as nutrition shakes or vitamins. Tell your provider if you have problems eating, or if you are getting sick to your stomach.
Reverse isolation
is a safety measure used to protect you from outside germs. You may have a weak immune system or trouble fighting infection. With reverse isolation, you are given a private room. Everyone should wash their hands when entering and leaving your room. Healthcare providers and visitors wear gloves, a mask, and a gown when they enter your room.
Long-term IV catheter:
You may get an IV catheter placed into a large vein in your body. It is usually placed in your arm or chest. You may have this IV catheter for several months. You and your healthcare provider will decide which catheter is right for you. Once you get your IV catheter, your healthcare provider will begin your chemotherapy medicine.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Jakafi
Jakafi (ruxolitinib) is used to treat myelofibrosis, polycythemia vera, and graft versus host ...
Gleevec
Gleevec is targeted cancer therapy for specific types of leukemia (blood cancer), bone marrow ...
Omvoh
Omvoh is used to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease in adults. This ...
Imkeldi
Imkeldi is used to treat specific types of leukemia (blood cancer), bone marrow disorders ...
Imatinib
Imatinib is used to treat certain types of leukemia, bone marrow disorders, and skin cancer ...
Ruxolitinib
Ruxolitinib systemic is used for graft versus host disease, myelofibrosis, myeloproliferative ...
A blood transfusion
replaces blood in your body to help it work properly. A blood transfusion is given through an IV. Blood is tested for safety before it is used.
Medicines:
- Antibiotics help treat or prevent a bacterial infection .
- Antifungals help treat or prevent a fungal infection.
- Antinausea medicine may be given to calm your stomach and prevent vomiting.
- Pain medicine may be given. Do not wait until the pain is severe before you ask for more medicine.
Tests:
- Blood tests may be done to check your blood cell levels.
- X-rays check for swollen lymph nodes in your chest.
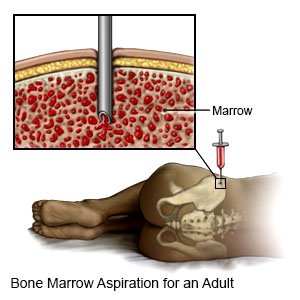
- A bone marrow biopsy is a procedure to take a sample of bone marrow from your hip bone. This test helps healthcare providers find out which type of leukemia you have.
- A lumbar puncture is a procedure to remove fluid from around your spinal cord. The fluid is tested for cancer cells.
- Other tests , such as an MRI or PET scan, may be done if ALL is diagnosed with any of the above tests. These tests will check if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body.
Treatment:
- Supportive care includes medicines and blood transfusions. Medicines may be given to prevent infections. Blood transfusions may be given to increase your level of red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets.
- Chemotherapy is used to kill cancer cells. Your healthcare provider may give you 2 or more kinds of chemotherapy.
- Targeted therapy is medicine that finds and kills cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy shrinks tumors and kills cancer cells with x-rays or gamma rays. It may be given alone or with chemotherapy to treat cancer.
- A stem cell transplant is a procedure to replace cancer cells with healthy blood cells. Stem cells are taken from a donor and injected into your blood. The stem cells go to your bone marrow and become new, healthy blood cells.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
RISKS:
You may have pain, discomfort, or fatigue from treatment. Even with treatment, ALL may not go away, or it may return.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
