COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
is a lung disease that causes breathing problems. COPD usually develops from years of irritation and inflammation in your lungs. Obstructive means airflow is blocked. This limits airflow out of your lungs. Smoking, breathing in pollution, genetics, or a history of lung infections can increase your risk for COPD.
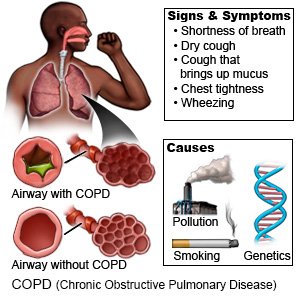 |
Common symptoms include the following:
- Shortness of breath
- A dry cough
- Coughing fits that bring up mucus from your lungs
- Wheezing and chest tightness
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You feel lightheaded, short of breath, and have chest pain.
Seek care immediately if:
- You cough up blood.
- You are confused, dizzy, or feel faint.
- Your arm or leg feels warm, tender, and painful. It may look swollen and red.
Call your doctor if:
- You have increased shortness of breath.
- You need more medicine than usual to control your symptoms.
- You are coughing or wheezing more than usual.
- You are coughing up more mucus, or it has a new color or odor.
- You gain more than 3 pounds in a week.
- You have a fever, a runny or stuffy nose, and a sore throat, or other cold or flu symptoms.
- Your skin, lips, or nails start to turn blue.
- You have swelling in your legs or ankles.
- You are very tired or weak for more than a day.
- You notice changes in your mood, or changes in your ability to think or concentrate.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment:
Healthcare providers will work with you to create a care plan. The plan will contain goals defined by you and your providers. It will include steps to help you reach your goals within a specific time frame. The plan may change over time as your goals and needs change. The following may be included in your plan:
- Medicines may be used to open your airway or decrease swelling and inflammation in your lungs. Antibiotics may be given for up to 5 days to treat a bacterial infection during an exacerbation. Medicines can relieve certain kinds of symptoms. A short-acting medicine relieves symptoms quickly. This may be called rescue medicine. A long-acting medicine controls or prevents symptoms. This may be called maintenance medicine. Your care plan will have directions for when to take each kind of medicine. Your healthcare provider will give you more information about the medicines you are given and how to use them safely.
- Extra oxygen may help you breathe easier and feel more alert if you have severe COPD. Do not increase your oxygen levels without speaking to your doctor first.
- Surgery is sometimes done if all other treatments have failed. A lung reduction is surgery to remove part of your damaged lung. A lung transplant is the replacement of your lung with a donor lung.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Help make breathing easier:
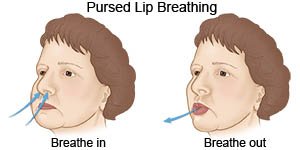
- Use pursed-lip breathing any time you feel short of breath. Take a deep breath in through your nose. Slowly breathe out through your mouth with your lips pursed. Try to take 2 times as long to breathe out as to breathe in. This helps you get rid of as much air from your lungs as possible. You can also practice this breathing pattern while you bend, lift, climb stairs, or exercise. It slows down your breathing and helps move more air in and out of your lungs.
- Avoid anything that makes your symptoms worse. Stay out of high altitudes and places with high humidity. Stay inside, or cover your mouth and nose with a scarf when you are outside in cold weather. Stay inside on days when air pollution or pollen counts are high. Do not use aerosol sprays such as deodorant, bug spray, and hairspray.
- Exercise as directed. Your healthcare provider may recommend at least 20 minutes of exercise each day to help increase your energy and decrease shortness of breath. Talk to your provider about the best exercise plan for you.

Manage COPD and help prevent exacerbations:
COPD is a serious condition that gets worse over time. A COPD exacerbation means your symptoms suddenly get worse. It is important to prevent exacerbations. An exacerbation can cause more lung damage. COPD cannot be cured, but you can take action to feel better and prevent exacerbations:
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause lung damage and make your COPD worse. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Avoid secondhand smoke. This is smoke another person exhales. Even if you have never smoked or have quit, it is important to avoid secondhand smoke. This smoke can also cause lung damage or trigger an exacerbation.
- Go to pulmonary rehabilitation (rehab) if directed. Rehab is a program run by specialists who help you learn to manage COPD. Examples include a pulmonologist (lung specialist), dietitian, or exercise therapist. The specialists will help you make a plan to avoid triggers that cause an exacerbation.
- Take your medicines as directed. Refill your medicines before you are out so that you do not miss a dose. Ask your healthcare provider if you have any questions on how to take your medicines.
- Protect yourself from germs. Germs can get into your lungs and cause an infection. An infection in your lungs can create more mucus and make it harder to breathe. An infection can also create swelling in your airway and prevent air from getting in. You can decrease your risk for infection by doing the following:
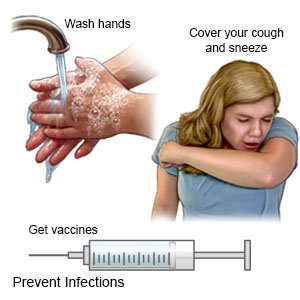
- Wash your hands often with soap and water. Carry germ-killing gel with you. You can use the gel to clean your hands when soap and water are not available.

- Do not touch your eyes, nose, or mouth unless you have washed your hands first.
- Always cover your mouth when you cough. Cough into a tissue or your shirtsleeve so you do not spread germs from your hands.
- Try to avoid people who have a cold or the flu. If you are sick, stay away from others as much as possible.
- Ask about vaccines you may need. Influenza (the flu), pneumonia, and COVID-19 can become life-threatening for a person who has COPD. Get a yearly flu vaccine as soon as recommended, usually in September or October. The pneumonia vaccine may be given every 5 years, or as directed. COVID-19 vaccines are available in shots given in 1 or 2 doses. Your healthcare provider can tell you if you should also get other vaccines, and when to get them.
- Wash your hands often with soap and water. Carry germ-killing gel with you. You can use the gel to clean your hands when soap and water are not available.
- Drink liquids as directed. You may need to drink more liquid than usual. Liquid will help to keep your air passages moist and help you cough up mucus. Ask how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
You may need more tests. Your doctor may refer you to a specialist, depending on your needs. Some specialist services may be available through your pulmonary rehab program. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about COPD
Treatment options
Care guides
- Asthma
- Asthma in Children
- Chronic Bronchitis
- COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
- Emphysema
- Moderate and Severe Persistent Asthma
- Reactive Airways Disease
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
