What is a Boxed Warning?
What is a Boxed Warning?
An FDA Boxed Warning is the strictest prescription drug safety warning issued by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Previously called a Black Box Warning, this medication safety alert was first implemented in 1979.
Boxed warnings ensure prescription medications are used appropriately and safely. The pharmaceutical warning appears within a black border on drug labeling to alert healthcare providers and patients about serious or life-threatening adverse effects, drug risks, and potential side effects associated with their medication.
While these FDA safety warnings signal significant pharmaceutical risks, many prescription drugs with boxed warnings remain widely prescribed because their therapeutic benefits can outweigh the medication risks when used correctly under medical supervision.
Figure 1. An Example of a Boxed Warning
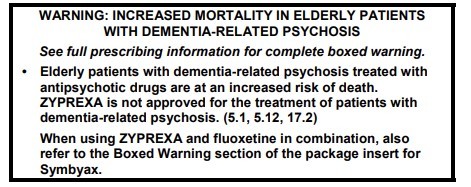
Why Do Medicines Receive a Boxed Warning?
A medicine is assigned a Boxed warning if it meets any of the following criteria:
- It has been associated with a serious side effect that could cause death or permanent disability
- The risk of severe side effects can be reduced if people and prescribers comply with specific administration or dosing guidelines, such as side effect monitoring, being alert for interacting medicines, and taking note of the recommended and maximum dosage.
- Mandatory prescribing restrictions apply, such as requiring special training for doctors or limiting the drug’s use to hospital settings.
Examples of Drugs with Boxed Warnings
Some commonly used medications that carry a Boxed Warning include:
- Accutane (isotretinoin): severe birth defects during pregnancy
- Methotrexate: liver toxicity and organ damage
- Ciprofloxacin: increased risk of tendon rupture
- Opioids (such as oxycodone, fentanyl): high risk of addiction and overdose
- Antidepressants (SSRIs, SNRIs): increased risk of suicidal thoughts in young adults
- Atypical antipsychotics (such as aripiprazole, olanzapine): increased risk of death and cerebrovascular events (such as a stroke) in dementia.
How to Check if a Drug Has a Boxed Warning
To find out if your medication has a Boxed warning, you can:
- Review the medication guide that comes with your prescription
- Visit the official FDA website for safety updates
- Search for the drug on Drugs.com and look under the “Warnings” section
- Consult your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
How Boxed Warnings Affect Drug Prescribing
Boxed warnings are primarily directed at healthcare professionals, who are responsible for:
- Informing patients about the risks before prescribing the medication
- Ensuring proper monitoring to minimize potential adverse effects
- Weighing the risks vs. benefits to decide if the drug is appropriate for a specific patient.
Some medications with boxed warnings also require an FDA Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS), which may include restrictions like special certification for prescribers or dispensing only in certified healthcare facilities.
Boxed Warning vs. Drug Recall: What’s the Difference?
A Boxed Warning means the drug remains available but must be used with extreme caution. A drug recall, however, occurs when a medication is removed from the market due to safety concerns.
FAQs About Boxed Warnings
✅ Are all drugs with Boxed warnings dangerous?
- No, many are safe when used properly. The warning ensures careful monitoring and proper patient selection.
✅ Can I still take a drug if it has a Boxed warning?
- Yes, but only under a doctor’s supervision who will weigh the benefits vs. risks.
✅ Are Boxed warnings permanent?
- Not always. Some warnings are updated or removed if new research shows improved safety.
Bottom Line
Boxed warnings help patients and doctors make informed decisions about medication safety.
If you are prescribed a drug with this warning, have a conversation with your doctor about possible alternative treatments (if any), risk management strategies, and possible side effects. Do not be afraid to ask questions and take some time to think it through.
Learn more
- Anticholinergic Drugs to Avoid in the Elderly
- The Meaning of Drug Toxicology Reports and Tests
- Tramadol - Top 8 Things You Need to Know
Treatment options
- Medications for Dementia
- Medications for Major Depressive Disorder
- Medications for Opioid Use Disorder
- Medications for Psychiatric Disorders
- Medications for Psychosis
Care guides
- Acute Delirium
- Altered Mental Status
- Alzheimer Disease
- Asperger Syndrome
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Bipolar Disorder
- Brief Psychotic Disorder
Symptoms and treatments
Sources
- O'Shea T. 10 Black Box Warnings Every Pharmacist Should Know 15 March 2016 pharmacytimes.com/contributor/timothy-o-shea/2016/03/10-black-box-warnings-every-pharmacist-should-know
- An FDA Guide to Drug Safety Terms
https://www.drugs.com/fda-consumer/an-fda-guide-to-drug-safety-terms-52.html - "Black box” 101: How the Food and Drug Administration evaluates, communicates, and manages drug benefit/risk Murphy, Shirley et al. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Volume 117, Issue 1, 34 - 39
- Delong C, Preuss CV. Box Warning. [Updated 2023 Jun 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538521/
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
