Type 2 Diabetes in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Type 2 diabetes
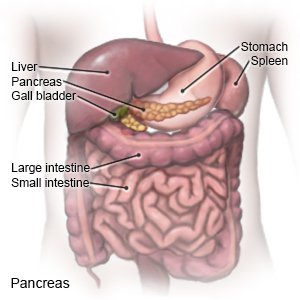
is a disease that affects how your child's body uses glucose (sugar). Normally, when the blood sugar level increases, the pancreas makes more insulin. Insulin helps move sugar out of the blood so it can be used for energy. Type 2 diabetes develops because either the body cannot make enough insulin, or it cannot use the insulin correctly. You can help your child manage diabetes with healthy nutrition and physical activity choices.
 |
Common symptoms include the following:
Your child may have had high blood sugar levels for a long time before symptoms appear. Your child may have no symptoms or any of the following:
- More hunger or thirst than usual
- Urinating more often
- Dark patches of skin under the arms or in the groin area
- Tired feeling
- Blurred vision
- Tingling, numbness, or pain in the hands or feet
Call you local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your child has a seizure or cannot be woken.
- Your child's heartbeat is fast and weak.
- Your child's breath has a fruity, sweet smell.
- Your child has a low blood sugar level and it does not improve with treatment.
Call your child's doctor or diabetes care team if:
- Your child's blood sugar levels are high after several checks.
- Your child's blood sugar level does not lower with extra insulin.
- Your child often has blood sugar levels that are too low.
- Your child has abdominal pain, diarrhea, or is vomiting.
- Your child has numbness in his or her arms or legs.
- Your child has warm, red patches of skin or a wound that does not heal.
- Your child is anxious or depressed.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Treatment:
Type 2 diabetes may be treated with lifestyle changes and sometimes medicines.
- The goal is to help control your child's blood sugar level. A controlled blood sugar level decreases or delays complications of diabetes, such as neuropathy and retinopathy. Type 2 diabetes can cause complications in children sooner than in adults.
- Your child will have a diabetes care team. The team may include physicians, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants. It may also include nurses, dietitians, exercise specialists, pharmacists, and a dentist. You, your child, and other family members will also be part of the team. The team will make goals and plans to manage diabetes and other health problems. The plans and goals will be specific to your child's needs.
- Your child's team will help you and your child decide which treatment is right for your child. Some children can control blood sugar levels with a nutrition plan and physical activity. Your child may start receiving insulin injections. Insulin is given if it is not clear if your child has type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Insulin is also given if your child's blood sugar level is above 250 mg/dL or A1c above 8.5%. Instead, your child may be given an oral or an injectable diabetes medicine. This medicine will help your child's body properly use insulin that is made naturally. Your child may need both insulin and other diabetes medicine to control his or her blood sugar levels.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Diabetes education:
Diabetes education will start right away. Members of your child's team will teach you and your child the following:
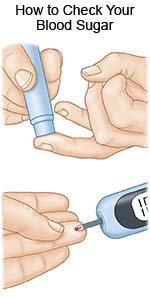
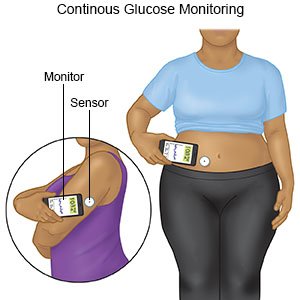
- When and how to check your child's blood sugar level: You and your child will learn what his or her blood sugar level should be. You will be given information on when to check your child's blood sugar level. You will learn what to do if his or her level is too high or too low. You may need to check a drop of your child's blood in a glucose machine. Your child's diabetes care team may recommend a continuous glucose monitor (CGM). A CGM is a device that is worn at all times. The CGM checks your child's blood sugar level every 5 minutes. It sends results to an electronic device such as a smart phone.
- About diabetes medicines: Oral diabetes medicine may be given to help control your child's blood sugar levels. Your child's healthcare provider will teach you and your child how and when to take diabetes medicine. You and your child will also be taught about side effects oral diabetes medicine can cause. Insulin may be added if oral diabetes medicine becomes less effective over time. Insulin may be injected, or given through a pump or pen. You and your child's care team will discuss which method is best for your child.
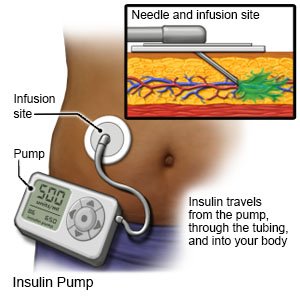
- An insulin pump is an implanted device that gives insulin 24 hours a day. An insulin pump prevents the need for multiple insulin injections in a day. A pump that is connected to a CGM is called an automated insulin delivery (AID) system.
- An insulin pen is a device prefilled with the right amount of insulin.
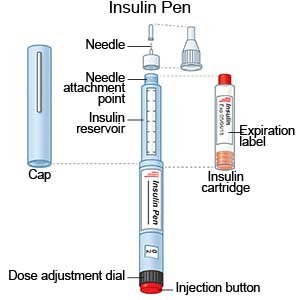
- You and your child will be taught how to draw up and give insulin if this is the best method for him or her. Your child's education team will also teach you how to dispose of needles and syringes.
- You and your child will learn how much insulin he or she needs and when to give it. You will be taught when not to give insulin. You will also be taught what to do if your child's blood sugar level drops too low. This may happen if your child takes insulin and does not eat the right amount of carbohydrates.
- An insulin pump is an implanted device that gives insulin 24 hours a day. An insulin pump prevents the need for multiple insulin injections in a day. A pump that is connected to a CGM is called an automated insulin delivery (AID) system.
- About nutrition: A dietitian will help you make a meal plan to keep your child's blood sugar level steady. You will learn how food affects your child's blood sugar level. You will also learn to keep track of sugar and starchy foods (carbohydrates). Do not let your child skip meals. Blood sugar levels may drop too low if your child has received insulin and does not eat.
- Physical activity and diabetes: You and your child will learn why physical activity, such as exercise, is important. A plan will be made for your child to get 60 minutes of moderate to intense aerobic activity every day. Your child can choose from activities such as brisk walking, dancing, running, or jumping rope. The plan may also include flexibility and resistance training, such as yoga and lifting weights, 3 days each week.


- How to manage blood sugar levels when your child is sick: Blood sugar levels can be too high or too low when your child is sick. Your child's care team will give you information about managing your child's diabetes during sick days.
- How to prevent complications of diabetes: Diabetes that is not controlled can lead to complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), neuropathy, and retinopathy. You will also learn how to prevent conditions that may happen with diabetes, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
Your child's nutrition:
A dietitian will help you and your child create a meal plan. The plan will help keep your child's blood sugar level steady. The following are tips to start helping with your child's nutrition:
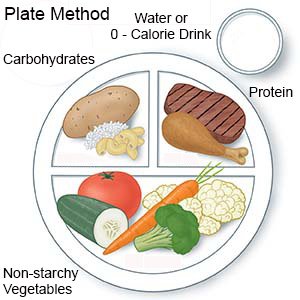
- Keep track of carbohydrates (sugar and starchy foods). Your child's blood sugar level can get too high if he or she eats too many carbohydrates. His or her dietitian will help you plan meals and snacks that have the right amount of carbohydrates. You may be taught the plate method. With the plate method, ½ of the plate contains non-starchy vegetables. The other half is divided so ¼ contains protein, and ¼ contains carbohydrates.
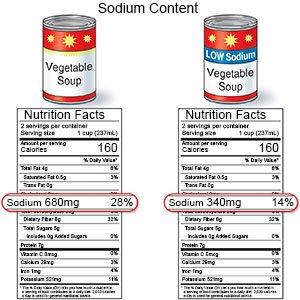
- Give your child low-fat and low-sodium foods. Examples of low-fat foods are lean meat, fish, skinless chicken or turkey, and low-fat milk. Limit high-sodium foods, such as potato chips and soup. Do not add salt to food you cook. Limit your child's use of table salt.
- Give your child high-fiber foods. Fiber helps improve blood sugar levels. Fiber also lowers your child's risk for heart disease and other problems diabetes can cause. Examples of high-fiber foods include vegetables, whole-grain bread, and beans such as pinto beans. A dietitian can tell you how much fiber to give your child each day.

Help your child manage type 2 diabetes:
- Talk to your child's care team if you or your child become stressed about diabetes care. Learning about diabetes care can be stressful. The stress can cause your child not to want to help in his or her own care. The stress can also cause you to feel overwhelmed. Your child's care team can help by offering tips. The care team may suggest you and your child talk to a mental health provider. The provider can listen and offer help with issues and feelings of being overwhelmed. You and your child may choose to see the provider at separate times. You and your child may, instead, choose to see the provider together.
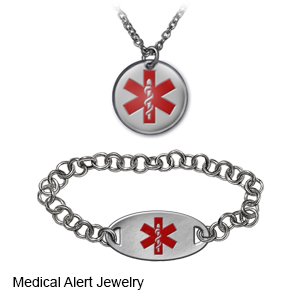
- Make sure your child always wears medical alert jewelry or carries a card that says he or she has diabetes. Ask your child's care team provider where to get these items.
- Give instructions to your child's school and care providers. Make sure your child's teachers and care providers know he or she has diabetes. Provide written instructions about what to do if your child has symptoms of high or low blood sugar levels.
- Help your child maintain a healthy weight. Ask your child's team what a healthy weight is for your child. A healthy weight can help control diabetes and prevent heart disease. Ask the team to help your child create a weight-loss plan, if needed. The team will help set a weight loss goal, such as 10% of his or her extra weight. Together you and your team can set manageable weight loss goals.
- Do not smoke around your child. Do not let others smoke around him or her. Do not let your older child smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause lung and heart damage. Cigarette smoke can worsen the problems that occur with diabetes. Ask your care team provider for information if you or your child currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your provider before you or your child use these products.
- Bring your child in for screenings as directed. Your child will need to be screened for complications of diabetes and other conditions that may develop. Some screenings may begin right away and some may happen within the first 5 years of diagnosis. Your child will need to continue screenings through his or her lifetime. Keep your child's follow-up appointments with all providers.
- Your child will need to have his or her A1c checked. This will help make sure that your child's diabetes is well controlled. His or her care plan may need to be adjusted if the level is higher than recommended.
- Your child will have screenings for complications or other problems. Examples include kidney problems, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, blood vessel problems, eye problems, and sleep apnea. Your child may also be screened for an eating disorder or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Your child's nerves, arteries, eyes, and kidneys can be damaged.
- Ask about vaccines your child may need. Your child has a higher risk for serious illness if he or she gets the flu, COVID-19, or pneumonia. Ask if your child should get vaccines to prevent these or other diseases, and when to get the vaccines.
Follow up with your child's doctor or diabetes care team as directed:
Your child will need to return to have his or her A1c checked. The care team will make sure that treatment is working. Your child's treatment may need to be adjusted. Write down questions that you and your child have so you remember to ask them during his or her visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Type 2 Diabetes
- Diabetes Medications and Alcohol Interactions
- FDA-Approved Weight Loss Drugs: Can They Help You?
- OneTouch Blood Glucose Meters
- Top 10 Diabetes Treatments You May Have Missed
- What is Insulin Resistance?
- Which Drugs Cause Weight Gain?
Treatment options
Care guides
- Diabetes and your Skin
- Diabetic Hyperglycemia
- How to Draw Up Insulin
- Type 2 Diabetes in Adults: New Diagnosis
- Type 2 Diabetes in Children
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
