Type 1 Diabetes in Adults: New Diagnosis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Oct 29, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Type 1 diabetes
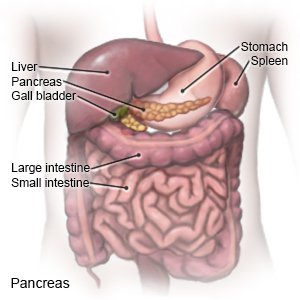
is a disease that affects how your body makes insulin and uses glucose (sugar). Normally, when the blood sugar level increases, the pancreas makes more insulin. Insulin helps move sugar out of the blood so it can be used for energy. Type 1 diabetes develops because the immune system destroys cells in the pancreas that make insulin. The pancreas cannot make enough insulin, so the blood sugar level continues to rise. A family history of type 1 diabetes may increase your risk. Type 1 diabetes is treated with insulin.
 |
Signs and symptoms of uncontrolled type 1 diabetes:
- More thirst than usual
- Urinating often
- Hunger most of the time
- Weight loss without trying
- Blurred vision
Have someone call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You cannot be woken.
- You have any of the following signs of a stroke:
- Numbness or drooping on one side of your face
- Weakness in an arm or leg
- Confusion or difficulty speaking
- Dizziness, a severe headache, or vision loss
- You have any of the following signs of a heart attack:
- Squeezing, pressure, or pain in your chest
- You may also have any of the following:
- Discomfort or pain in your back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or a sudden cold sweat
Seek care immediately if:
- Your blood sugar level is above 240 mg/dL and does not come down with treatment.
- You have signs of a high blood sugar level, such as blurred or double vision.
- You have signs of a high ketone level, such as breath has a fruity, sweet smell, or your breathing is shallow.
- You have symptoms of a low blood sugar level, such as trouble thinking, sweating, or a pounding heartbeat.
- Your blood sugar level is lower than normal and does not improve with treatment.
Call your doctor or diabetes care team if:
- Your blood sugar levels are higher than your target goals.
- You often have lower blood sugar levels than your target goals.
- Your skin is red, dry, warm, or swollen.
- You have a wound that does not heal.
- You have trouble managing type 1 diabetes, or you feel anxious or depressed.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Diabetes education
will start right away. Diabetes education may also happen later to refresh your memory. Your diabetes care team may include physicians, nurse practitioners, community health providers, and physician assistants. It may also include nurses, dietitians, exercise specialists, pharmacists, dentists, and podiatrists. Family members, or others who are close to you, may also be part of the team. You and your team will make goals and plans to manage diabetes and other health problems. The plans and goals will be specific to your needs. Members of your diabetes care team will teach you the following:
- About your blood sugar level: You will be given information on when and how to check your blood sugar level. You will learn what your blood sugar level should be and what to do if it is too high or too low. Write down the times of your checks and your levels. Take them to all follow-up appointments.
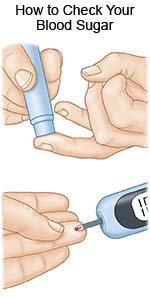
- A glucose meter is a device that uses a test strip to check your blood sugar level. You put a small drop of blood from a finger on the test strip. The strip is put into the device. The device then figures out how much sugar is in your blood.
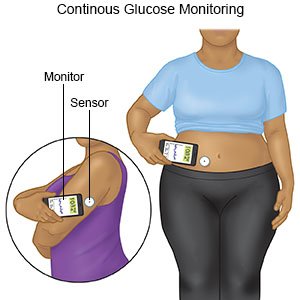
- A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) uses a sensor to check your blood sugar level. The sensor is placed on your abdomen or arm. A transmitter on the sensor gets a glucose reading. CGM data may be linked to an insulin pump.
- A glucose meter is a device that uses a test strip to check your blood sugar level. You put a small drop of blood from a finger on the test strip. The strip is put into the device. The device then figures out how much sugar is in your blood.
- About insulin: You will need insulin every day. You will learn how much insulin you need and when to use it. You will also be taught how to match insulin with blood sugar levels, activity, and carbohydrates. Insulin may be given through a pump or pen, or injected. You and your care team will discuss the best method for you:
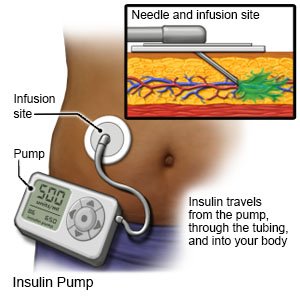
- An insulin pump is a wearable medical device that gives continuous insulin. An insulin pump prevents the need for multiple insulin injections in a day.
- An insulin pen is a device prefilled with insulin. Most insulin pens are disposable. You throw the pen away after it is empty or used for a certain amount of time. Some pens have a replaceable cartridge filled with insulin. You keep the pen and only throw away the cartridge.
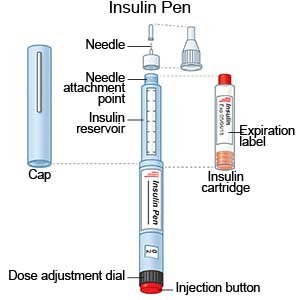
- Insulin injections are given with a needle and syringe. You and your family members will be taught how to draw up and give insulin if this is the best method for you. You will also be taught how to dispose of used needles and syringes.
- An insulin pump is a wearable medical device that gives continuous insulin. An insulin pump prevents the need for multiple insulin injections in a day.
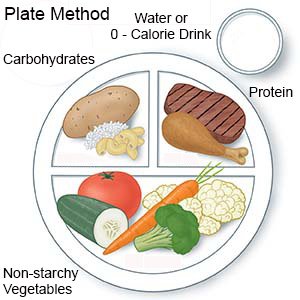
- About nutrition: A dietitian will help you make a meal plan to keep your blood sugar level steady. You will learn how food affects your blood sugar levels. You will also learn to keep track of carbohydrates (sugar and starchy foods). You will learn why it is important not to skip meals. Your blood sugar level may drop too low if you have taken diabetes medicine and do not eat. You may be taught the plate method for portion control. With the plate method, ½ of your plate contains non-starchy vegetables, ¼ contains protein, and ¼ contains carbohydrates. Your dietitian will give you examples of each kind of food to include. Ask your care team for more information about meal planning.
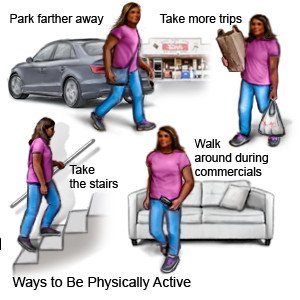
- About physical activity and diabetes: You will learn why physical activity, such as exercise, is important. You and your provider will make a plan for your activity. Your provider will tell you what a healthy weight is for you. Your provider will help you make a plan to get to that weight and stay there.

Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Check your blood sugar level as directed:
Write down your results, and show them to your care team. Your team may make changes to your medicine, food, or exercise schedules.
- You will need to check your blood sugar level at least 3 times every day. Ask your care team when and how often to check during the day.
- If you check your blood sugar level before a meal , it should be between 80 and 130 mg/dL.
- If you check your blood sugar level 1 to 2 hours after a meal , it should be less than 180 mg/dL.
- You may need to check for ketones in your urine or blood if your level is higher than directed.
If your blood sugar level is too low:
Your blood sugar level is too low if it goes below 70 mg/dL. If the level is too low, eat or drink 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrate. These are found naturally in fruits. Fast-acting carbohydrates will raise your blood sugar level quickly. Examples of 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrate are 4 ounces (½ cup) of fruit juice or 4 ounces of a regular soft drink. Other examples are 2 tablespoons of raisins or 3 to 4 glucose tablets. Check your blood sugar level 15 minutes later. If the level is still low (less than 100 mg/dL), eat another 15 grams of carbohydrate. When the level returns to 100 mg/dL, eat a snack or meal that contains carbohydrates. This will help prevent another drop in blood sugar. Always carefully follow your provider's instructions on how to treat low blood sugar levels.
 |
Other ways to help manage type 1 diabetes:
- Talk to your care team if you have increased stress about your diagnosis. Stress about your diagnosis can keep you from taking care of yourself properly. Your care team can help by offering tips about self-care. Your care team may suggest you talk to a mental health provider. The provider can listen and offer help with self-care issues.
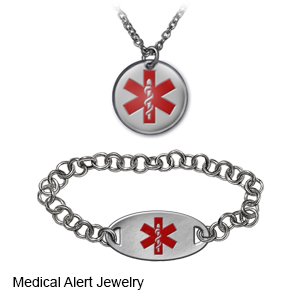
- Wear medical alert identification. Wear medical alert jewelry or carry a card that says you have diabetes. Ask your diabetes care team provider where to get these items.
- Know the risks if you choose to drink alcohol. Alcohol can cause your blood sugar levels to be low if you use insulin. Alcohol can cause high blood sugar levels and weight gain if you drink too much. Women 21 years or older and men 65 years or older should limit alcohol to 1 drink a day. Men aged 21 to 64 years should limit alcohol to 2 drinks a day. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1½ ounces of liquor.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause lung damage and make it more difficult to manage type 1 diabetes. Ask your provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. Do not use e-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco in place of cigarettes or to help you quit. They still contain nicotine.
- Check your feet every day for sores. Wear shoes and socks that fit correctly. Ask your care team for more information about foot care.
- Ask about vaccines you may need. You have a higher risk for serious illness if you get the flu, pneumonia, COVID-19, or hepatitis. Ask your provider if you should get vaccines to prevent these or other diseases, and when to get the vaccines.
- Have screening tests as directed. Type 1 diabetes increases your risk for other autoimmune diseases. Talk to your provider about how often you should be screened.
Follow up with your diabetes care team as directed:
You will need to return to have your blood sugar level checked. Your levels will let your care team know if your treatment plan is working for you. You will need to have your feet checked during at least 1 visit each year. You will need an eye exam 1 time each year to check for retinopathy. You will also need tests to check for kidney or heart disease, and high blood pressure. Talk to your care team if you cannot afford your medicine. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Type 1 Diabetes: New Diagnosis
- Diabetes Medications and Alcohol Interactions
- OneTouch Blood Glucose Meters
- Top 10 Diabetes Treatments You May Have Missed
Treatment options
Care guides
- Diabetes and your Skin
- Diabetic Hyperglycemia
- How to Draw Up Insulin
- Type 1 Diabetes in Adults: New Diagnosis
- Type 1 Diabetes in Children
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
