Bronchiolitis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
What is bronchiolitis?
Bronchiolitis is a viral infection of the bronchioles (small airways) in your child's lungs. It causes the small airways to become swollen and filled with fluid and mucus. This makes it hard for your child to breathe. Bronchiolitis usually goes away on its own. Most children can be treated at home.
What causes bronchiolitis?
Bronchiolitis is most often caused by the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). The viruses that cause the flu and the common cold may also cause bronchiolitis. Bronchiolitis may be spread from person to person through coughing, sneezing, or close contact. Germs may be left on objects such as doorknobs, beds, tables, cribs, and toys. Your child can get infected by putting objects that carry the virus into his or her mouth. Your child can also get infected by touching objects that carry the virus and then rubbing his or her eyes or nose.
What increases my child's risk for bronchiolitis?
Bronchiolitis most often happens to children younger than 2 years, usually in the fall, winter, or early spring. Your child may get RSV from a school-aged sibling or at a daycare center. Any of the following may increase your child's risk for bronchiolitis:
- Premature (early) birth, or a low birth weight
- A weak immune system
- A heart or lung problem
- Being formula fed, or little or no breastfeeding
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
What are the signs and symptoms of mild bronchiolitis?
Bronchiolitis begins like a common cold. Symptoms usually go away within 1 to 2 weeks. Some symptoms, such as a cough, may last several weeks. Your child's symptoms may be worse on the second or third day of his or her illness. Your child may have any of the following:
- Runny or stuffy nose
- A fever
- Fussiness or not eating or sleeping as well as usual
- Wheezing or a cough
What are the signs and symptoms of severe bronchiolitis?
- Very fast breathing (at least 60 breaths in 1 minute), or pauses in breathing of at least 15 seconds
- Grunting and increased wheezing or noisy breathing
- Wider nostrils when breathing in
- Pale or bluish skin, lips, fingernails, or toenails
- Pulling in of the skin between the ribs and around the neck with each breath
- A fast heartbeat
- Loss of appetite or poor feeding, or being fussier or more irritable than usual
- More sleepy than usual, trouble staying awake, or not responding to you
How is bronchiolitis diagnosed?
Your child's healthcare provider will examine your child and ask about his or her symptoms. The provider may measure your child's blood oxygen level with a small sticky strip.
How is bronchiolitis treated?
Most children do not need treatment for bronchiolitis. Medicine may be given to decrease pain and fever. Your child may need to be monitored and treated in the hospital if he or she has severe bronchiolitis.
How can I manage my child's symptoms?
- Have your child rest. Rest can help your child's body fight the infection.
- Give your child plenty of liquids. Liquids will help thin and loosen mucus so your child can cough it up. Liquids will also keep your child hydrated. Do not give your child liquids with caffeine. Caffeine can increase your child's risk for dehydration. Liquids that help prevent dehydration include water, fruit juice, or broth. Ask your child's healthcare provider how much liquid to give your child each day. If you are breastfeeding, continue to breastfeed your baby. Breast milk helps your baby fight infection.
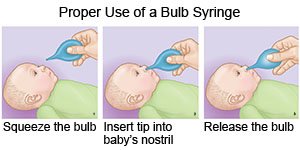
- Remove mucus from your child's nose. Do this before you feed your child so it is easier for him or her to drink and eat. You can also do this before your child sleeps. Place saline (saltwater) spray or drops into your child's nose to help remove mucus. Saline spray and drops are available over-the-counter. Follow directions on the spray or drops bottle. Have your child blow his or her nose after you use these products. Use a bulb syringe to help remove mucus from an infant or young child's nose. Ask your child's healthcare provider how to use a bulb syringe.
- Use a cool mist humidifier in your child's room. Cool mist can help thin mucus and make it easier for your child to breathe. Be sure to clean the humidifier as directed.
- Keep your child away from smoke. Do not smoke near your child. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can make your child's symptoms worse. Ask your child's healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit.
How can I help prevent bronchiolitis?
- Wash your hands and your child's hands often. Wash hands several times each day. Wash after you use the bathroom, change a child's diaper, and before you prepare or eat food. Teach your child how to wash his or her hands. Use soap and water every time. Rub your soapy hands together, lacing your fingers. Wash the front and back of each hand, and in between all fingers. Use the fingers of one hand to scrub under the fingernails of the other hand. Wash for at least 20 seconds. Rinse with warm, running water for several seconds. Then dry your hands with a clean towel or paper towel. You and your older child can use hand sanitizer that contains alcohol if soap and water are not available. No one should touch his or her eyes, nose, or mouth without washing hands first.

- Clean toys and other objects with a disinfectant solution. Clean tables, counters, doorknobs, and cribs. Also clean toys that are shared with other children. Use a disinfecting wipe, a single-use sponge, or a cloth you can wash and reuse. Use disinfecting cleaners if you do not have wipes. You can create a disinfecting cleaner by mixing 1 part bleach with 10 parts water. Wash sheets and towels in hot, soapy water, and dry on high.
- Do not smoke near your child. Do not let others smoke near your child. Secondhand smoke can increase your child's risk for bronchiolitis and other infections.
- Keep your child away from people who are sick. Keep your child away from crowds or people with colds and other respiratory infections. Do not let other sick children sleep in the same bed as your child.
- Ask if the medicine that protects against RSV is right for your child. It may be given if your child has a high risk of becoming severely ill from RSV. When needed, your child will receive 1 dose every month for 5 months. The first dose is usually given in early November.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) for any of the following:
- Your child stops breathing.
- Your child has pauses in his or her breathing.
- Your child is grunting and has increased wheezing or noisy breathing.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your child is 6 months or younger and takes more than 60 breaths in 1 minute.
- Your child is 6 to 11 months old and takes more than 50 breaths in 1 minute.
- Your child is 1 year or older and takes more than 40 breaths in 1 minute.
- Your child's nostrils become wider when he or she breathes in.
- Your child's skin, lips, fingernails, or toes are pale or blue.
- Your child's heart is beating faster than usual.
- Your child has any of the following signs of dehydration:
- Crying without tears
- Dry mouth or cracked lips
- More irritable or sleepy than usual
- Sunken soft spot on the top of the head, if he or she is younger than 1 year
- Having less wet diapers than usual, or urinating less than usual or not at all
- Your child's temperature reaches 105°F (40.6°C).
When should I call my child's doctor?
- Your child is younger than 2 years and has a fever for more than 24 hours.
- Your child is 2 years or older and has a fever for more than 72 hours.
- Your child's nasal drainage is thick, yellow, green, or gray.
- Your child's symptoms do not get better, or they get worse.
- Your child is not eating, has nausea, or is vomiting.
- Your child is very tired or weak, or he or she is sleeping more than usual.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your child's care. Learn about your child's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your child's healthcare providers to decide what care you want for your child. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Bronchiolitis
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
