Embolectomy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
What do I need to know about an embolectomy?
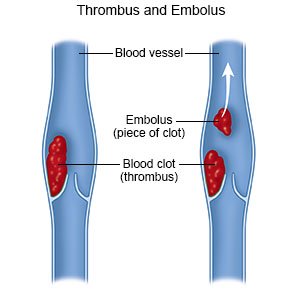
An embolectomy is surgery to remove an embolus from an artery or vein. An embolus is part of a blood clot that broke free. It can travel through your bloodstream and become stuck in another area. This is called an embolism. An embolism can block blood flow to the area. An embolus in your vein can reach your lungs. This is called a pulmonary embolism, or PE. An embolus in your artery can reach your brain. This can cause a stroke. An embolus in a femoral artery in your leg can cause tissue death in the leg. An embolus in an artery in your abdomen can cause pain and vomiting. An embolectomy is used when medicines or procedures cannot be used, or are not successful.
 |
How do I prepare for an embolectomy?
An embolectomy may need to be done as immediate emergency surgery. The following is general information if you are able to plan for surgery.
- Your surgeon will tell you how to prepare. He or she may tell you not to eat or drink anything after midnight on the day of surgery. Arrange to have someone drive you home after you are discharged.
- Tell your surgeon about any allergies you have, including to anesthesia, contrast liquid, or medicines. Contrast liquid may be used during surgery to help your surgeon see the blood vessel and embolus better.
- Tell your surgeon about all medicines you currently take. He or she will tell you if you need to stop any medicine for surgery, and when to stop. He or she will tell you which medicines to take or not to take on the day of surgery.
What will happen during an embolectomy?
- You may be given local anesthesia to numb the area so you do not feel pain. You may instead be given general anesthesia to keep you asleep and free from pain.
- The following are ways the embolus may be removed:
- A catheter embolectomy is a minimally invasive surgery. A catheter (thin tube) is guided into the vein or artery that has the embolus. Suction is used to remove the embolus through the catheter.
- A balloon embolectomy is also minimally invasive. A catheter with a balloon on the end is guided into the vein, past the clot. The balloon is inflated (filled) and pulled back out of the vein. The embolus comes back through the vein with the catheter. The balloon helps move the embolus and keep it from continuing into the vein.
- An open embolectomy is usually only done for a large embolus, most often to treat a PE. Your surgeon will make an incision in the skin over the embolus. He or she will open the vein or artery and remove the embolus.
- A filter may be placed to prevent another embolus from being able to travel through your body. Your surgeon will check that all of the embolus was removed. He or she may place a filter in the blood vessel. The filter helps prevent pieces of the embolus from continuing to travel. When blood flows freely, your surgeon will close the vein or artery. The incision area will be covered with a pressure bandage.
What should I expect after an embolectomy?
- You may have swelling or pain in the surgery area. You may be given medicines to reduce pain or swelling. You may need to stay in the hospital for up to 1 week, depending on where you had the embolectomy. You may need to lie still for several hours right after your surgery.
- Healthcare providers will help you walk around the same day of your surgery, or the day after. Movement will help prevent blood clots. You may also be given exercises to do in bed. Do not get out of bed on your own until your healthcare provider says you can. Ask before you get up the first time. You may need help to stand up safely.
- Healthcare providers will change the bandage over the embolectomy site as needed.
What are the risks of an embolectomy?
You may bleed more than expected or develop an infection. The blood vessel or tissues near the area may be damaged. Your surgeon may not be able to remove the embolus. Pieces of the embolus may break free and continue through the blood vessel.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
