Vitamin K1 Dosage
Generic name: Phytonadione 10mg in 1mL
Dosage form: injection, emulsion
Drug classes: Anticoagulant reversal agents, Vitamins
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 6, 2024.
Whenever possible, Vitamin K1 Injection (Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP) should be given by the subcutaneous route. (See Box Warning.) When intravenous administration is considered unavoidable, the drug should be injected very slowly, not exceeding 1 mg per minute.
Protect from light at all times.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Directions for Dilution
Vitamin K1 Injection may be diluted with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, 5% Dextrose Injection, or 5% Dextrose and Sodium Chloride Injection. Benzyl alcohol as a preservative has been associated with toxicity in newborns. Therefore,all of the above diluents should be preservative-free (see WARNINGS). Other diluents should not be used. When dilutions are indicated, administration should be started immediately after mixture with the diluent, and unused portions of the dilution should be discarded, as well as unused contents of the ampul.
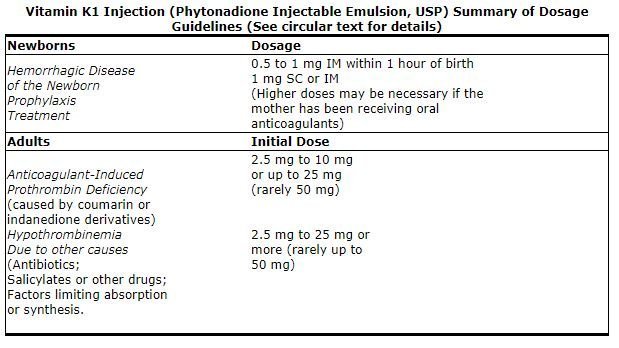
Prophylaxis of Hemorrhagic Disease of the Newborn
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that vitamin K1 be given to the newborn. A single intramuscular dose of Vitamin K1 Injection 0.5 to 1 mg within one hour of birth is recommended.
Treatment of Hemorrhagic Disease of the Newborn
Empiric administration of vitamin K1 should not replace proper laboratory evaluation of the coagulation mechanism. A prompt response (shortening of the prothrombin time in 2 to 4 hours) following administration of vitamin K1 is usually diagnostic of hemorrhagic disease of the newborn, and failure to respond indicates another diagnosis or coagulation disorder. Vitamin K1 Injection 1 mg should be given either subcutaneously or intramuscularly. Higher doses may be necessary if the mother has been receiving oral anticoagulants. Whole blood or component therapy may be indicated if bleeding is excessive. This therapy, however, does not correct the underlying disorder and Vitamin K1 Injection should be given concurrently.
Anticoagulant-Induced Prothrombin Deficiency in Adults
To correct excessively prolonged prothrombin time caused by oral anticoagulant therapy—2.5 to 10 mg or up to 25 mg initially is recommended. In rare instances 50 mg may be required. Frequency and amount of subsequent doses should be determined by prothrombin time response or clinical condition (see WARNINGS). If in 6 to 8 hours after parenteral administration the prothrombin time has not been shortened satisfactorily, the dose should be repeated.
In the event of shock or excessive blood loss, the use of whole blood or component therapy is indicated.
Hypoprothrombinemia Due to Other Causes in Adults
A dosage of 2.5 to 25 mg or more (rarely up to 50 mg) is recommended, the amount and route of administration depending upon the severity of the condition and response obtained.
If possible, discontinuation or reduction of the dosage of drugs interfering with coagulation mechanisms (such as salicylates; antibiotics) is suggested as an alternative to administering concurrent Vitamin K1 Injection. The severity of the coagulation disorder should determine whether the immediate administration of Vitamin K1 Injection is required in addition to discontinuation or reduction of interfering drugs.
More about Vitamin K1 (phytonadione)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (2)
- Latest FDA alerts (1)
- Side effects
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: anticoagulant reversal agents
- Breastfeeding
- En español
Patient resources
Other brands
Professional resources
Other brands
Related treatment guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.

