Mesalamine Rectal Suspension: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Dosage form: rectal suspension
Drug class: 5-aminosalicylates
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Oct 21, 2024.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Overdosage
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
MESALAMINE rectal suspension enema
Initial U.S. Approval: 1987
Indications and Usage for Mesalamine Rectal Suspension
Mesalamine rectal suspension enema is an aminosalicylate indicated for treatment of active mild to moderate distal ulcerative colitis, proctosigmoiditis or proctitis in adults. (1)
Mesalamine Rectal Suspension Dosage and Administration
• Evaluate renal function prior to initiation of mesalamine rectal suspension enema and periodically while on therapy. (2, 5.1)
• The recommended dosage is one rectal instillation (4 grams) once a day, preferably at bedtime, and retained for approximately eight hours for 3 to 6 weeks depending on symptoms and sigmoidoscopic findings. (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Rectal Suspension: 4 g/60 mL enema bottle (3)
Contraindications
Warnings and Precautions
• Hypersensitivity Reactions: Sulfite-related reactions (mesalamine rectal suspension enema contains potassium metabisulfite) and sulfasalazine-associated reactions (myocarditis and pericarditis) can occur; evaluate patients immediately and discontinue mesalamine rectal suspension enema if a hypersensitivity reaction is suspected. (5.3)
• Renal Impairment: Assess renal function at the beginning of treatment and periodically during treatment. Evaluate the risks and benefits of mesalamine rectal suspension enema in patients with known renal impairment or taking nephrotoxic drug. Discontinue mesalamine rectal suspension enema if renal function deteriorates while on therapy. (5.1, 7.1)
• Mesalamine-Induced Acute Intolerance Syndrome: Discontinue treatment if acute intolerance syndrome (cramping, acute abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, sometimes fever, headache and rash) is suspected. (5.2)
• Hepatic Failure: Evaluate the risks and benefits of using mesalamine rectal suspension enema in patients with known liver impairment. (5.4)
• Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions: Discontinue at the first signs or symptoms of severe cutaneous adverse reactions or other signs of hypersensitivity and consider further evaluation. (5.5)
• Photosensitivity: Avoid sun exposure if pre-existing skin conditions. (5.6)
• Nephrolithiasis: Cases of nephrolithiasis have been reported with the use of mesalamine. Mesalamine-containing stones
are undetectable by standard radiography or computed tomography (CT). Ensure adequate hydration during treatment.
(5.7)
• Interference with Laboratory Tests: Mesalamine may lead to elevated urinary normetanephrine test results. (5.8)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥1%) are: gas/flatulence, flu, fever, leg/joint pain, hemorrhoids, rectal pain and hair loss. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Padagis® at 1-866-634-9120 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
• Nephrotoxic Agents including Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs
(NSAIDs): Increased risk of nephrotoxicity; monitor for changes in renal function and mesalamine-related adverse reactions. (7.1)
• Azathioprine or 6-Mercaptopurine: Increased risk of blood dyscrasias; monitor complete blood cell counts and platelet counts. (7.2)
Use In Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients: Increased risk of blood dyscrasias; monitor complete blood cell counts and platelet counts. (8.5)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 8/2024
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Mesalamine Rectal Suspension
Mesalamine rectal suspension enema is indicated for the treatment of active mild to moderate distal ulcerative colitis, proctosigmoiditis or proctitis in adults.
2. Mesalamine Rectal Suspension Dosage and Administration
Evaluate renal function before initiating therapy with mesalamine rectal suspension enema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage is one rectal instillation (4 grams) once a day, preferably at bedtime, and retained for approximately eight hours for 3 to 6 weeks depending on symptoms and sigmoidoscopic findings.
Administration Instructions
- • Shake the bottle to ensure the suspension is homogeneous.
- • Remove the protective sheath from the applicator tip.
- • Assume the correct body position:
- ° Lie on the left side with the lower leg extended and the upper right leg flexed forward for balance.
- ° Alternatively, sit in the knee to chest position.
- • Gently insert the applicator tip in the rectum pointing toward the umbilicus.
- • Steadily squeeze the bottle to discharge the medication.
- • Remain in the position for at least 30 minutes. Administer at bedtime with the objective of retaining it all night.
- • Drink an adequate amount of fluids during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Rectal Suspension: 4 g/60 mL enema bottle; off-white to tan colored suspension
4. Contraindications
Mesalamine rectal suspension enema is contraindicated in patients with known or suspected hypersensitivity to salicylates, aminosalicylates, sulfites or any other component of this medication [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Sulfite-Related Reactions
Mesalamine rectal suspension enema contains potassium metabisulfite, a sulfite that may cause allergic-type reactions including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in certain susceptible people. The overall prevalence of sulfite sensitivity in the general population is unknown but probably low. Sulfite sensitivity is seen more frequently in asthmatic or in atopic nonasthmatic persons.
Epinephrine is the preferred treatment for serious allergic or emergency situations even though epinephrine injection contains sodium or potassium metabisulfite with the above-mentioned potential liabilities. The alternatives to using epinephrine in a life-threatening situation may not be satisfactory. The presence of a sulfite(s) in epinephrine injection should not deter the administration of the drug for treatment of serious allergic or other emergency situations.
Sulfasalazine-Associated Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported in patients taking sulfasalazine. Some patients may have a similar reaction to mesalamine rectal suspension enema or to other compounds that contain or are converted to mesalamine.
As with sulfasalazine, mesalamine-induced hypersensitivity reactions may present as internal organ involvement, including myocarditis, pericarditis, nephritis, hepatitis, pneumonitis and hematologic abnormalities. Evaluate patients immediately if signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction are present. Discontinue mesalamine rectal suspension enema if an alternative etiology for the signs and symptoms cannot be established.
5.2 Renal Impairment
Renal impairment, including minimal change disease, acute and chronic interstitial nephritis, and renal failure have been reported in patients given mesalamine rectal suspension enema or other products that contain mesalamine or are converted to mesalamine. In animal studies, the kidney was the principal organ of mesalamine toxicity [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)].
Evaluate the risks and benefits of using mesalamine rectal suspension enema in patients with known renal impairment or a history of renal disease or taking concomitant nephrotoxic drugs. Evaluate renal function in all patients prior to initiation and periodically while on mesalamine rectal suspension enema therapy. Discontinue mesalamine rectal suspension enema if renal function deteriorates while on therapy [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
5.3 Mesalamine-Induced Acute Intolerance Syndrome
Mesalamine has been associated with an acute intolerance syndrome that may be difficult to distinguish from a flare of inflammatory bowel disease. Although the exact frequency of occurrence cannot be ascertained, it has occurred in 3% of patients in controlled clinical trials of mesalamine or sulfasalazine. Symptoms include cramping, acute abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea, sometimes fever, headache, and rash. Monitor patients for worsening of these symptoms while on treatment. If acute intolerance syndrome is suspected, promptly discontinue treatment with mesalamine rectal suspension enema.
5.4 Hepatic Failure
There have been reports of hepatic failure in patients with pre-existing liver disease who have been administered other products containing mesalamine. Evaluate the risks and benefits of using mesalamine rectal suspension enema in patients with known liver impairment.
5.5 Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) have been reported with the use of mesalamine [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Discontinue mesalamine rectal suspension enema at the first signs or symptoms of severe cutaneous adverse reactions or other signs of hypersensitivity and consider further evaluation.
5.6 Photosensitivity
Patients with pre-existing skin conditions such as atopic dermatitis and atopic eczema have reported more severe photosensitivity reactions. Advise patients to avoid sun exposure, wear protective clothing, and use a broad-spectrum sunscreen when outdoors.
5.7 Nephrolithiasis
Cases of nephrolithiasis have been reported with the use of mesalamine, including stones with 100% mesalamine content. Mesalamine-containing stones are radiotransparent and undetectable by standard radiography or computed tomography (CT). Ensure adequate fluid intake during treatment.
5.8 Interference with Laboratory Tests
Use of mesalamine may lead to spuriously elevated test results when measuring urinary normetanephrine by liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection because of the similarity in the chromatograms of normetanephrine and the main metabolite of mesalamine, N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid (N-Ac-5-ASA). Consider an alternative, selective
assay for normetanephrine.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- • Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- • Renal impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- • Mesalamine-induced acute intolerance syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- • Hepatic failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- • Severe cutaneous adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- • Photosensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- • Nephrolithiasis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions* in Clinical Trials of Mesalamine Rectal Suspension Enema in Adult Patients with Ulcerative Colitis, Proctosigmoiditis or Proctitis
|
Adverse Reaction |
Mesalamine Rectal Suspension Enema (N=815) % |
Placebo (N=128) % |
|
Gas/Flatulence |
6 |
4 |
|
Flu |
5 |
1 |
|
Fever |
3 |
0 |
|
Leg/Joint pain |
2 |
1 |
|
Hemorrhoids |
1 |
1 |
|
Rectal pain |
1 |
0 |
|
Hair loss |
1 |
0 |
*reported in 1% or more of mesalamine rectal suspension enema-treated patients and greater than placebo
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of mesalamine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiac Disorders: myocarditis, pericarditis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Gastrointestinal Disorders: pancreatitis
Hematologic Disorders: agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, eosinophilia, leukopenia, neutropenia, pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia
Hepatic Disorders: elevated liver enzymes, hepatic failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Nervous System: intracranial hypertension
Renal and Urinary Disorders: acute renal failure, chronic renal failure, interstitial nephritis, nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, nephrolithiasis, nephrotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), (5.7)]
- • Urine discoloration occurring ex-vivo caused by contact of mesalamine including inactive metabolite, with surfaces or water treated with hypochlorite-containing bleach
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders: reversible oligospermia
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders: fibrosing alveolitis,
pleurisy/pleuritis
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: AGEP, DRESS, SJS/TEN [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Nephrotoxic Agents, Including Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
The concurrent use of mesalamine with known nephrotoxic agents, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may increase the risk of nephrotoxicity. Monitor patients taking nephrotoxic drugs for changes in renal function and mesalamine-related adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
7.2 Azathioprine or 6-Mercaptopurine
The concurrent use of mesalamine with azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine and/or any other drugs known to cause myelotoxicity may increase the risk for blood disorders, bone marrow failure, and associated complications. If concomitant use of mesalamine rectal suspension enema and azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine cannot be avoided, monitor blood tests, including complete blood cell counts and platelet counts.
7.3 Interference with Urinary Normetanephrine Measurements
Use of mesalamine rectal suspension enema may lead to spuriously elevated test results when measuring urinary normetanephrine by liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. Consider an alternative, selective assay for normetanephrine.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Published data from meta-analyses, cohort studies and case series on the use of mesalamine during pregnancy have not reliably informed an association with mesalamine and major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes (see Data). There are adverse effects on maternal and fetal outcomes associated with ulcerative colitis in
pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations). In animal reproduction studies, rats and rabbits administered mesalamine during organogenesis at oral doses up to 5 and 8 times the maximum recommended human dose, respectively, did not reveal any evidence of harm to the embryo or the fetus (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and embryo/fetal risk
Published data suggest that increased disease activity is associated with the risk of developing adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with ulcerative colitis. Adverse pregnancy outcomes include preterm delivery (before 37 weeks of gestation), low birth weight (less than 2500 g) infants, and small for gestational age at birth.
Data
Human Data
Published data from meta-analyses, cohort studies and case series on the use of mesalamine, the active moiety of mesalamine rectal suspension enema, during early pregnancy (first trimester) and throughout pregnancy have not reliably informed an association of mesalamine and major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. There is no clear evidence that mesalamine exposure in early pregnancy is associated with an increase risk in major congenital malformations, including cardiac malformations. Published epidemiologic studies have important methodological limitations which hinder interpretation of the data, including inability to control for confounders, such as underlying maternal disease, and maternal use of concomitant medications, and missing information on the dose and duration of use for mesalamine products.
Animal Data
Reproduction studies have been performed with mesalamine in rats and rabbits during organogenesis at oral doses up to 5 and 8 times respectively, the maximum recommended human dose, and have revealed no evidence of harm to the embryo or the fetus.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Data from published literature report the presence of mesalamine and its metabolite, N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid in human milk in small amounts with relative infant doses (RID) of 0.1% or less for mesalamine (see Data). There are case reports of diarrhea observed in breastfed infants exposed to mesalamine (see Clinical Considerations). There is no information on the effects of mesalamine on milk production. The lack of clinical data during lactation precludes a clear determination of the risk of mesalamine rectal suspension enema to an infant during lactation; therefore, the developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for mesalamine rectal suspension enema and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from mesalamine rectal
suspension enema or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
Advise the caregiver to monitor the breastfed infant for diarrhea.
Data
In published lactation studies, maternal mesalamine doses from various oral and rectal formulations and products ranged from 500 mg to 4.8 g daily. The average concentration of mesalamine in milk ranged from non-detectable to 0.5 mg/L. The average concentration of N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid in milk ranged from 0.2 to 9.3 mg/L. Based on these
concentrations, estimated infant daily dosages for an exclusively breastfed infant are 0 to 0.075 mg/kg/day of mesalamine (RID 0% to 0.1%) and 0.03 to 1.4 mg/kg/day of N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical trials of mesalamine rectal suspension enema did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Reports from uncontrolled clinical studies and postmarketing reporting systems suggested a higher incidence of blood dyscrasias (i.e., agranulocytosis, neutropenia and pancytopenia) in patients receiving mesalamine-containing products such as mesalamine rectal suspension enema who were 65 years or older compared to younger adult patients, which may also be associated with ulcerative colitis, use of interacting drugs, or reduced renal function.
Consider monitoring complete blood cell counts and platelet counts in patients 65 years and over during treatment with mesalamine rectal suspension enema. In general, consider the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concurrent disease or other drug therapy in patients 65 years and over when prescribing mesalamine rectal suspension enema.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Mesalamine is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Evaluate renal function in all patients prior to initiation and periodically while on mesalamine rectal suspension enema therapy. Monitor patients with known renal impairment or history of renal disease
or taking nephrotoxic drugs for decreased renal function and mesalamine-related adverse reactions. Discontinue mesalamine rectal suspension enema if renal function deteriorates while on therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
10. Overdosage
Mesalamine rectal suspension enema is an aminosalicylate, and symptoms of salicylate toxicity include nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain, tachypnea, hyperpnea, tinnitus, and neurologic symptoms (headache, dizziness, confusion, seizures). Severe salicylate intoxication may lead to electrolyte and blood pH imbalance and potentially to other organ (e.g., renal and liver) involvement.
There is no specific antidote for mesalamine overdose; however, conventional therapy for salicylate toxicity may be beneficial in the event of acute overdosage and may include gastrointestinal tract decontamination to prevent further absorption. Correct fluid and electrolyte imbalance by the administration of appropriate intravenous therapy and maintain adequate renal function.
11. Mesalamine Rectal Suspension Description
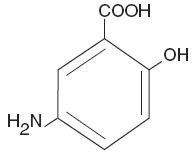
The active ingredient in Mesalamine Rectal Suspension, USP Enema, a disposable (60 mL) unit, is mesalamine, also known as 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA). Chemically, mesalamine is 5-amino-2-hydroxybenzoic acid.
The empirical formula is C7H7NO3, representing a molecular weight of 153.14. The structural formula is:
Mesalamine rectal suspension enema is supplied as a suspension for rectal administration. Each rectal suspension enema unit contains 4 grams of mesalamine. The inactive ingredients are carbomer 974P, edetate disodium, potassium acetate, potassium metabisulfite, purified water and xanthan gum. Sodium benzoate is added as a preservative.
The disposable unit consists of an applicator tip protected by a polyethylene cover and lubricated with USP white petrolatum. The unit has a one-way valve to prevent back flow of the dispensed product.
12. Mesalamine Rectal Suspension - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of 5-ASA (mesalamine) is not fully understood, but appears to be a topical anti-inflammatory effect on colonic epithelial cells. Mucosal production of arachidonic acid metabolites, both through the cyclooxygenase pathways (i.e., prostanoids), and through the lipoxygenase pathways (i.e., leukotrienes and hydroxyeicosatetraenoic
acids) is increased in patients with ulcerative colitis, and it is possible that mesalamine diminishes inflammation by blocking cyclooxygenase and inhibiting prostaglandin production in the colon.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The exposure-response relationship and time course of pharmacodynamic response for the safety and effectiveness of mesalamine have not been fully characterized.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Mesalamine administered rectally as mesalamine rectal suspension enema is poorly absorbed from the colon and is excreted principally in the feces during subsequent bowel movements. The extent of absorption is dependent upon the retention time of the drug product, and there is considerable individual variation. Under clinical conditions patients demonstrated plasma levels 10 to 12 hours post mesalamine administration of 2 mcg/mL, about two-thirds of which was the N-acetyl metabolite. In addition, steady state plasma levels demonstrated a lack of accumulation of either parent drug or N-acetyl metabolite during repeated daily rectal administrations.
Distribution
Other than the kidney, the organ distribution and other bioavailability characteristics of absorbed mesalamine in man are not known. The poor colonic absorption of rectally administered mesalamine is substantiated by the low serum concentration of 5-ASA and N-acetyl-5-ASA seen in ulcerative colitis patients after dosage with mesalamine.
Elimination
- Metabolism
It is known that the compound undergoes acetylation but whether this
process takes place at colonic or systemic sites has not been elucidated.
- Excretion
Whatever the metabolic site, most of the absorbed mesalamine is excreted in the urine as the N-acetyl-5-ASA metabolite. At steady state, approximately 10 to 30% of the daily 4-gram dose can be recovered in cumulative 24-hour urine collections. While the elimination half-life of mesalamine is short (0.5 to 1.5 hours), the acetylated metabolite exhibits a half-life of 5 to 10 hours.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
In a 2-year carcinogenicity study in Wistar rats fed up to 320 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.78 times the maximum recommended human dose, based on a body surface area comparison) of mesalamine admixed with diet, mesalamine did not cause an increase in the incidence of neoplastic lesions over controls.
Mutagenesis
Mesalamine is not mutagenic to Salmonella typhimurium tester strains TA98, TA100, TA1535, TA1537, TA1538. There were no reverse mutations in an assay using E. coli strain WP2UVRA. There were no evidence of genotoxicity in an in vivo mouse micronucleus assay at 600 mg/kg and in an in vivo sister chromatid exchange assay at doses up to 610 mg/kg.
Impairment of Fertility
Mesalamine had no effects on fertility in rats at doses up to 320 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.78 times the maximum recommended human dose, based on a body surface area comparison).
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Preclinical studies have shown the kidney to be the major target organ for mesalamine toxicity. Adverse renal function changes were observed in rats after a single 600 mg/kg oral dose, but not after a 200 mg/kg dose. Gross kidney lesions, including papillary necrosis, were observed after a single oral >900 mg/kg dose, and after I.V. doses of >214 mg/kg.
Mice responded similarly. In a 13-week oral (gavage) dose study in rats, the high dose of 640 mg/kg/day mesalamine caused deaths, probably due to renal failure, and dose-related renal lesions (papillary necrosis and/or multifocal tubular injury) were seen in most rats given the high dose (males and females) as well as in males receiving lower doses 160
mg/kg/day. Renal lesions were not observed in the 160 mg/kg/day female rats. Minimal tubular epithelial damage was seen in the 40 mg/kg/day males and was reversible. In a six-month oral study in dogs, the no-observable dose level of mesalamine was 40 mg/kg/day and doses of 80 mg/kg/day and higher caused renal pathology similar to that described for the rat. In a combined 52-week toxicity and 127-week carcinogenicity study in rats, degeneration in kidneys was observed at doses of 100 mg/kg/day and above admixed with diet for 52 weeks, and at 127 weeks increased incidence of kidney degeneration and hyalinization of basement membranes and Bowman's capsule were seen at 100 mg/kg/day and above. In the 12-month eye toxicity study in dogs, Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca (KCS) occurred at oral doses of 40 mg/kg/day
and above. The oral preclinical studies were done with a highly bioavailable suspension where absorption throughout the gastrointestinal tract occurred.
14. Clinical Studies
In a 6-week placebo-controlled trial, international, multicenter trial of 153 patients with active distal ulcerative colitis, proctosigmoiditis or proctitis, mesalamine rectal suspension enema reduced the overall disease activity
index (DAI) and individual components as follows:
EFFECT OF TREATMENT ON SEVERITY OF DISEASE DATA FROM U.S.-CANADA TRIAL COMBINED RESULTS OF EIGHT CENTERS
Activity Indices, mean
|
N |
Baseline |
Day 22 |
End Point |
Change Baseline to End Point* |
||
|
Overall DAI |
Mesalamine Rectal Suspension Enema |
76 |
7.42 |
4.05† |
3.37‡ |
-55.07%‡ |
|
Placebo |
77 |
7.40 |
6.03 |
5.83 |
-21.58% |
|
|
Stool Frequency |
Mesalamine Rectal Suspension Enema |
1.58 |
1.11§ |
1.01† |
-0.57§ |
|
|
Placebo |
1.92 |
1.47 |
1.50 |
-0.41 |
||
|
Rectal Bleeding |
Mesalamine Rectal Suspension Enema |
1.82 |
0.59‡ |
0.51‡ |
-1.30‡ |
|
|
Placebo |
1.73 |
1.21 |
1.11 |
-0.61 |
||
|
Mucosal Inflammation |
Mesalamine Rectal Suspension Enema |
2.17 |
1.22† |
0.96‡ |
-1.21† |
|
|
Placebo |
2.18 |
1.74 |
1.61 |
-0.56 |
||
|
Physician’s Assessment of Disease Severity |
Mesalamine Rectal Suspension Enema |
1.86 |
1.13‡ |
0.88‡ |
-0.97‡ |
|
|
Placebo |
1.87 |
1.62 |
1.55 |
-0.30 |
Each parameter has a 4-point scale with a numerical rating:
0 = normal, 1 = mild, 2 = moderate, 3 = severe. The four parameters are added together to produce a maximum overall DAI of 12.
* Percent change for overall DAI only (calculated by taking the average of the change for each individual patient).
† Significant mesalamine rectal suspension enema /placebo difference. p < 0.01
‡ Significant mesalamine rectal suspension enema /placebo difference. p < 0.001
§ Significant mesalamine rectal suspension enema /placebo difference. p < 0.05
Differences between mesalamine rectal suspension enema and placebo were also statistically different in subgroups of patients on concurrent sulfasalazine and in those having an upper disease boundary between 5 and 20 or 20 and 40 cm. Significant differences between mesalamine rectal suspension enema and placebo were not achieved in those subgroups of patients on concurrent prednisone or with an upper disease boundary between 40 and 50 cm.
16. How is Mesalamine Rectal Suspension supplied
Mesalamine Rectal Suspension, USP Enema is an off-white to tan colored suspension. Each disposable enema bottle contains 4 grams of mesalamine in 60 mL aqueous suspension. Enema bottles are supplied in boxed, foil-wrapped trays as follows:
- NDC 45802-098-51Carton of 7 Bottles
- NDC 45802-098-28Carton of 28 Bottles
- NDC 45802-923-41Combo Kit with 7 Bottles and Wipes
- NDC 45802-929-49Combo Kit with 28 Bottles and Wipes
Mesalamine rectal suspension enema is for rectal use only.
Storage
Store at controlled room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); Excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Once the foil wrapped unit of seven bottles is opened, all enemas should be used promptly as directed by your physician. Contents of enemas removed from the foil pouch may darken with time. Slight darkening will not affect potency, however, enemas with dark brown contents should be discarded.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Instructions for Use).
Renal Impairment
Inform patients that mesalamine rectal suspension enema may decrease their renal function, especially if they have known renal impairment or are taking nephrotoxic drugs, and periodic monitoring of renal function will be performed while they are on therapy. Advise patients to complete all blood tests ordered by their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Mesalamine-Induced Acute Intolerance Syndrome and Other Hypersensitivity Reactions
Instruct patients to stop taking mesalamine rectal suspension enema and report to their healthcare provider if they experience new or worsening symptoms of acute intolerance syndrome (cramping, abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, fever, headache, and rash) or other symptoms suggestive of mesalamine-induced hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)].
Hepatic Failure
Advise patients with known liver disease to contact their healthcare provider if they experience signs or symptoms of worsening liver function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions
Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of severe cutaneous adverse reactions. Instruct patients to stop taking mesalamine rectal suspension enema and report to their healthcare provider at first appearance of a severe cutaneous adverse reaction or other sign of hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Photosensitivity
Advise patients with pre-existing skin conditions to avoid sun exposure, wear protective clothing, and use a broad-spectrum sunscreen when outdoors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Nephrolithiasis
Instruct patients to drink an adequate amount of fluids during treatment in order to minimize the risk of kidney stone formation and to contact their healthcare provider if they experience signs or symptoms of a kidney stone (e.g., severe side or back pain, blood in the urine) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Blood Disorders
Inform elderly patients and those taking azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine of the risk for blood disorders and the need for periodic monitoring of complete blood cell counts and platelet counts while on therapy. Advise patients to complete all blood tests ordered by their healthcare provider [see Drug Interactions (7.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Administration
Advise patients that mesalamine rectal suspension enema will cause staining of direct contact surfaces, including but not limited to fabrics, flooring, painted surfaces, marble, granite, vinyl, and enamel. Administer the product in a suitable location.
Instruct patients:
- • Shake the bottle to ensure the suspension is homogeneous.
- • Remove the protective sheath from the applicator tip.
- • Lie on the left side with the lower leg extended and the upper right leg flexed forward for balance. Alternatively, get in the knee-chest position.
- • Gently insert the applicator tip in the rectum pointing toward the umbilicus.
- • Steadily squeeze the bottle to discharge the medication.
- • Administer at bedtime with the objective of retaining it all night.
- • Drink an adequate amount of fluids during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
- • Advise patients that urine may become discolored reddish-brown while taking mesalamine rectal suspension enema when it comes in contact with surfaces or water treated with hypochlorite-containing bleach. If discolored urine is observed, advise patients to observe their urine flow. Report to the healthcare provider only if urine is discolored on leaving the body, before contact with any surface or water (e.g., in the toilet).
Manufactured by Padagis®, Yeruham, Israel
www.padagis.com
Rev 08-24
2N900 RC PH15
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Mesalamine [me-SAL-a-meen]
rectal suspension enema
This Instructions for Use contains information on how to use mesalamine rectal suspension enema. Read these Instructions for Use that come with your mesalamine rectal suspension enema before you start using it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
How should I store mesalamine rectal suspension enema?
• Store mesalamine rectal suspension enema at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
• Mesalamine rectal suspension enema is an off-white to tan colored suspension. The medicine removed from the foil
pouch may darken with time. Slight darkening will not affect how well mesalamine rectal suspension enema works.
• Throw away mesalamine rectal suspension enema with dark brown medicine.
• Keep mesalamine rectal suspension enema and all medicines out of the reach of children.
Important information you need to know before using mesalamine rectal suspension enema
• Mesalamine rectal suspension enema is for rectal use only.
• Do not share mesalamine rectal suspension enema with other people, it may harm them.
• If a caregiver is giving mesalamine rectal suspension enema make sure they read and understand these Instructions for
Use.
• Use mesalamine rectal suspension enema exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
• It is recommended to use 1 mesalamine rectal suspension enema bottle each day.
• After the foil wrapped unit of 7 bottles is opened, use each bottle of mesalamine rectal suspension enema right away.
• Empty bowels right before the medicine is given.
• Give at bedtime.
• Mesalamine rectal suspension enema will stain some surfaces including but not limited to fabrics, flooring, painted
surfaces, marble, granite, vinyl, and enamel. Take care in choosing the right place for giving the mesalamine rectal
suspension enema.
Preparing to use mesalamine rectal suspension enema
Step 1. Remove the bottles.
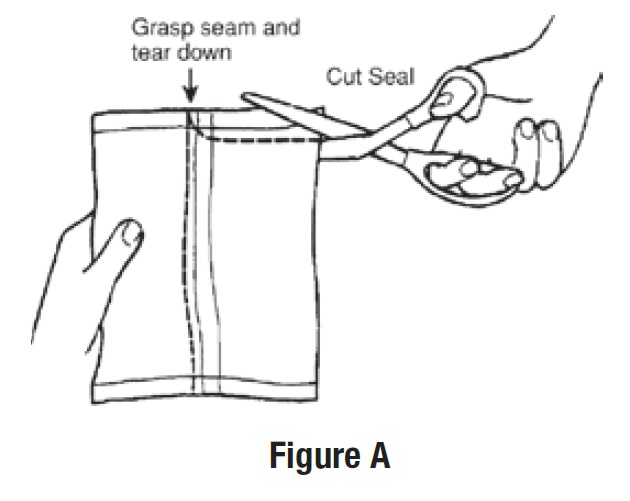
• Remove all the bottles from the protective foil pouch by grasping at the seam and tearing downward or by using scissors
at the top of the foil pouch (See Figure A).
• Be careful not to squeeze or puncture bottles.
Step 2. Prepare to give the medicine.
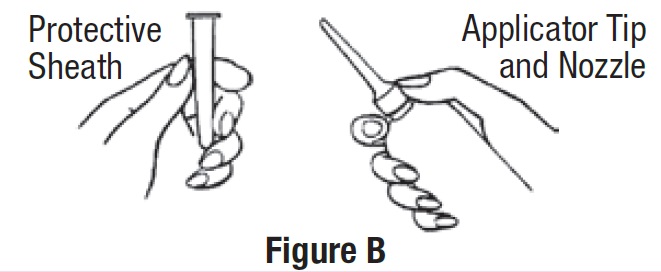
• Shake the first bottle well to make sure that the medicine is mixed well.
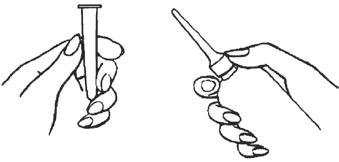
• Remove the protective sheath from the applicator tip. Hold the bottle at the neck so as not to cause any of the
medicine to be released (See Figure B).
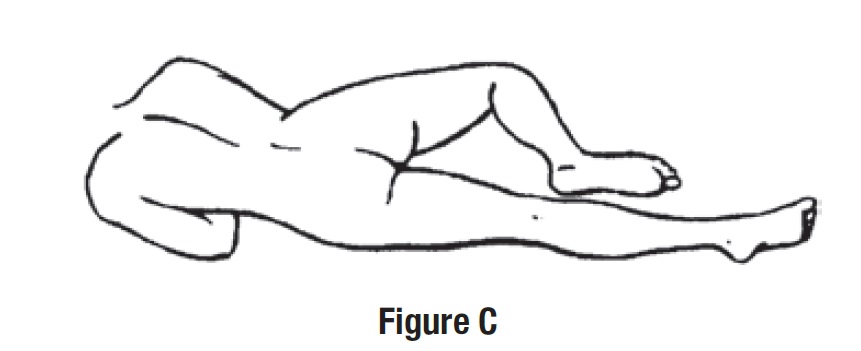
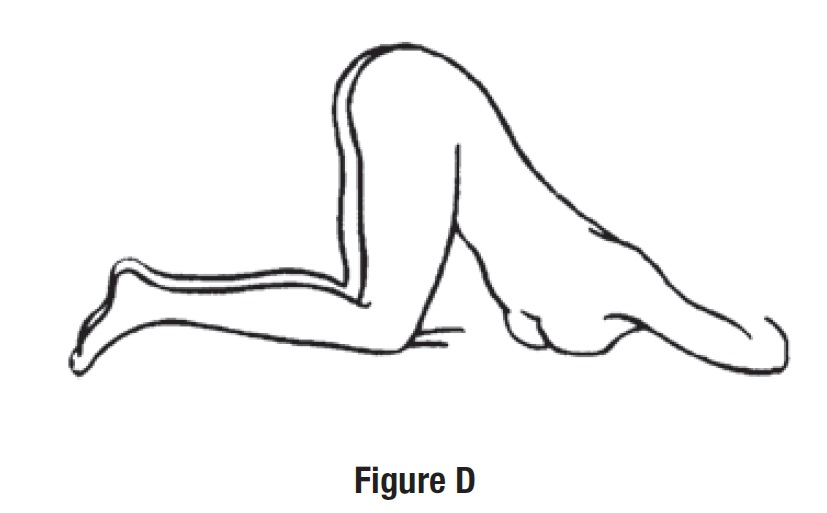
Step 3. Get in position.
• Lay on your left side with your left leg extended and your right leg flexed forward for balance (See Figure C).
- or
• Get in the knee-chest position as shown here (See Figure D).
Step 4. Giving the medicine.
• Lubricate the applicator tip.
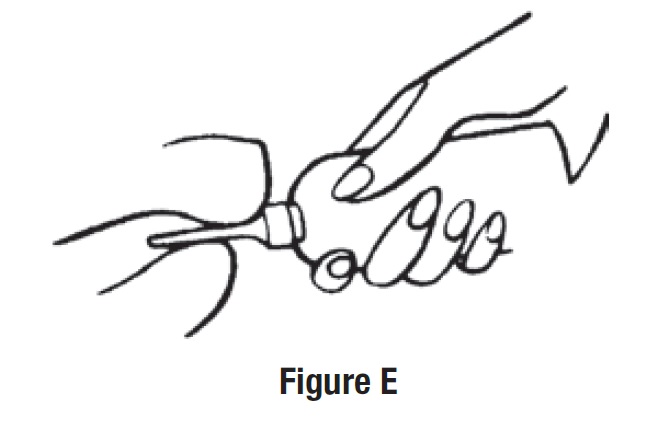
• Gently insert the lubricated applicator tip into the rectum pointing slightly toward the belly button (navel) to prevent
damage to the rectal wall.
• Grasp the bottle firmly, then tilt slightly so that the nozzle is aimed toward the back.
• Squeeze the bottle slowly to release the medicine into the rectum (See Figure E).
• Steady hand pressure will release most of the medicine.
• After giving the medicine, withdraw the applicator tip.
• Remain in position for at least 30 minutes to allow the medicine to spread inside the body.
• Throw away (discard) the bottle.
• Try to keep the medicine inside your body all night, if possible.
Manufactured by Padagis®
Yeruham, Israel
www.padagis.com
Rev 08-24
2N900 RC PH15
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 45802-929-49
Rx Only
Mesalamine Rectal Suspension, USP Enema
4g/60 mL
Unit-Dose
For Rectal Use Only
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USING
4 (7 X 60 mL UNIT-DOSE BOTTLES) KITS
The following image is a placeholder representing the product identifier that is either affixed or imprinted on the drug package label during the packaging operation.
| MESALAMINE
mesalamine kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Padagis Israel Pharmaceuticals Ltd (600093611) |
Frequently asked questions
More about mesalamine
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (426)
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: 5-aminosalicylates
- Breastfeeding
Patient resources
Professional resources
- Mesalamine monograph
- Mesalamine (FDA)
- Mesalamine Capsules (FDA)
- Mesalamine Controlled-Release Capsules (FDA)
- Mesalamine Delayed Release Tablets (FDA)
- Mesalamine Suppository (FDA)
Other brands
Lialda, Pentasa, Asacol, Apriso, ... +5 more