Veraflox (pradofloxacin) oral suspension (Canada)
This treatment applies to the following species: Company: Elanco
Company: Elanco
(pradofloxacin) oral suspension
25 mg/mL
VETERINARY USE ONLY
DIN 02436744
Description
Veraflox (pradofloxacin) oral suspension 25 mg/mL is a yellowish-to-beige, flavoured suspension.
THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION:
Fluoroquinolone antimicrobial
Veraflox (pradofloxacin) oral suspension Indications:
Veraflox (pradofloxacin) oral suspension is indicated in cats 12 weeks of age and older for the treatment of:
● Skin infections (wounds and abscesses) caused by susceptible strains of Pasteurella multocida, Streptococcus canis, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus felis, and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius.
Dosage and Administration
Shake well before use. To ensure a correct dosage, bodyweight should be determined as accurately as possible. The dose of Veraflox oral suspension is 7.5 mg/kg bodyweight, orally, once a day.
Use the syringe provided to ensure accuracy of dosing to the nearest 0.1 mL. Rinse syringe between doses.
|
Indication |
Dose (mg/kg/day) |
Duration of Treatment (Days) |
|
Wound infections and abscesses |
7.5 |
7 |
The choice of Veraflox as the most appropriate treatment should be confirmed by clinical experience and where possible by pathogen culture and drug susceptibility testing. Treatment should be reconsidered if no improvement of the clinical condition is observed within 3 days of starting the treatment with Veraflox.
Contraindications
Do not use in cats with known hypersensitivity to fluoroquinolones.
Do not use in cats with pre-existing articular cartilage lesions, as these lesions may worsen during treatment with fluoroquinolones.
CAUTIONS:
The safety of pradofloxacin in cats younger than 12 weeks of age has not been established.
The use of pradofloxacin for longer than 7 days induced reversible leukocyte, neutrophil and lymphocyte decreases in healthy 12 week old kittens (See Animal Safety Section). If an unexplained drop in leukocyte, neutrophil and/or lymphocyte counts is noted during pradofloxacin therapy, discontinuation of treatment is recommended.
Pradofloxacin may increase sensitivity of the skin to sunlight. During treatment cats should not be exposed to excessive sunlight.
The safety of pradofloxacin has not been established in cats that are used for breeding or that are pregnant and/or lactating.
Excretion via kidneys is an important elimination route for pradofloxacin in cats. As for other fluoroquinolones, the renal excretion rate of pradofloxacin may be decreased in cats with impaired kidney function and therefore, Veraflox oral suspension should be used with caution in such animals.
Quinolones have been shown to produce erosions of cartilage of weight-bearing joints and other signs of arthropathy in immature animals of various species.
Quinolones should be used with caution in animals with known or suspected central nervous system (CNS) disorders. In such animals, quinolones have, in rare instances, been associated with CNS stimulation and may lead to convulsive seizures.
The safety of pradofloxacin in immune-compromised cats (i.e. cats infected with feline leukemia virus and/or feline immune-deficiency virus) has not been evaluated.
Warnings
To limit the development of antimicrobial resistance:
● Fluoroquinolone drugs such as Veraflox should not be used indiscriminately.
● Veraflox oral suspension is for use in cats only.
Keep out of reach of children. Individuals with a history of quinolone hypersensitivity should avoid this product. Avoid contact with eyes and skin. In case of ocular contact, immediately flush eyes with copious amounts of water. In case of dermal contact, wash skin with soap and water immediately for at least 20 seconds. Consult a physician if irritation persists following ocular or dermal exposure, or in case of accidental ingestion. In humans, there is a risk of photosensitization within a few hours after exposure to quinolones. If excessive accidental exposure occurs, avoid direct sunlight. Do not eat, drink or smoke while handling this product. It is recommended that used syringes be kept out of reach of children and disposed of properly. Dispose the unused drug in accordance with the Provincial/Municipal guidelines.
Adverse Reactions
Slight and transient digestive tract disorders may occur in very rare cases. This is thought to occur as a result of the action of an oral anti-infective.
Field Studies:
In a multi-site field study, 282 cats (ages 0.3 to 19 years) were evaluated for safety when given either Veraflox oral suspension at a dose of 7.5 mg/kg or placebo (vehicle without active ingredient) at a dose of 0.3 mL/kg. Each group was treated once daily for 7 consecutive days. Adverse reactions are summarized in Table 1.
|
Table 1: Number of Adverse Reactions among Cats Treated with Pradofloxacin (N = 190) or Vehicle (N = 92)* |
||
|
Adverse Reactions |
Pradofloxacin |
Vehicle |
|
Diarrhea / loose stools |
7 |
2 |
|
Leukocytosis with neutrophilia |
4 |
6 |
|
Elevated CPK levels |
4 |
4 |
|
Sneezing |
4 |
1 |
|
Hematuria |
2 |
2 |
|
Hypersalivation |
2 |
1 |
|
Pruritus |
2 |
0 |
|
Inappetence |
1 |
3 |
|
Lethargy |
1 |
2 |
|
Cardiac murmur |
1 |
1 |
|
Reclusive behavior |
1 |
1 |
|
Vomiting |
1 |
1 |
|
Bacteriuria |
1 |
0 |
|
Lymphadenopathy |
1 |
0 |
|
Polydipsia |
1 |
0 |
|
Upper respiratory infection |
1 |
0 |
* Some cats may have experienced more than one adverse reaction or more than one occurrence of the same adverse reaction during the study.
Post-Market Experience:
Although all adverse reactions are not reported, the following adverse reaction information is based on voluntary post-approval drug experience reporting. It is generally recognized that this method of reporting results in significant under-reporting of adverse drug reactions. It should be noted that suspected adverse drug reactions listed reflect reporting and not causality. The following adverse reactions have been reported very rarely and are listed in decreasing order of frequency by body system:
Digestive tract disorders: vomiting, hypersalivation, diarrhea
To report suspected adverse drug events or for technical assistance, contact Elanco Canada Limited at 1-800-265-5475.
Clinical Pharmacology
Mode of Action:
The primary mode of action of the fluoroquinolones involves interaction with enzymes essential for major DNA functions such as replication, transcription and recombination. The primary targets for pradofloxacin are the bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV enzymes. Reversible association between pradofloxacin and DNA gyrase or DNA topoisomerase IV in the target bacteria results in inhibition of these enzymes and rapid death of the bacterial cell. The rapidity and extent of bacterial killing are directly proportional to the drug concentration.
Pharmacokinetics:
Pradofloxacin is rapidly absorbed following oral administration of Veraflox oral suspension to fasted cats, with peak serum concentrations occurring in less than 1 hour. However, food markedly diminishes the serum bioavailability of pradofloxacin; mean peak serum concentrations (Cmax) are reduced 53% and mean exposures (AUC) are decreased by 26%. The relative bioavailability of pradofloxacin, when administered as the 2.5% oral suspension to fed and fasted cats, is provided in Table 2 and Figure 1.
|
Table 2: Mean (1 SD) serum pradofloxacin derived pharmacokinetics parameters in cats (N = 12) following a 5 mg/kg oral dose of Veraflox oral suspension under fasted and fed conditions |
||
|
|
Veraflox oral suspension 5 mg/kg Dose |
|
|
Parameter |
Fasted |
Fed |
|
Cmax (ng/mL) |
2116 (549) |
999 (400) |
|
Tmax (hr) |
0.8 |
1.4 |
|
AUC0-24 |
9111 (1939) |
6745 (1524) |
|
Half-life (hr) |
7.3 (1.7) |
6.4 (1.2) |
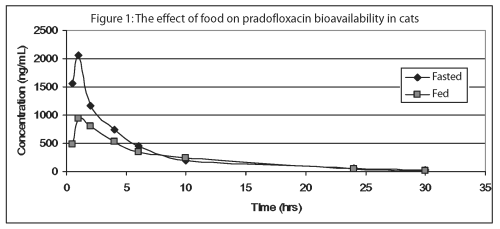
Approximately 30% of the total drug concentrations are bound to plasma proteins in drug concentrations ranging from 150 to 1500 ng/mL. Dose proportional increases in drug concentrations are observed when the oral suspension is administered to fasted cats in doses ranging from 2.5 mg/kg to 10 mg/kg bodyweight. Due to its short elimination half-life, there is minimal pradofloxacin accumulation following multiple daily administrations.
Pharmacodynamics:
Pharmacodynamics was determined using in vitro susceptibility that showed the pathogens Pasteurella multocida, Staphylococcus pseudintermedius, and Streptococcus spp. had a pradofloxacin MIC90 of ≤0.015 to 0.12 µg/mL. The pharmacodynamics metrics (Cmax/MIC90 and AUC/MIC90) were estimated using linear regression analysis of free drug steady-state pradofloxacin pharmacokinetics parameters from fasted cats and a pradofloxacin MIC90 value of 0.12 µg/mL. The 95% Confidence Intervals about predicted mean Cmax/MIC90 and AUC/MIC90 values were 15 to 17 and 70 to 81, respectively. It was concluded that the magnitude of the Cmax/MIC90 and AUC/MIC90 values is predictive of product effectiveness when an oral dose of 7.5 mg/kg body weight of the pradofloxacin liquid formulation is administered to fasted cats. In addition, effectiveness was shown for cats dosed at 7.5 mg/kg body weight and fed free choice, or within two hours of dosing, in a field study.
MICROBIOLOGY:
Veraflox is bactericidal, with activity against Gram-negative, Gram-positive, and anaerobic bacteria. The mechanism of action is dual targeting through inhibition of DNA gyrase and topoisomeriase IV.
The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) for pradofloxacin against Pasteurella multocida, Streptococcus canis, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus felis, and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolated from skin infections (wounds and abscesses) in cats in a U.S. field study from 2008 to 2009 are listed in Table 3. Only two isolates from two pradofloxacin Treatment Failure cases had elevated pradofloxacin MICs (non-hemolytic Staph. aureus - MIC = 2 µg/mL, E. coli - MIC = 4 µg/mL).
|
Table 3: Activity of Veraflox oral suspension against pathogens isolated from cats treated with Veraflox oral suspension in a clinical trial in the US in 2008. |
|||||||
|
Disease |
Pathogen |
Clinical Treatment Outcome |
Number of Isolates |
Sample Collection (Time Relative to Treatment) |
MIC50 µg/mL |
MIC90 µg/mL |
MIC Range µg/mL |
|
Skin Infections |
Pasteurella multocida |
Success |
40 |
Pre-Treatment |
0.008 |
0.015 |
≤0.004 - 0.03 |
|
Failure |
11 |
Pre-Treatment |
0.008 |
0.008 |
≤0.004 - 0.015 |
||
|
Streptococcus canis |
Success |
13 |
Pre-Treatment |
0.12 |
0.12 |
0.03 - 0.25 |
|
|
Failure |
2 |
Pre-Treatment |
|
|
0.06 - 0.12 |
||
|
Staphylococcus aureus |
Success |
10 |
Pre-Treatment |
0.12 |
0.12 |
0.015 - 0.12 |
|
|
Failure |
0 |
n/a |
|
|
|
||
|
Staphylococcus felis |
Success |
13 |
Pre-Treatment |
0.03 |
0.06 |
0.03 - 0.12 |
|
|
Failure |
1 |
Pre-Treatment |
|
|
0.06 |
||
|
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius |
Success |
10 |
Pre-Treatment |
0.06 |
0.06 |
0.03 - 0.06 |
|
|
Failure |
1 |
Pre-Treatment |
|
|
0.03 |
||
Effectiveness
The clinical effectiveness of Veraflox oral suspension for the treatment of skin infections (wounds and abscesses) was demonstrated in a multi-site (16 sites) field study. In this masked and randomized study, the effectiveness of Veraflox oral suspension was compared to a placebo control (vehicle without active ingredient). Of the 282 cats enrolled in this study, 190 were treated with Veraflox oral suspension once daily at 7.5 mg/kg bodyweight for 7 consecutive days and 92 were treated with placebo once daily at 0.3 mL/kg bodyweight for 7 consecutive days. The effectiveness database included 182 cats: 66 placebo (vehicle)-treated cats and 116 Veraflox oral suspension-treated cats. The analysis of this effectiveness database showed that the cure rate was greater in the Veraflox oral suspension group on Day 15, as summarized in Table 4. Study cure rates were determined approximately 15 days after initiation of therapy. The statistical evaluation of the primary effectiveness endpoint (Study Cures) showed that Veraflox oral suspension was different from placebo with 73.4% Veraflox oral suspension study cures versus 38.9% placebo study cures.
|
Table 4: Day 15 Case Classification |
|
|
Treatment Group |
Percent Cures |
|
Veraflox oral suspension (N = 116) |
73.4% |
|
Placebo (N = 66) |
38.9% |
|
P-value |
0.0053 |
SAFETY:
Target Animal Safety Study:
Safety was evaluated in 32 healthy, 12-week-old kittens administered Veraflox oral suspension once daily at doses of 0, 7.9, 23.7, or 39.5 mg/kg bodyweight (0, 1, 3, and 5 times the recommended dose) for 21 consecutive days. Additional control (0X) and high-dose (5X) animals were maintained for 45 days after treatment cessation. There were statistically significant decreases in neutrophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes in the 3X and 5X groups compared to the controls. During the treatment period, one 3X and three 5X cats had absolute neutrophil counts below the reference range. Bone marrow cytology results consistent with bone marrow suppression (myeloid hypoplasia) were seen in the 3X neutropenic cat and two of the three 5X cats. The 3X cat was neutropenic on the last day of the study prior to the scheduled euthanasia, while the absolute neutrophil values for the three 5X cats returned to normal either during treatment or after the cessation of treatment. The most frequent abnormal clinical finding was soft feces. While this was seen in both treated and control groups, it was observed more frequently in the 3X and 5X kittens.
Ocular Safety Study:
Ocular safety was evaluated in 20 healthy adult cats using pradofloxacin in capsules administered orally, once daily at doses of 30 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg bodyweight for 23 days. No effects were seen in the following investigated ocular parameters: ophthalmic examinations, ERGs, and optical coherence tomography. Cats receiving 50 mg/kg bodyweight/day of pradofloxacin showed mild weight loss. Cats receiving 30 and 50 mg/kg bodyweight/day of pradofloxacin exhibited hypersalivation and vomiting throughout the study. Dose-dependent reductions in white blood cell counts were noted in the pradofloxacin-treated cats. One cat receiving 30 mg/kg bodyweight/day of pradofloxacin exhibited minimal photoceptor degeneration on light and electron microscopy of a type that differed from enrofloxacin-treated cats (comparator used in this study); the effects of pradofloxacin on these retinal changes is unknown.
Chondrotoxicity:
In studies using pradofloxacin up to 30 mg/kg bodyweight, pradofloxacin had no effects on the developing cartilage of kittens 6 weeks of age and older.
Pilot Toxicity Study:
In an oral toxicity study, 4 cats received pradofloxacin at 50 mg/kg/day for 25 days. All cats exhibited fluoroquinolone-induced neurologic signs (decreased mobility, staggering and vocalization) on day 5 of the study.
STORAGE INFORMATION:
Once opened, use within 3 months. Store in the original container. Do not store above 30°C. Keep the bottle tightly closed.
How Supplied
Package
Carton containing 15 mL bottle
Carton containing 30 mL bottle
Elanco Canada Limited, 1919 Minnesota Court, Suite 401, Mississauga, Ontario L5N 0C9
Veraflox, Elanco and the diagonal bar logo are trademarks of Elanco or its affiliates.
© 2022 Elanco or its affiliates.
13Jun2022
CPN: 1231223.1
1919 MINNESOTA COURT, SUITE 401, MISSISSAUGA, ON, L5N 0C9
| Customer Service: | 800-265-5475 | |
| Fax: | 519-821-7831 | |
| Website: | www.elanco.ca | |
| Email: | elancocanadacustomerservice@elancoah.com |
 |
THIS SERVICE AND DATA ARE PROVIDED "AS IS". Animalytix assumes no liability, and each user assumes full risk, responsibility, and liability, related to its use of the Animalytix service and data. See the Terms of Use for further details. |

Copyright © 2024 Animalytix LLC. Updated: 2024-02-27
