Epilepsy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
Epilepsy is a brain disorder that causes seizures. It is also called a seizure disorder. A seizure means an abnormal area in your brain sometimes sends bursts of electrical activity. A seizure may start in one part of your brain, or both sides may be affected. Depending on the type of seizure, you may have movements you cannot control, lose consciousness, or stare straight ahead. You may be confused or tired after the seizure. A seizure may last a few seconds or longer than 5 minutes. A birth defect, tumor, stroke, dementia, injury, or infection may cause epilepsy. The cause of your epilepsy may not be known. If your seizures are not controlled, epilepsy may become life-threatening.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US), or have someone else call, for any of the following:
- Your seizure lasts longer than 5 minutes.
- You have trouble breathing after a seizure.
- You have diabetes or are pregnant and have a seizure.
- You have a seizure in water, such as a swimming pool or bathtub.
Call your doctor if:
- You have a second seizure within 24 hours of the first.
- You are injured during a seizure.
- You feel you are not able to cope with your condition.
- Your seizures start to happen more often.
- You are confused longer than usual after a seizure.
- You are planning to get pregnant or are currently pregnant.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
- Antiseizure medicine may control or prevent another seizure. Do not stop taking this medicine. Another person may need to give you rescue medicine to stop a seizure at home. Ask your healthcare provider for more information about rescue medicine.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Follow up with your neurologist as directed:
You may need tests to check the level of antiseizure medicine in your blood. Your neurologist may need to change or adjust your medicine. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
Prevent a complication of epilepsy:
- Sudden unexplained death in epilepsy (SUDEP) is a rare complication of epilepsy. In 1 year, 1 adult in 1,000 adults with epilepsy will have this complication. The risk of SUDEP increases if you have 3 or more generalized tonic-clonic seizures in 1 year. Your risk also increases if you have nocturnal seizures (seizures during sleep). After a nocturnal seizure, your breathing can become shallow.
- Your healthcare provider may recommend a change in medicine to decrease the number of seizures. For nocturnal seizures, he or she may recommend that someone sleep near you. The person must be older than 10 years. The person must also be close enough to know that you are having a seizure.
What you can do to prevent a seizure:
You may not be able to prevent every seizure. The following can help you manage triggers that may make a seizure start:
- Take your medicine every day at the same time. This will also help prevent medicine side effects. Set an alarm to help remind you to take your medicine every day.
- Manage stress. Stress can be a trigger for epilepsy. Exercise can help you reduce stress. Talk to your healthcare provider about exercise that is safe for you. Illness can be a form of stress. Eat a variety of healthy foods and drink plenty of liquids during an illness. Talk to your healthcare provider about other ways to manage stress.
- Set a regular sleep schedule. A lack of sleep can trigger a seizure. Try to go to sleep and wake up at the same time every day. Keep your bedroom quiet and dark. Talk to your healthcare provider if you are having trouble sleeping.
- Limit or do not drink alcohol as directed. Alcohol can trigger a seizure, especially if you drink a large amount at one time. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 1½ ounces of liquor, or 5 ounces of wine. Talk to your healthcare provider about a safe amount of alcohol for you. Your provider may recommend that you do not drink any alcohol. Tell him or her if you need help to quit drinking.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
What you can do to manage epilepsy:
- Keep a seizure diary. This can help you find your triggers and avoid them. Write down the dates of your seizures, where you were, and what you were doing. Include how you felt before and after. Possible triggers include illness, lack of sleep, hormonal changes, alcohol, drugs, lights, or stress.
- Record any auras you have before a seizure. An aura is a sign that you are about to have a seizure. Auras happen before certain types of seizures that are in only 1 part of the brain. The aura may happen seconds before a seizure, or up to an hour before. You may feel, see, hear, or smell something. Examples include part of your body becoming hot. You may see a flash of light or hear something. You may have anxiety or déjà vu. If you have an aura, include it in your seizure diary.
- Create a care plan. Tell family, friends, and coworkers about your epilepsy. Give them instructions that tell them how they can keep you safe if you have a seizure.
- Find support. You may be referred to a psychologist or social worker. Ask your healthcare provider about support groups for people with epilepsy.
- Ask what safety precautions you should take. Talk with your healthcare provider about driving. You may not be able to drive until you are seizure-free for a period of time. You will need to check the law where you live. Also talk to your healthcare provider about swimming and bathing. You may drown or develop life-threatening heart or lung damage if you have a seizure in water.
- Carry medical alert identification. Wear medical alert jewelry or carry a card that says you have epilepsy. Ask your healthcare provider where to get these items.
How others can keep you safe during a seizure:
Give the following instructions to family, friends, and coworkers:
- Do not panic.
- Do not hold me down or put anything in my mouth.
- Gently guide me to the floor or a soft surface.
- Place me on my side to help prevent me from swallowing saliva or vomit.
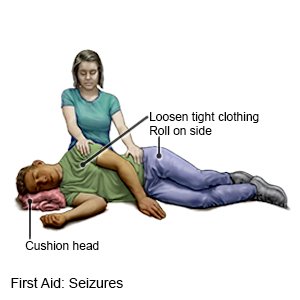
- Protect me from injury. Remove sharp or hard objects from the area surrounding me, or cushion my head.
- Loosen the clothing around my head and neck.
- Time how long my seizure lasts. Call 911 if my seizure lasts longer than 5 minutes or if I have a second seizure.
- Stay with me until my seizure ends. Let me rest until I am fully awake.
- Perform CPR if I stop breathing or you cannot feel my pulse.
- Do not give me anything to eat or drink until I am fully awake.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Epilepsy
Treatment options
Care guides
- Epilepsy
- Epilepsy in Children
- Generalized Tonic Clonic Seizures
- Generalized Tonic Clonic Seizures in Children
- New Onset Absence Seizures in Adults
- New-Onset Seizure in Adults
- New-Onset Seizure in Children
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
